- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The types of variability. The causes of modification variability презентация
Содержание
- 2. The types of variability. The causes of modification variability.
- 3. learning Objectives classify the types of variability explain the causes of modification variability
- 4. Success criteria 1.Know about types of
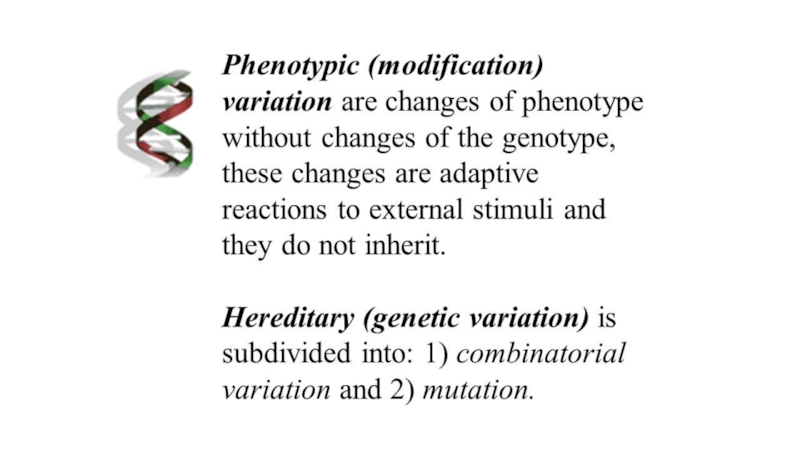
- 5. Terminology Heritable, environmental effects on the
- 6. Variation Results from genetic and environmental
