- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
5. Human ecology презентация
Содержание
- 1. 5. Human ecology
- 2. As the human population increases
- 3. Pollutants are substances added to the environment,
- 4. The high level of industry
- 5. Human ecology is an academic discipline
- 6. Human ecology is about investigating how individuals
- 7. Human ecology views human communities and human
- 8. Nowadays the main
- 9. Human ecology explores not only the influence
- 10. The object of investigation is the system: Human Environment
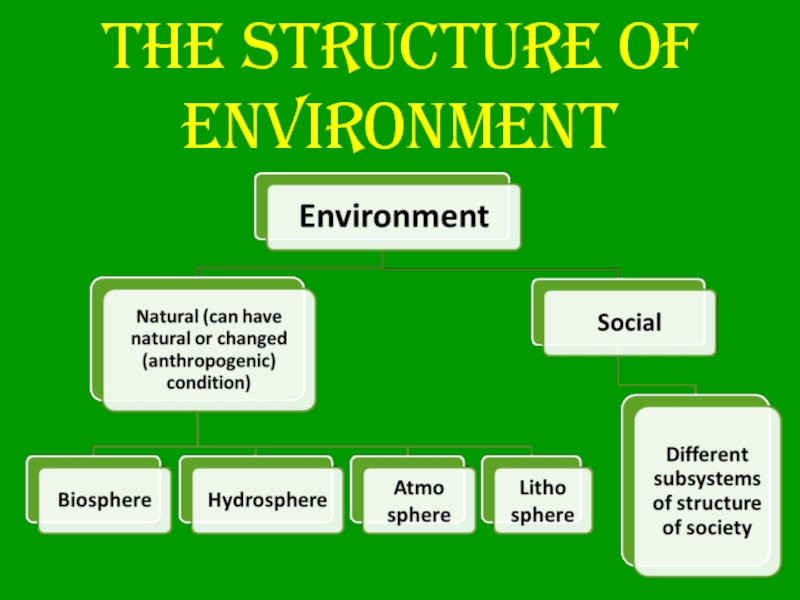
- 11. The structure of environment
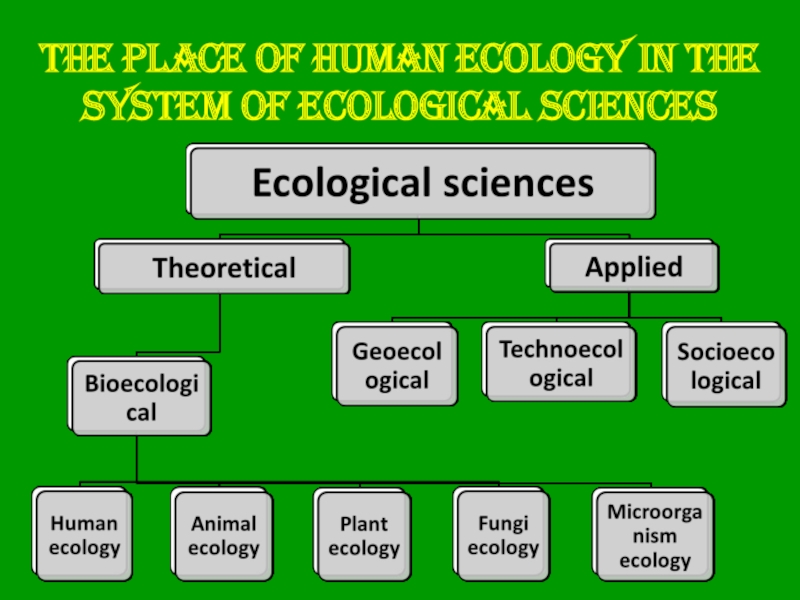
- 12. The place of human ecology in the system of ecological sciences
- 13. The main tasks of human ecology: the
- 14. Human ecology uses many methods of investigation:
- 15. The main terms of human ecology: Hygiene
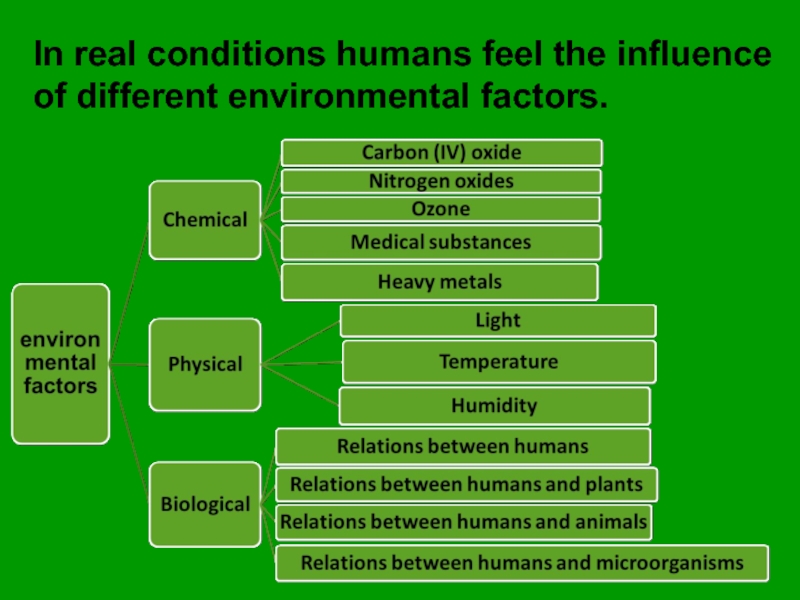
- 16. In real conditions humans feel the influence of different environmental factors.
