- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Skills Outlook 2015 Youth, Skills and Employability презентация
Содержание
- 1. Skills Outlook 2015 Youth, Skills and Employability
- 2. Young people in OECD countries
- 3. Youth neither employed nor in
- 4. Youth who are neither employed
- 5. Young workers in routine jobs Share
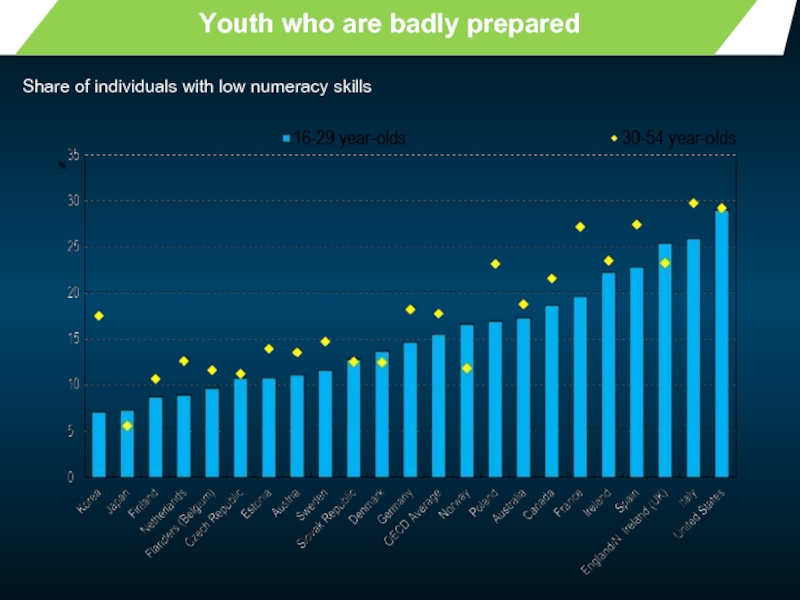
- 6. Youth who are badly prepared Share of individuals with low numeracy skills
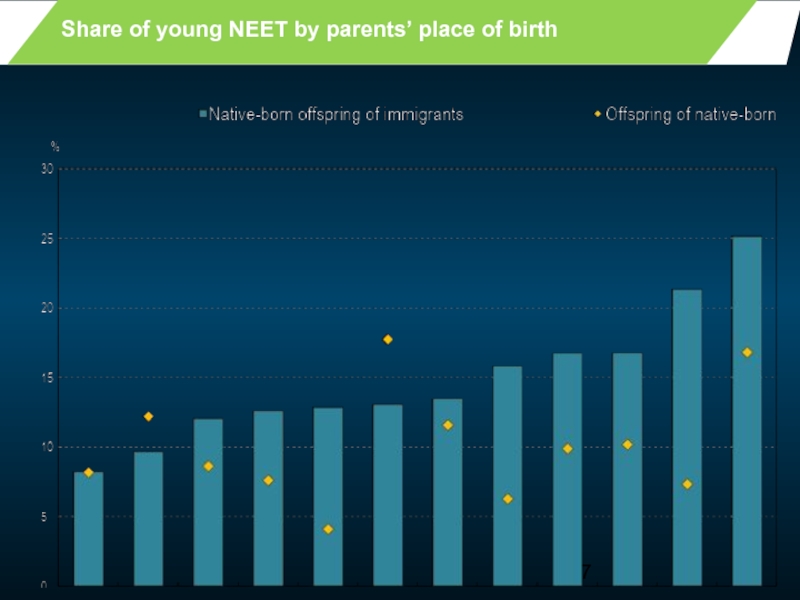
- 7. Share of young NEET by parents’ place of birth
- 8. What can we do
