- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Sale and Distribution презентация
Содержание
- 1. Sale and Distribution
- 2. Sale
- 3. The Steps of a Sale Preapproach Approaching the customer Determining needs Presenting the product
- 4. The Steps of a Sale Handling questions
- 5. The Preapproach-Getting ready to sell. Finding new
- 6. Sources and Methods of Prospecting Employer leads
- 7. Preparing for the Sale Industrial Sales Analyze
- 8. Preparing for the Sale Industrial Sales Ask
- 9. Preparing for the Sale Retail Sales The
- 10. Approaching the Customer First impressions count; if
- 11. Approaching the Customer Be aware of the
- 12. The Approach in Industrial Sales Setup an
- 13. The Approach in Industrial Sales Engage in
- 14. The Approach in Retail Sales Service Approach
- 15. The Approach in Retail Sales Greeting Approach
- 16. The Approach in Retail Sales Merchandise Approach
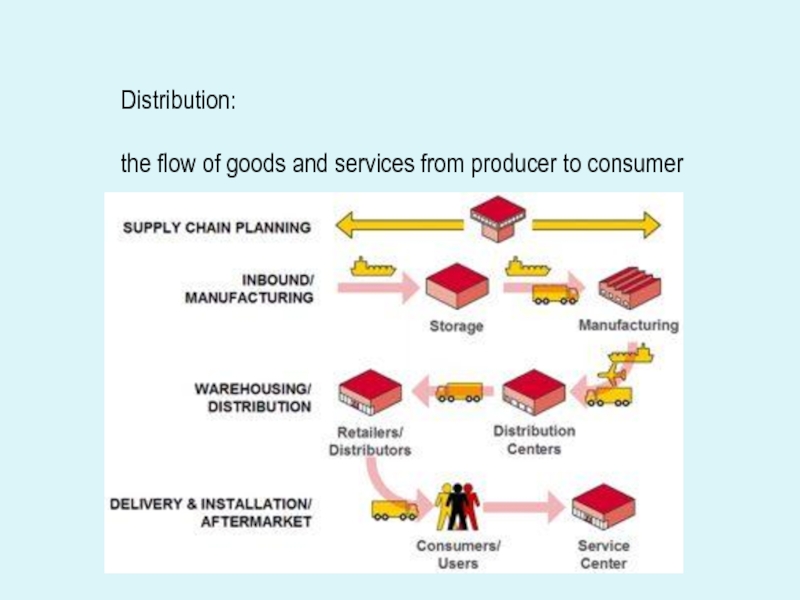
- 17. Distribution
- 18. Distribution: the flow of goods and services from producer to consumer
- 19. Canada’s sheer size and sparse population cause
- 20. There are six elements in the distribution
- 21. Producers: Extract raw materials from the
- 22. Processors: Few materials are useful in
- 23. Manufacturers: Manufacturers alter the processed raw
- 24. Wholesalers: Wholesalers are businesspeople who purchase
- 25. Merchant Wholesalers: They take full ownership
- 26. Agent Wholesalers: Agent wholesalers never take
- 27. Example: A manufacturer in Singapore wishes
- 28. The Singapore manufacturer will invoice the store
- 29. Manufacturers’ Representatives: Some manufacturers set up
- 30. Retailers: Retailers sell directly to the
- 31. Types of Retailers: Specialty Stores
- 32. Specialty Stores: They carry a broad
- 33. Single-line Store: Carry a wide variety
- 34. Convenience Stores: Are located in most
- 35. Department Stores: Are usually part of
- 36. Supermarkets; They are large-scale food retailers.
- 37. Machine Vendors: Are businesspeople who place
- 38. Roadside Establishments: Usually located in agricultural
- 39. e-tailing: The selling of retail goods
- 40. Discount Stores: These stores depend on
Слайд 3The Steps of a Sale
Preapproach
Approaching the customer
Determining needs
Presenting the product
Слайд 4The Steps of a Sale
Handling questions and objections
Closing the sale
Suggestions selling
Reassuring
and following up
Слайд 5The Preapproach-Getting ready to sell.
Finding new customers by prospecting
Retail sales
not a prevalent because the customers come into the store.
Important for the salesperson to open new accounts to generate sales volume.
Important for the salesperson to open new accounts to generate sales volume.
Слайд 6Sources and Methods of Prospecting
Employer leads
Telephone Directories
Trade and Professional Directories
Newspapers
Commercial Lists
Customer
Referrals
Cold Canvassing
Cold Canvassing
Слайд 7Preparing for the Sale
Industrial Sales
Analyze past sales records.
View notes about the
personal aspects of the customer.
Qualify new customers.
Inquire with other salespeople who are with non-competing lines.
Qualify new customers.
Inquire with other salespeople who are with non-competing lines.
Слайд 8Preparing for the Sale
Industrial Sales
Ask questions in a pre-visit phone call.
Make
an appointment to see the prospect in order to have time to explain the features of your product.
Слайд 9Preparing for the Sale
Retail Sales
The customer comes to you, so most
of the preparation is in the retail store.
Stockkeeping and housekeeping duties are important.