- 17. The influence of physical factors to human
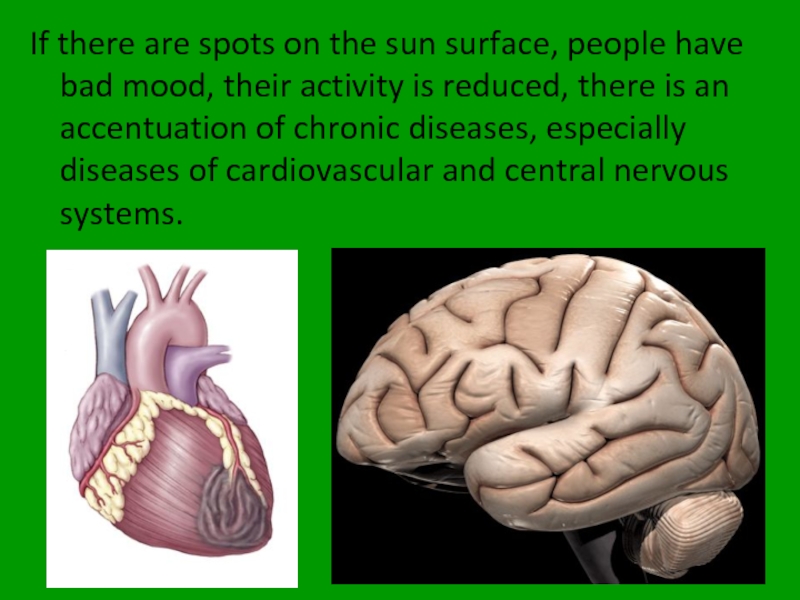
- 18. If there are spots on the sun
- 19. weather – it can have different influence
- 20. temperature – high temperature can change
- 21. The influence of anthropogenic factors to human
- 22. greenhouse effect – it is the increase
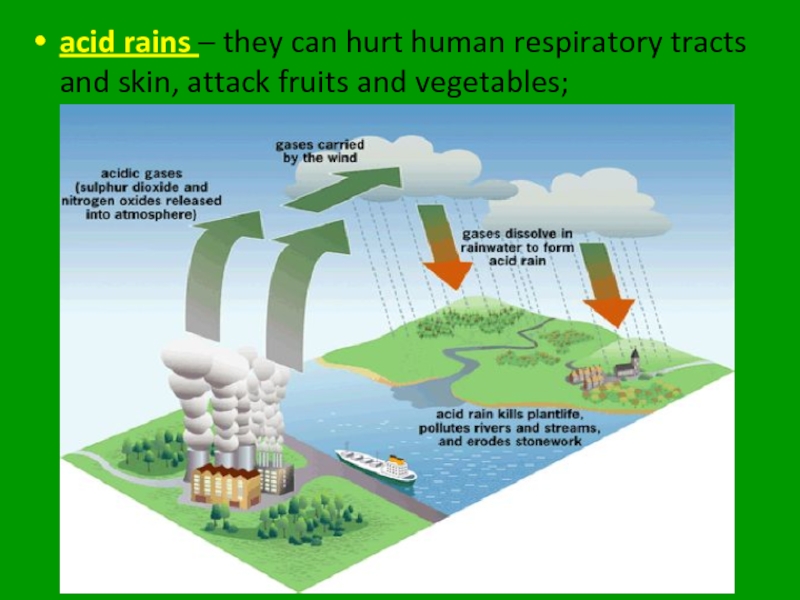
- 23. acid rains – they can hurt human respiratory tracts and skin, attack fruits and vegetables;
- 24. photochemical fogs – it is the mixture
- 25. heavy metals – lead, mercury, manganese, zinc,
- 26. Water pollution Water is the most spread
- 27. Hydrosphere is polluted with human help. Industrial
- 29. Every year 5 million peoples die in
- 30. land pollution The geosphere and biosphere are
- 31. The main sources of soil pollution are: Industry; Transport; Agriculture.