- 9. Skills Scoreboard: strengths and
- 10. Preparing youths Ensure that all youths leave school with relevant skills
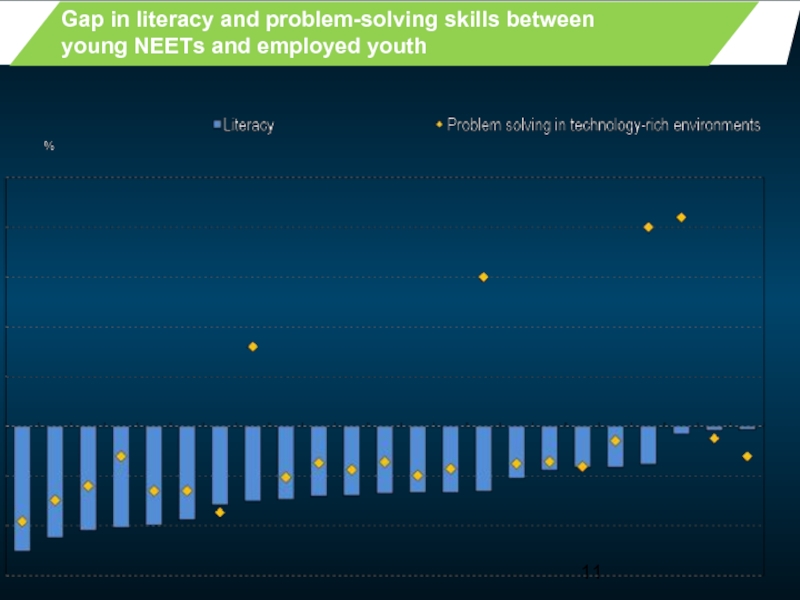
- 11. Gap in literacy and problem-solving
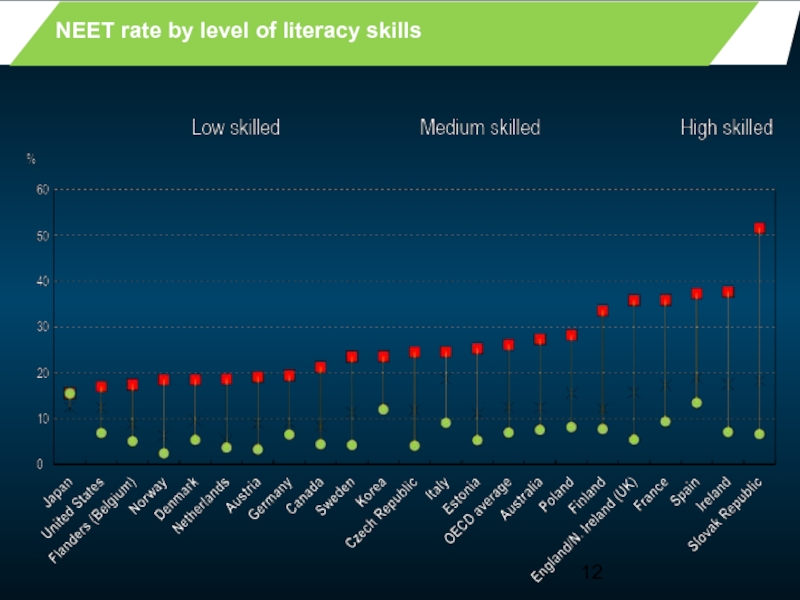
- 12. NEET rate by level of literacy skills
- 13. New graduates (
- 14. Youth who lack basic ICT skills
- 15. Self-reported ICT skills deficiency
- 16. Students and their experience with the labour market
- 17. Share of upper secondary graduates who are NEET by programme orientation
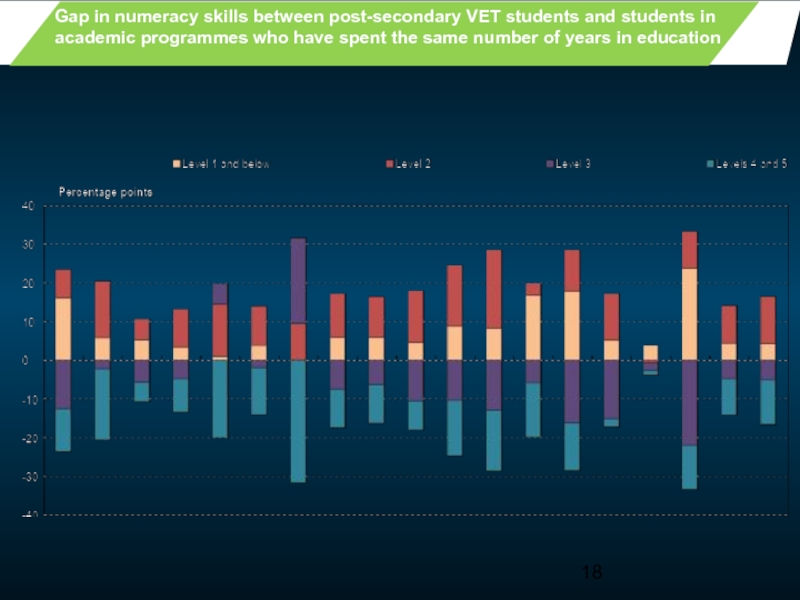