- 7. Genotypic variations Genotypic variations are caused
- 8. Genetic Variation Causes Genetic variation occurs mainly
- 9. Environmentally factors Environmentally caused variations may result
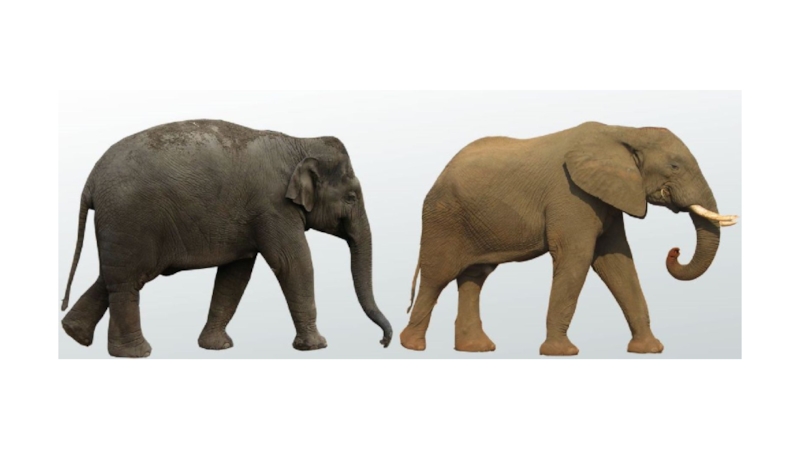
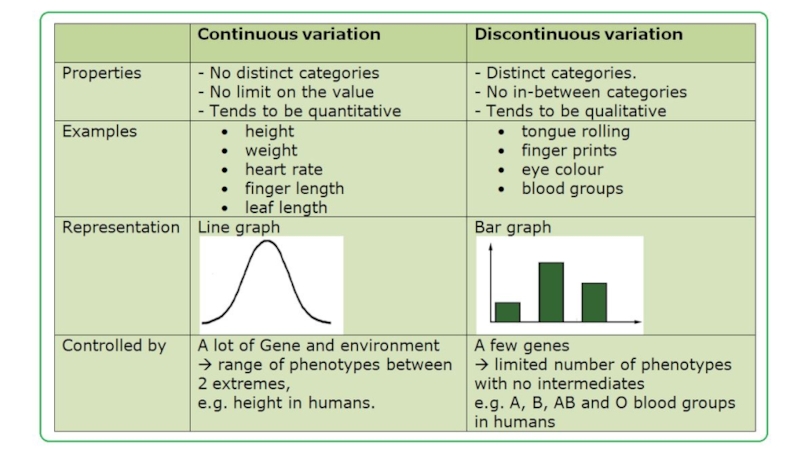
- 11. Classification of variation continuous, or quantitative discontinuous, or qualitative
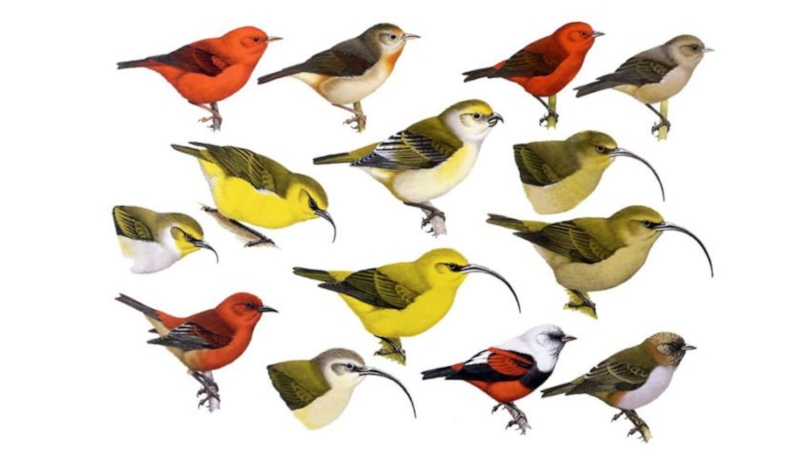
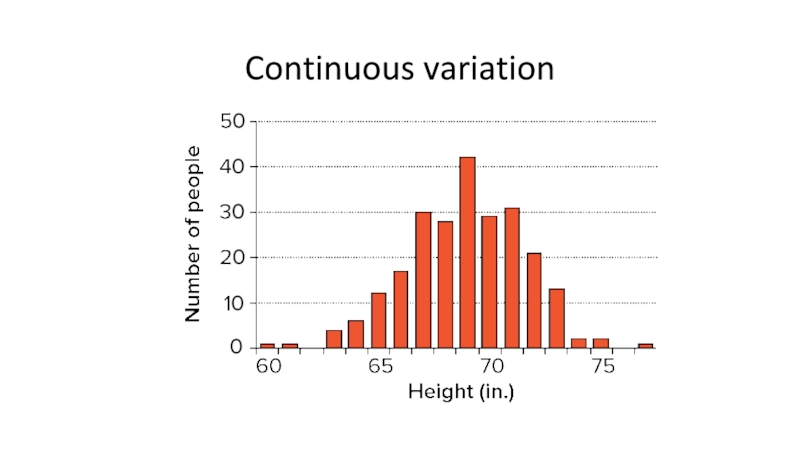
- 12. Continuous variation