- 33. In agriculture people use pesticides and nitrates.
- 34. Human population poses a threat to
- 35. The results of air pollution: Photochemical smog;
- 36. Love your planet! don’t harm it!
- 37. Thank you for attention !
Слайд 2As the human
population
increases in
size, the space
allotted to
natural
ecosystems
is reduced in
size. Natural
ecosystems
are then no longer able to process and rid the biosphere of wastes, which accumulate and are called pollutants.
Слайд 3Pollutants are substances added to the environment, particularly by human activities,
Слайд 4The high level of industry
life in many countries is
ecologically dangerous. The pollution of environment (water pollution, air pollution, land pollution) has the bad influence to human health. That is why nowadays a new branch of ecological science begins to develop. It is human ecology.
Слайд 5Human ecology
is an academic discipline that deals with the association
Слайд 6Human ecology is about investigating how
individuals and individual societies
interrelate with
environment. It integrates knowledge from
all academic disciplines and from personal
experience to
investigate, and
ultimately improve,
the relationships
between human
beings and our
social and natural
communities.
Слайд 7Human ecology views human communities and human populations as part of
In the world, human ecology was established as a sociological field in the 1920's, although geographers were using the term much earlier.
Слайд 8Nowadays the main human ecology
Слайд 9Human ecology explores not only the influence of humans on their
questions and ways
to answer those
questions.
?
?
?
?
?
?
Слайд 13The main tasks of human ecology:
the investigation of human health condition;
the
the forecast of the health condition of the future generations;
the investigation of the processes of human health protection;
the analysis of global and regional problems of human ecology;
the research of influence of environmental factors to human health;
the composition of medical-geographical maps that show the territorial differentiation of human diseases;
the addition of medical-geographical maps and environmental pollution maps and the determination of correlative dependence between human diseases and environmental pollution;
the determination of value of boundary technogenic load limit to human organism.
Слайд 14Human ecology uses many methods of investigation:
mathematical;
statistical;
biochemical;
physical;
bacteriological;
clinical;
physiological etc.
Human ecology is connected
immunology;
hygiene of environment;
ecotoxicology;
medical geography etc.
Слайд 15The main terms of human ecology:
Hygiene standard – is the definite
Maximum permissible concentration – is maximum amount of toxic substance in unit of volume or mass of water, air or soil which does not have any influence to human health;
Maximum permissible level – is periodical or permanent influence of the environmental factor to human organism which can not cause any diseases or changes in human health condition;
Maximum permissible dose – is the amount of toxic substance which penetrating in human organism does not hurt it.
Слайд 17The influence of physical factors to human organism
solar activity – there
Слайд 18If there are spots on the sun surface, people have bad
Слайд 19weather – it can have different influence to human organism. It
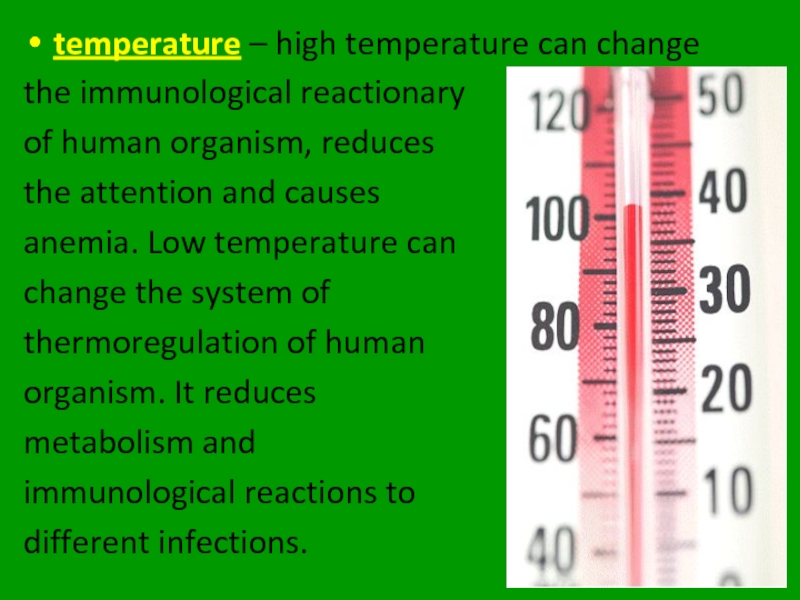
Слайд 20temperature – high temperature can change
the immunological reactionary
of human
the attention and causes
anemia. Low temperature can
change the system of
thermoregulation of human
organism. It reduces
metabolism and
immunological reactions to
different infections.