Learn about the merchandise and the prices of the merchandise.
Stockkeeping and housekeeping duties are important.
Learn about the merchandise and the prices of the merchandise.
Слайд 10Approaching the Customer
First impressions count; if a customer is turned off
by the approach it will be difficult to win him or her over.
Be alert to what interests the customer.
Establish rapport.
Be alert to what interests the customer.
Establish rapport.
Слайд 11Approaching the Customer
Be aware of the customer’s buying style.
Follow good guidelines
for establishing a positive relationship with customers.
Слайд 12The Approach in Industrial Sales
Setup an appointment during the preapproach, and
arrive early to the appointment.
Introduce yourself, smile, and shake hands.
Introduce yourself, smile, and shake hands.
Слайд 13The Approach in Industrial Sales
Engage in small talk to build a
relationship with the customer.
Comment on important things to keep the customer interested.
Comment on important things to keep the customer interested.
Слайд 14The Approach in Retail Sales
Service Approach Method
“May I help you”
Appropriate when
the customer is obviously in a hurry or you are simply an order taker.
Ineffective in most situations; you lose control of the sales situation.
Ineffective in most situations; you lose control of the sales situation.
Слайд 15The Approach in Retail Sales
Greeting Approach Method
“Good afternoon, Mr. Wright” or
an appropriate personal comment.
This approach begins conversation and establishes a positive rapport.
Do not focus on the merchandise.
This approach begins conversation and establishes a positive rapport.
Do not focus on the merchandise.
Слайд 16The Approach in Retail Sales
Merchandise Approach Method
The salesperson makes a comment
or asks questions about a product that the customer is looking at.
Ask questions about the item.
Usually the most effective approach because it immediately focuses attention on the merchandise.
Ask questions about the item.
Usually the most effective approach because it immediately focuses attention on the merchandise.
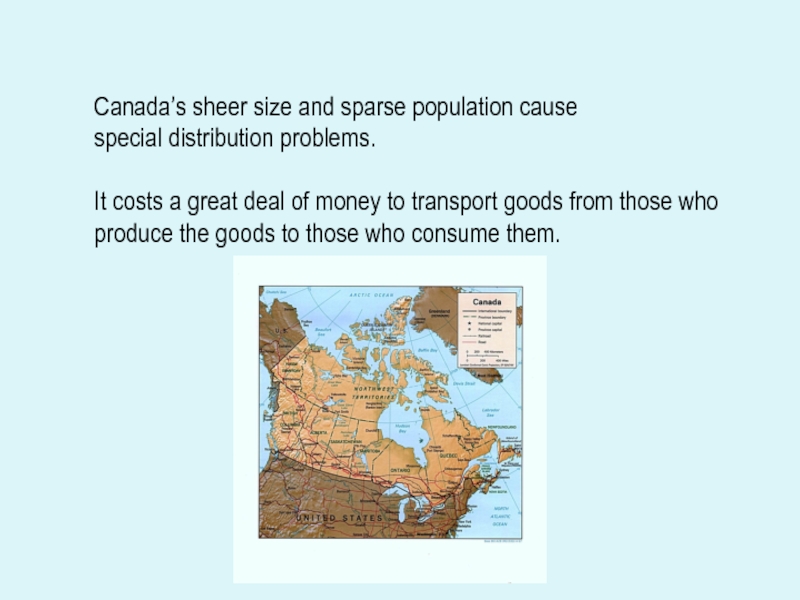
Слайд 19Canada’s sheer size and sparse population cause
special distribution problems.
It costs
a great deal of money to transport goods from those who
produce the goods to those who consume them.
produce the goods to those who consume them.
Слайд 20There are six elements in the distribution process:
Producers
Processors
Manufacturers
Wholesalers
Retailers
Consumers
Retailers
Consumers
Слайд 21Producers:
Extract raw materials from the earth.
Mining, agriculture, oil exploration are examples.
Слайд 22Processors:
Few materials are useful in their raw state, they must be
altered to
be useful. Processors alter the raw materials.
Iron ore is made into steel
Oil is turned into gasoline
be useful. Processors alter the raw materials.
Iron ore is made into steel
Oil is turned into gasoline
Слайд 23Manufacturers:
Manufacturers alter the processed raw materials into products
for the consumer.
Steel
is turned into an automobile.
Слайд 24Wholesalers:
Wholesalers are businesspeople who purchase goods and in
large quantities and resell
them in smaller quantities at higher prices.
There are three major types of wholesalers:
Merchant Wholesalers
Agent Wholesalers
Manufacturers’ Representatives
There are three major types of wholesalers:
Merchant Wholesalers
Agent Wholesalers
Manufacturers’ Representatives
Слайд 25Merchant Wholesalers:
They take full ownership of the goods purchased from the
manufacturers.
Once the sale is completed, the wholesaler takes possession of
the goods, then stores and and warehouses them.
The merchant wholesaler then finds customers for the goods.
Merchant wholesalers earn their profits by marking up the price of the
goods they purchase beyond the price that they paid.