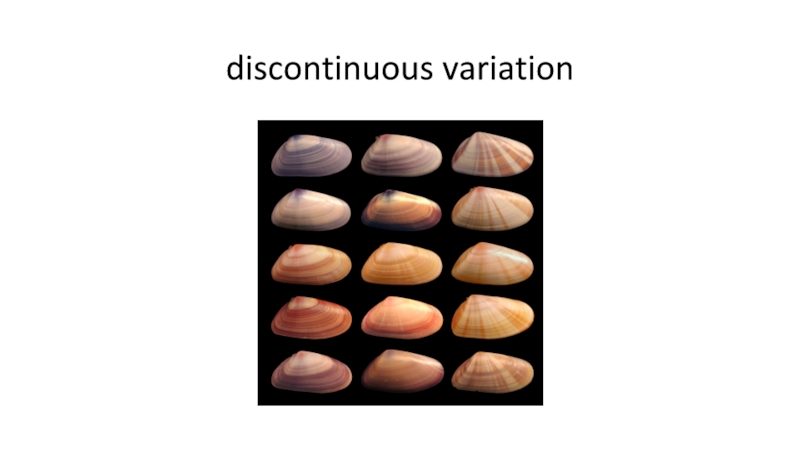
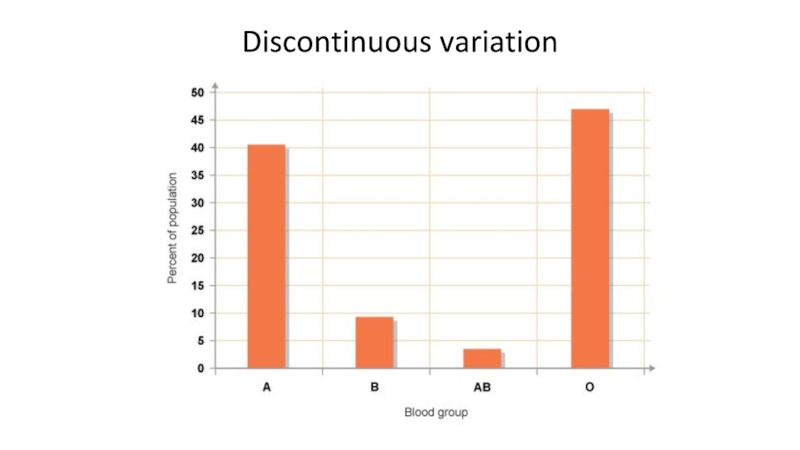
- 13. Discontinuous variation
- 15. The genetic basis of discontinuous variation In
- 16. continuous variation
- 17. The genetic basis of continuous variation In
- 18. discontinuous variation
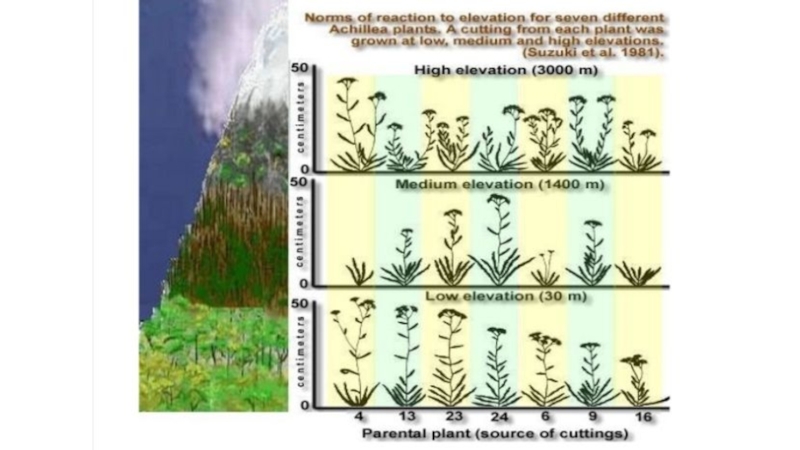
- 19. Environmental effects on the phenotype
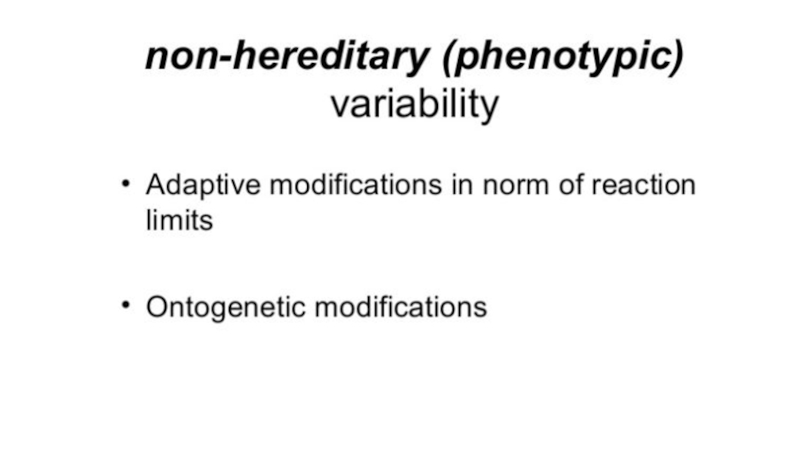
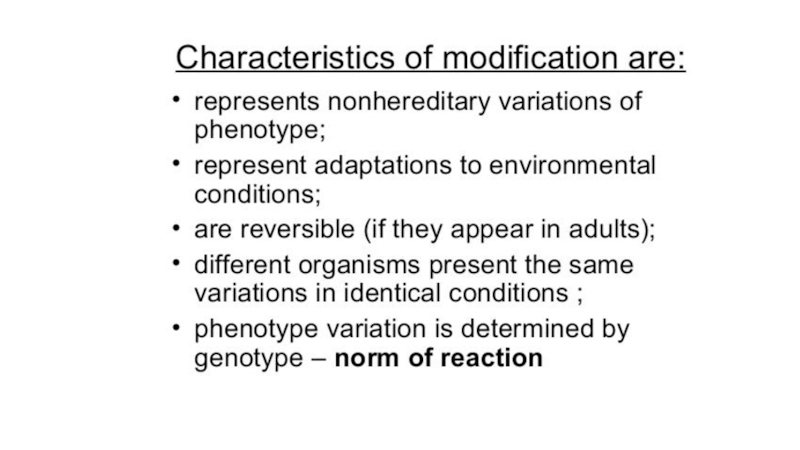
- 23. The causes of modification variability