- 18. Gap in numeracy skills between
- 19. Students in upper secondary vocational education who are participating in work-based learning
- 20. Participation in work-based learning of
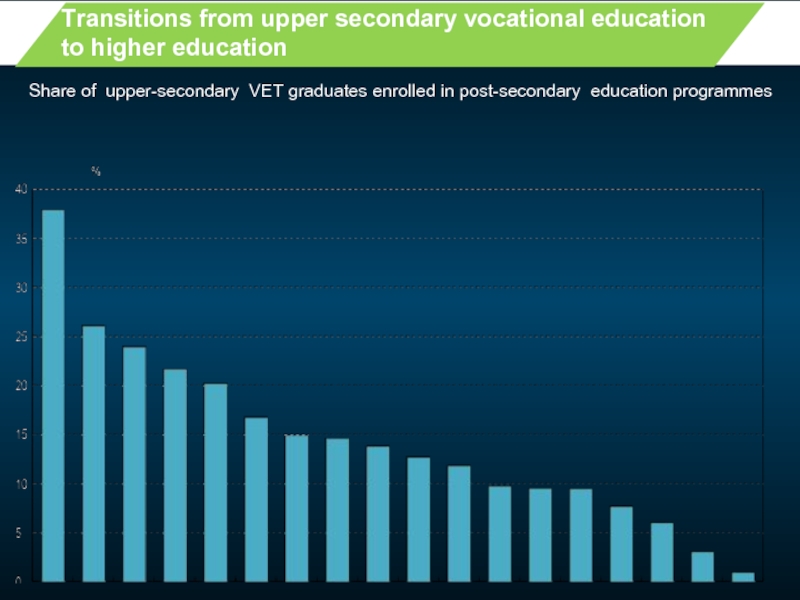
- 21. Transitions from upper secondary vocational
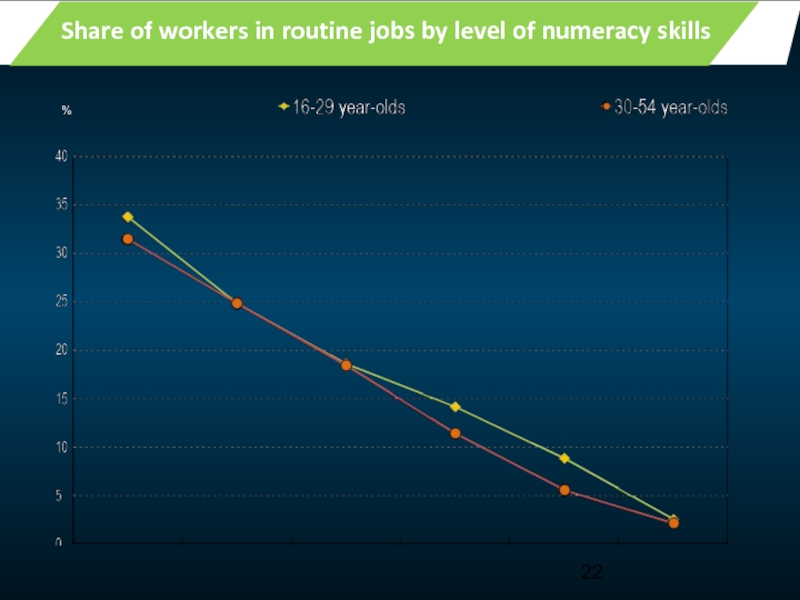
- 22. % Share of workers in routine jobs by level of numeracy skills
- 23. Skills Scoreboard: Is the development
- 24. Ensure that all young people
- 25. Reengage youths Identify and help NEETs to reengage
- 26. Youth who risk of
- 27. Skills scoreboard: How close are