Слайд 21The influence of anthropogenic factors to human organism
ozone hole – it
Слайд 22greenhouse effect – it is the increase of environmental temperature (global
Слайд 24photochemical fogs – it is the mixture of different gases that
Слайд 25heavy metals – lead, mercury, manganese, zinc, chromium etc. – they
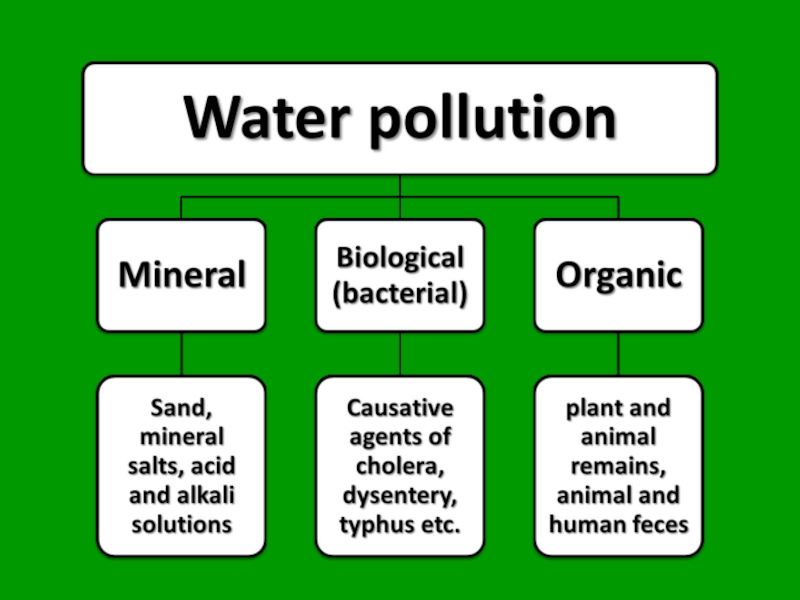
Слайд 26Water pollution
Water is the most spread nonorganic substance in whole world.
Слайд 27Hydrosphere is polluted with human help. Industrial wastes
can include heavy
pesticides. These materials are not destroyed under natural
conditions. So they accumulate in the bottom mud of deltas
of highly polluted rivers and cause environmental problems.
Слайд 29Every year 5 million peoples die in the result of poisoning
Itay-itay – it is the disease caused by water with high concentration of cadmium;
Minomata – it is the disease caused by water with high concentration of mercury;
Molybdenum podagra – it is the disease caused by water with high concentration of molybdenum;
Fluorosis - it is the disease caused by water with high concentration of fluor.
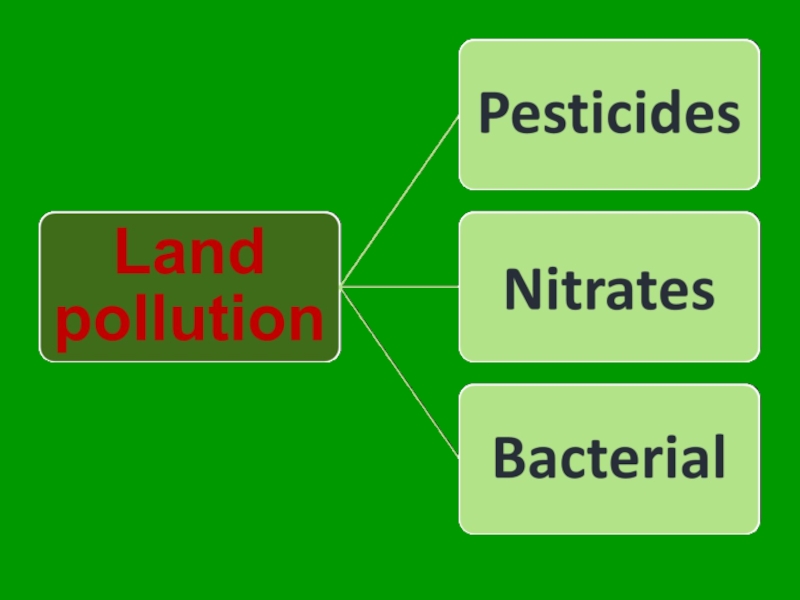
Слайд 30land pollution
The geosphere and biosphere are intimately connected through soils, which
Слайд 33In agriculture people use pesticides and nitrates. These substances are very
Слайд 34Human population
poses a threat to
the biosphere by
habitat destruction,
especially
destruction of
tropical rainforests
(deforestation).
This process is driving thousands of species to extinction each year and reducing biological diversity.
air pollution