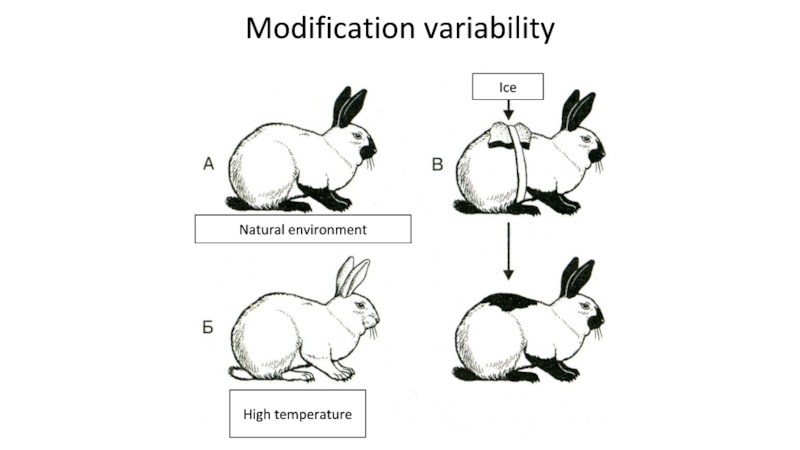
- 28. Modification variability Ice Natural environment High temperature
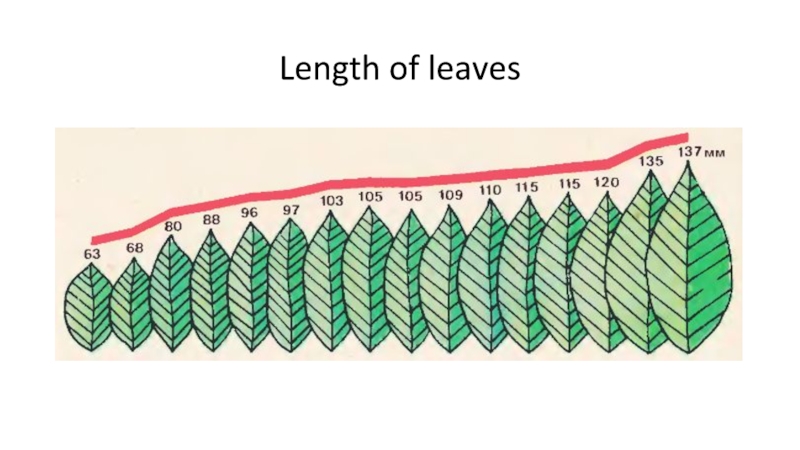
- 29. Length of leaves
- 30. Dandelion leaves valley Highlands of the Alps
- 37. variation curve of pumpkin seeds along the
- 38. Success criteria 1.Know about types of
Слайд 3learning Objectives
classify the types of variability
explain the causes of modification
variability
Слайд 4Success criteria
1.Know about types of variation.