- 28. Identify and help the NEETs
- 29. Reengaging youths Remove institutional barriers to youth employment
- 30. It’s not just skills: some NEETs
- 31. Remove institutional barriers to
- 32. Using skills Make better use of young workers skills
- 33. Use of skills by upper
- 34. Young workers on temporary contracts
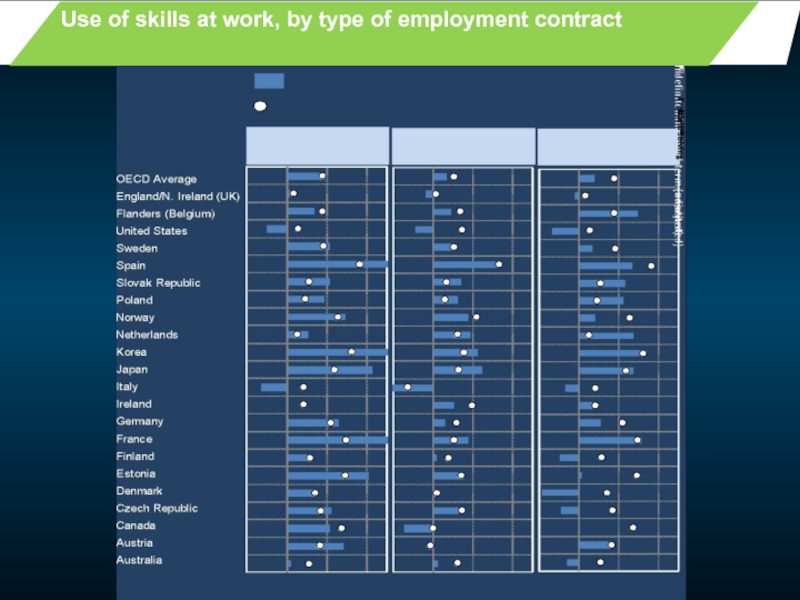
- 35. Use of skills at work, by type of employment contract
- 36. Skills Scoreboard: do workplaces promote skills?
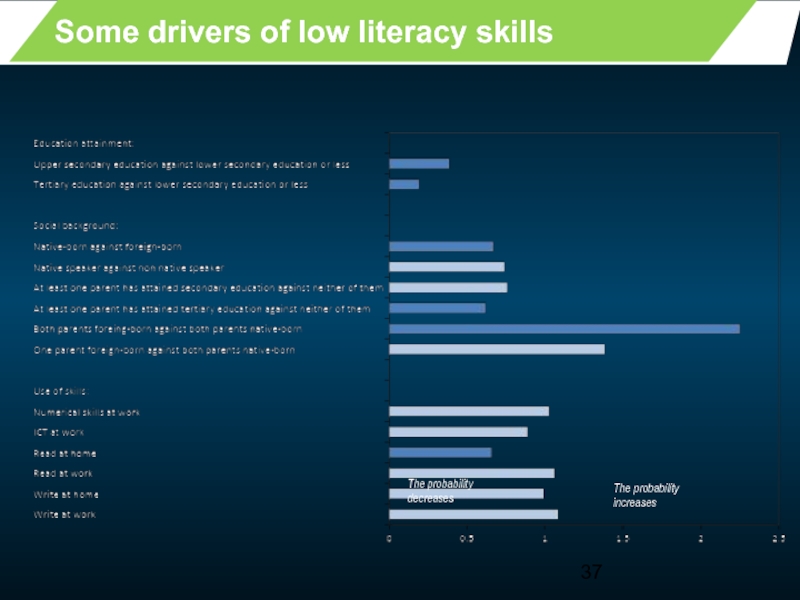