Слайд 26Agent Wholesalers:
Agent wholesalers never take ownership of the goods.
They arrange
for the sale of the goods between manufacturers and
those that wish to purchase the manufacturers’ goods.
Agent wholesalers are usually paid on commission, a percentage
of the sale, by the manufacturer.
Manufacturers often prefer to deal with agents because of their
expertise. Agents know the product, the parts of the country that
represent the best sales opportunities and the types of consumers
who will purchase the item.
those that wish to purchase the manufacturers’ goods.
Agent wholesalers are usually paid on commission, a percentage
of the sale, by the manufacturer.
Manufacturers often prefer to deal with agents because of their
expertise. Agents know the product, the parts of the country that
represent the best sales opportunities and the types of consumers
who will purchase the item.
Слайд 27Example:
A manufacturer in Singapore wishes to sell a new line of
ski boots
in Canada.
The Singapore manufacturer will contact an agent wholesaler in
Canada who specializes in skiwear.
This agent will be familiar with the retail stores and the parts of
Canada that represent the best possible market for the item.
The agent will visit the stores, bring samples and take orders.
The orders will be sent by the agent to the manufacturer and the
manufacturer will ship the product directly to the store.
in Canada.
The Singapore manufacturer will contact an agent wholesaler in
Canada who specializes in skiwear.
This agent will be familiar with the retail stores and the parts of
Canada that represent the best possible market for the item.
The agent will visit the stores, bring samples and take orders.
The orders will be sent by the agent to the manufacturer and the
manufacturer will ship the product directly to the store.
Слайд 28The Singapore manufacturer will invoice the store for the cost of
the
boots.
The agent will receive the predetermined commission from the
Singapore manufacturer once the sale is completed.
boots.
The agent will receive the predetermined commission from the
Singapore manufacturer once the sale is completed.
Слайд 29Manufacturers’ Representatives:
Some manufacturers set up their own wholesale divisions.
The division is
comprised of manufacturers’ representatives who
specialize in the wholesaling of the manufacturer’s products
specialize in the wholesaling of the manufacturer’s products
Слайд 30Retailers:
Retailers sell directly to the consumer and make it convenient for
consumers
to purchase goods.
Without retailers, consumers would be forced to seek out wholesalers
or go directly to manufacturers’ factories to obtain goods they need.
Without retailers, consumers would be forced to seek out wholesalers
or go directly to manufacturers’ factories to obtain goods they need.
Слайд 31Types of Retailers:
Specialty Stores
Single-line Stores
Convenience Stores
Department Stores
Supermarkets
Machine Vendors
Roadside Establishments
e-tailing
Discount Stores
Machine Vendors
Roadside Establishments
e-tailing
Discount Stores
Слайд 32Specialty Stores:
They carry a broad line of goods, all directly related.
A
women’s wear store carries skirts, blouses, suits, belts, hosiery,
coats, slacks, and accessories for women.
A sporting goods store carries sports equipment, clothing, and
accessories for a wide range of sports.
coats, slacks, and accessories for women.
A sporting goods store carries sports equipment, clothing, and
accessories for a wide range of sports.
Слайд 33Single-line Store:
Carry a wide variety of one product.
Opticians and Second Cup
are examples of single-line stores.
Слайд 34Convenience Stores:
Are located in most neighbourhoods and obtained their name
because
they are situated close to those who use them and in most
cases are open long hours.
They carry a large variety of necessities for the home, including milk,
eggs, bread, and other everyday items.
cases are open long hours.
They carry a large variety of necessities for the home, including milk,
eggs, bread, and other everyday items.
Слайд 35Department Stores:
Are usually part of large chains (a chain is a
group of stores that are
managed through a central office).
These stores provide a wide range of consumer goods in specialized
divisions or departments such as sporting goods, ladies’ wear, or
furniture.
Examples are Sears, The Bay, Walmart.
managed through a central office).
These stores provide a wide range of consumer goods in specialized
divisions or departments such as sporting goods, ladies’ wear, or
furniture.
Examples are Sears, The Bay, Walmart.
Слайд 36Supermarkets;
They are large-scale food retailers.
Examples are Loblaws, Sobey’s, Longo’s, No Frills,
and Metro.
Слайд 37Machine Vendors:
Are businesspeople who place vending machines in certain contracted
locations.
The vendor
is responsible for stocking and maintaining the machines.
Слайд 38Roadside Establishments:
Usually located in agricultural growing areas.
They are highly seasonal operations
that do large volumes of business
when crops are being harvested.
Consumers are often encouraged to stop and purchase fresh fruit,
vegetables or pies.
when crops are being harvested.
Consumers are often encouraged to stop and purchase fresh fruit,
vegetables or pies.
Слайд 40Discount Stores:
These stores depend on selling a large quantity of goods
at a low price
in order to maintain profitable operations.
Prices are kept at a minimum.
Examples include Dollarama, Giant Tiger, and Honest Ed’s.
This category also includes Costco.
in order to maintain profitable operations.
Prices are kept at a minimum.
Examples include Dollarama, Giant Tiger, and Honest Ed’s.
This category also includes Costco.