2.Explain the types of variation:
modification variability, mutation variability, variability of discontinuous and continuous.
3.Carry out research on reasons of emergence of modification variability.
4.Describe research methods indicating the number of measurements they plan to take, e.g. how many people they select and what range should be selected.
5.Describe research process. Explain reasons of emergence of modification variability.
6.Draw conclusions.
3.Carry out research on reasons of emergence of modification variability.
4.Describe research methods indicating the number of measurements they plan to take, e.g. how many people they select and what range should be selected.
5.Describe research process. Explain reasons of emergence of modification variability.
6.Draw conclusions.
Слайд 5Terminology
Heritable, environmental effects on the phenotype, modification variability.
Non-heritable, mutation variability,
the genetic basis of continuous and discontinuous variation (variability of intermittent and uninterruptible)
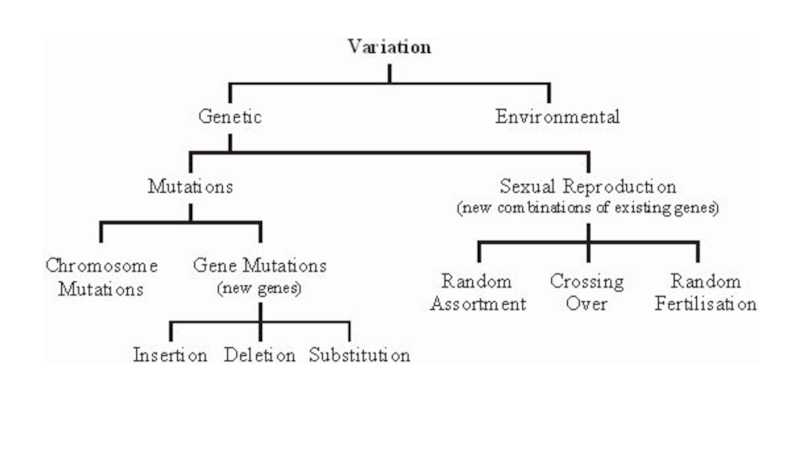
genetic recombination: free assortment, crossing over, random fusion;
genetic recombination: free assortment, crossing over, random fusion;
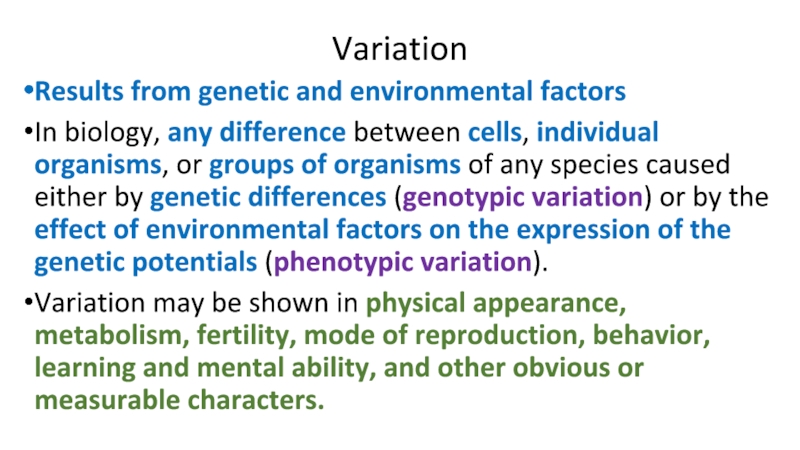
Слайд 6Variation
Results from genetic and environmental factors
In biology, any difference between
cells, individual organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by genetic differences (genotypic variation) or by the effect of environmental factors on the expression of the genetic potentials (phenotypic variation).
Variation may be shown in physical appearance, metabolism, fertility, mode of reproduction, behavior, learning and mental ability, and other obvious or measurable characters.