- 37. Some drivers of low literacy skills The probability increases The probability decreases
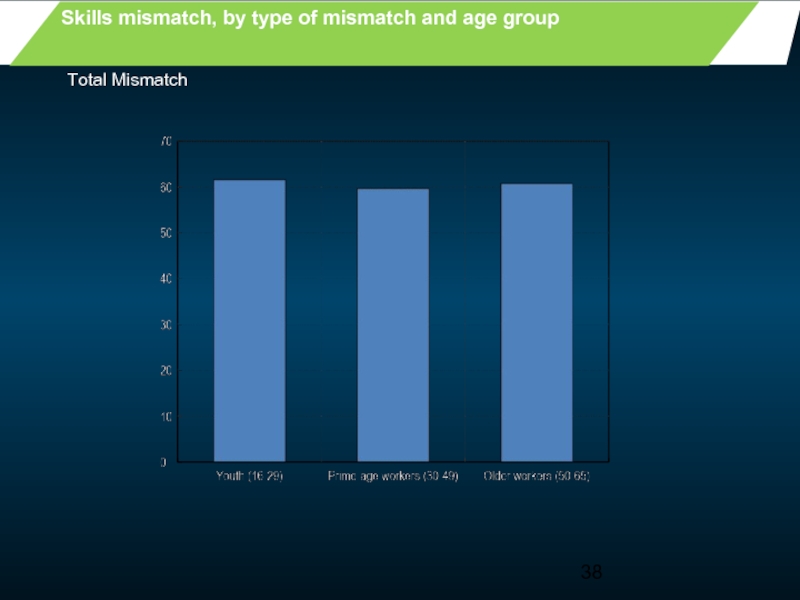
- 38. Skills mismatch, by type of mismatch and age group Total Mismatch
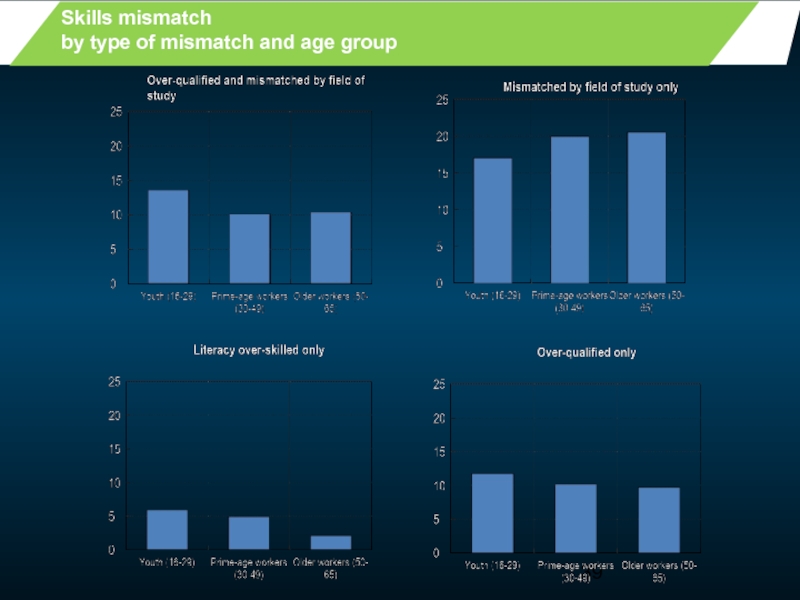
- 39. Skills mismatch by type of mismatch and age group
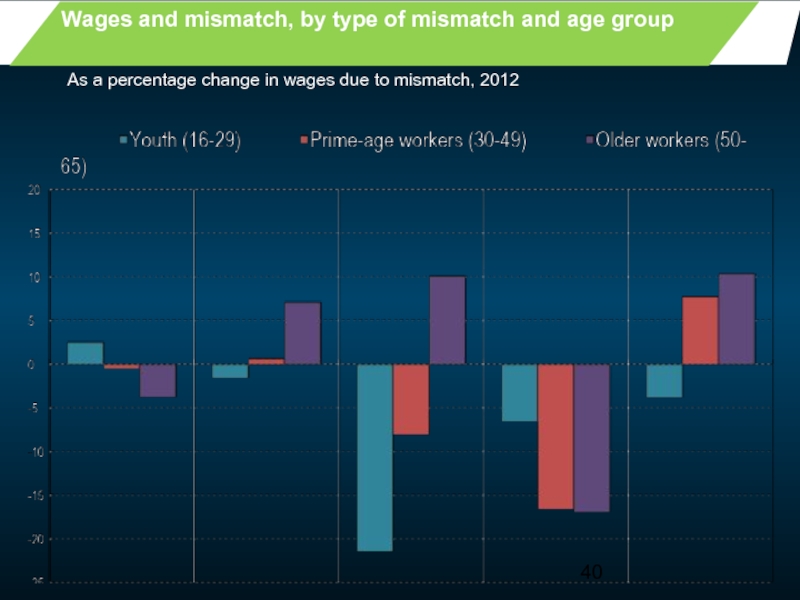
- 40. Wages and mismatch, by type
- 41. Share of individuals interested in entrepreneurship, European countries
- 42. Making a better use of
- 43. Find Out More at: http://skills.oecd.org/skillsoutlook.htm All
Слайд 2Young people in OECD countries
Many young people struggle