Variation may be shown in physical appearance, metabolism, fertility, mode of reproduction, behavior, learning and mental ability, and other obvious or measurable characters.
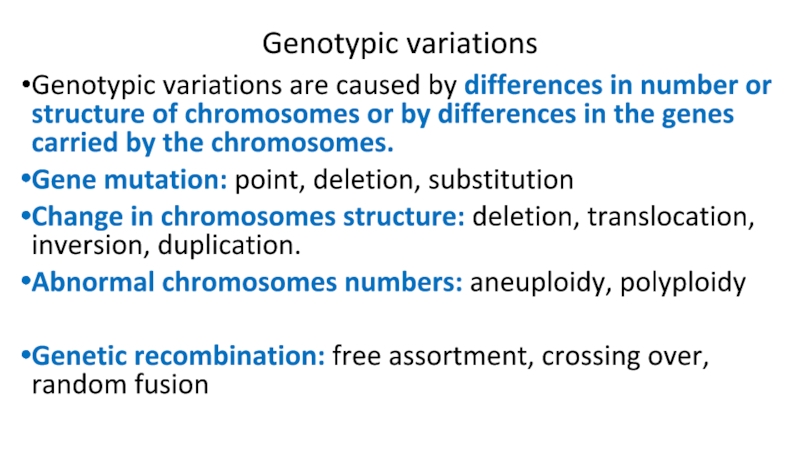
Слайд 7Genotypic variations
Genotypic variations are caused by differences in number or
structure of chromosomes or by differences in the genes carried by the chromosomes.
Gene mutation: point, deletion, substitution
Change in chromosomes structure: deletion, translocation, inversion, duplication.
Abnormal chromosomes numbers: aneuploidy, polyploidy
Genetic recombination: free assortment, crossing over, random fusion
Gene mutation: point, deletion, substitution
Change in chromosomes structure: deletion, translocation, inversion, duplication.
Abnormal chromosomes numbers: aneuploidy, polyploidy
Genetic recombination: free assortment, crossing over, random fusion
Слайд 8Genetic Variation Causes
Genetic variation occurs mainly through DNA mutation, gene flow
(movement of genes from one population to another) and sexual reproduction. Due to the fact that environments are unstable, populations that are genetically variable will be able to adapt to changing situations better than those that do not contain genetic variation.
Слайд 9Environmentally factors
Environmentally caused variations may result from one factor or the
combined effects of several factors, such as climate, food supply, and actions of other organisms.
Phenotypic variations also include stages in an organism’s life cycle and seasonal variations in an individual. These variations do not involve any hereditary alteration and in general are not transmitted to future generations;
consequently, they are not significant in the process of evolution.
Phenotypic variations also include stages in an organism’s life cycle and seasonal variations in an individual. These variations do not involve any hereditary alteration and in general are not transmitted to future generations;
consequently, they are not significant in the process of evolution.
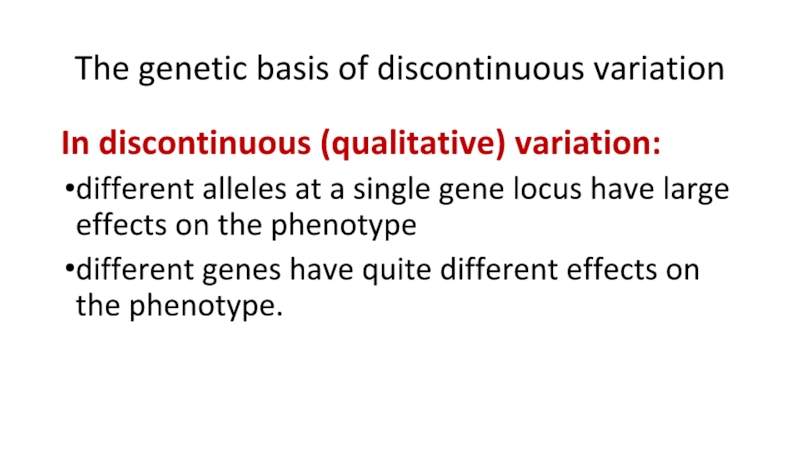
Слайд 15The genetic basis of discontinuous variation
In discontinuous (qualitative) variation:
different alleles at
a single gene locus have large effects on the phenotype
different genes have quite different effects on the phenotype.
different genes have quite different effects on the phenotype.
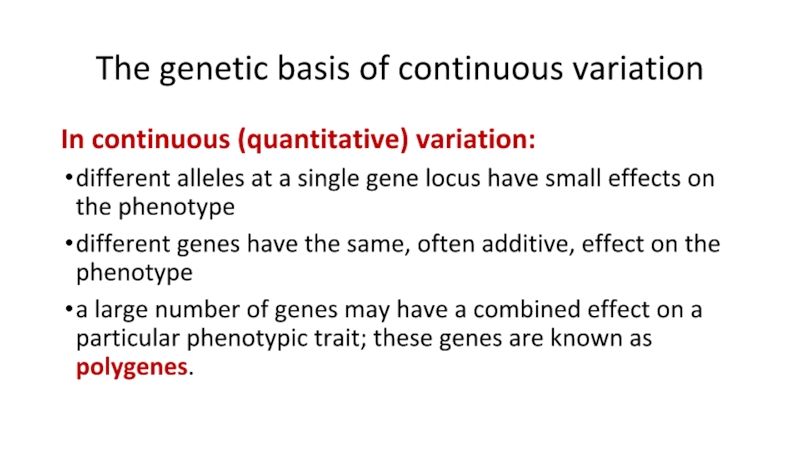
Слайд 17The genetic basis of continuous variation
In continuous (quantitative) variation:
different alleles at
a single gene locus have small effects on the phenotype
different genes have the same, often additive, effect on the phenotype
a large number of genes may have a combined effect on a particular phenotypic trait; these genes are known as polygenes.
different genes have the same, often additive, effect on the phenotype
a large number of genes may have a combined effect on a particular phenotypic trait; these genes are known as polygenes.
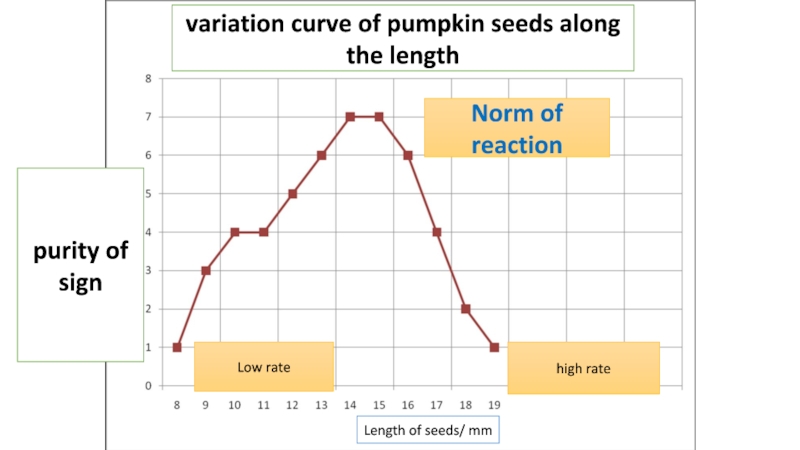
Слайд 37variation curve of pumpkin seeds along the length
Length of seeds/ mm
purity
of sign
Norm of reaction
high rate
Low rate
Слайд 38Success criteria
1.Know about types of variation.
2.Explain the types of variation:
modification variability, mutation variability, variability of discontinuous and continuous.
3.Carry out research on reasons of emergence of modification variability.
4.Describe research methods indicating the number of measurements they plan to take, e.g. how many people they select and what range should be selected.
5.Describe research process. Explain reasons of emergence of modification variability.
6.Draw conclusions.
3.Carry out research on reasons of emergence of modification variability.
4.Describe research methods indicating the number of measurements they plan to take, e.g. how many people they select and what range should be selected.
5.Describe research process. Explain reasons of emergence of modification variability.
6.Draw conclusions.