in their transition
Слайд 3
Youth neither employed nor in education or training (NEET)
%
As a percentage
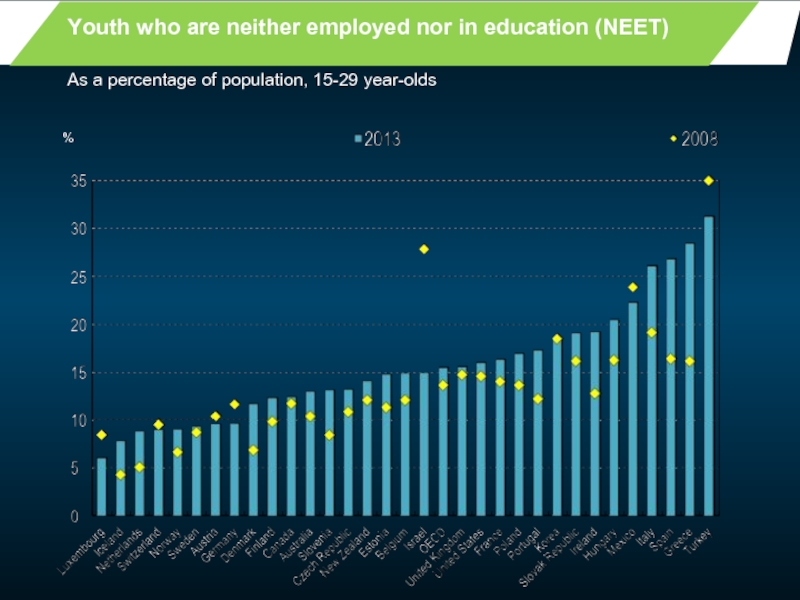
Слайд 4
Youth who are neither employed nor in education (NEET)
%
As a percentage
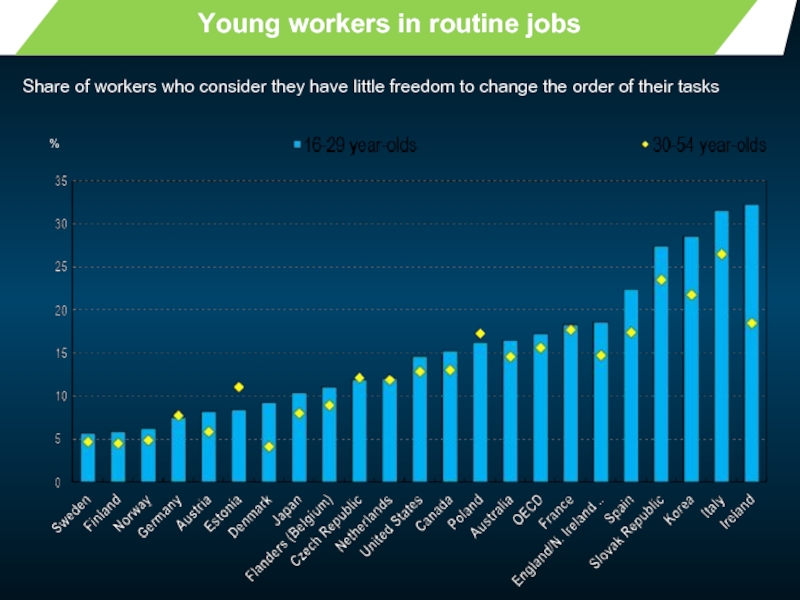
Слайд 5
Young workers in routine jobs
Share of workers who consider they have
%
Слайд 8
What can we do to strengthen young people’s skills
and employability?
Build
Слайд 9
Skills Scoreboard: strengths and weaknesses
France Ireland
Italy
Spain
Denmark Korea Norway Poland
Austria
Check Rep.
Australia Belgium Canada Estonia Finland Germany Japan Netherlands
Слайд 18
Gap in numeracy skills between post-secondary VET students and students in
Слайд 19
Students in upper secondary vocational education
who are participating in work-based
Слайд 20
Participation in work-based learning of students in post-secondary VET and academic
Students in vocational programmes
Students in academic programmes
Слайд 21
Transitions from upper secondary vocational education
to higher education
Share of upper-secondary
Слайд 23
Skills Scoreboard: Is the development of skills inclusive?
Inequity
Equity
Low performance at school
Strong
Strong influence of migration background
Слайд 24
Ensure that all young people leave school with relevant skills
Take a
Provide multiple pathways within the education system. Give disengaged youth a second chance to reintegrate into the education system
Develop work-based learning programmes across different types of education, including universities
Design high quality vocational education and training programmes that develop cognitive and social and emotional skills, and labour market experience
Base career guidance services on relevant assessment of the market returns of various career paths
Engage employers and other stakeholders in the education system at all levels .
Слайд 26
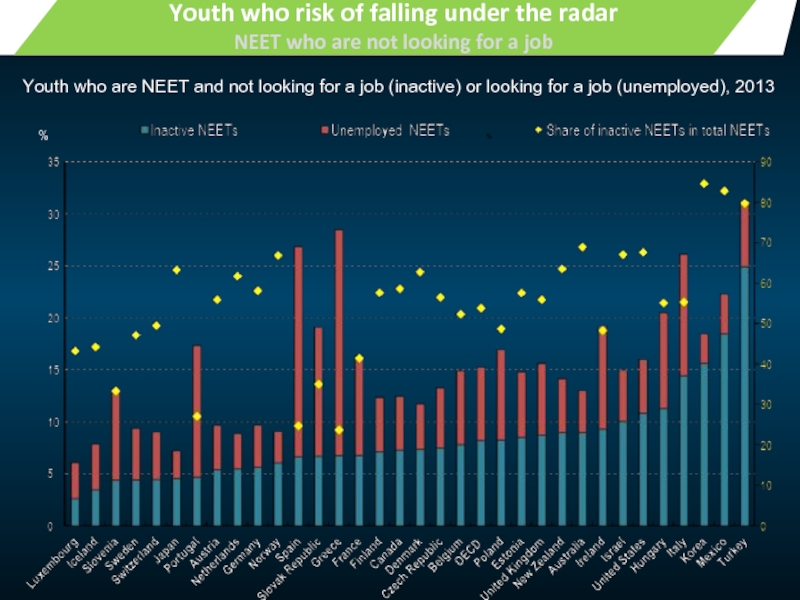
Youth who risk of falling under the radar
NEET who are
%
%
Youth who are NEET and not looking for a job (inactive) or looking for a job (unemployed), 2013
Слайд 27
Skills scoreboard: How close are NEETs to the labour market?
Close
Far
High share
Share of NEETs with poor skills
Share of NEETs without baseline qualifications
Share of long-term unemployed NEETs
Слайд 28
Identify and help the NEETs to re-engage
Develop a system of mutual
Encourage employment through efficient job-search assistance and training, monitoring and financial incentives
Target places in training programmes and job subsidies to youth with low skills and those who face specific barriers in the labour market .
Слайд 30
It’s not just skills: some NEETs have good education and cognitive
Cognitive skills of youth neither in employment nor in education or training
Слайд 31
Remove institutional barriers to youth employment
Design skills-friendly tax policies to foster
Continue to lower the gap in employment protection legislation between temporary and permanent contracts
Encourage end-of-study internships within a framework that combines flexibility and obligations to firms .
Слайд 33
Use of skills by upper secondary vocational students who are combining
Слайд 36
Skills Scoreboard: do workplaces promote skills?
To a large extent
To a small
Task discretion
Learning by doing
Use of problem-solving skills at work
Use of co-operation skills at work
Слайд 40
Wages and mismatch, by type of mismatch and age group
As a
Слайд 42
Making a better use of young workers’ skills
Remove barriers to geographical
Develop (inter)national qualification frameworks and formal recognition of skills acquired through non-formal and informal learning
Promote more effective work organisation and human resource management strategies
Remove barriers to entrepreneurship
Invest in tools for assessing and anticipating skills needs .
Слайд 43Find Out More at:
http://skills.oecd.org/skillsoutlook.htm
All national and international publications
The complete micro-level
…and remember:
Email
Andreas.Schleicher@OECD.org
Twitter
@SchleicherEDU