- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The Role of Environmental Impact in Building Material’s Selection презентация
Содержание
- 1. The Role of Environmental Impact in Building Material’s Selection
- 2. Titles Content Introduction Impact of Building Materials
- 3. Annually three billion metric tons of raw
- 4. The shapes of countries have been stretched
- 5. Buildings and associated uses are responsible for
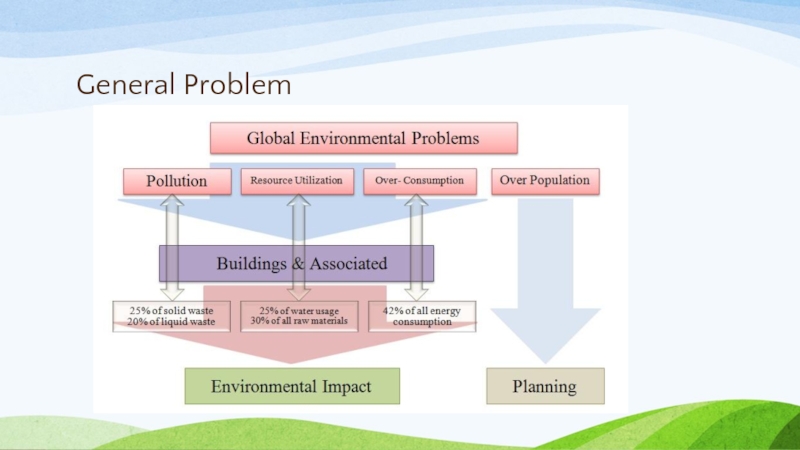
- 6. General Problem
- 7. Research aim to diagnose the environmental impact
- 8. 2. Impact of Building Materials on Human
- 9. Activities caused air pollution Production of electricity
- 10. Air pollutants can cause cancer reproductive
- 11. 2.2. Smog “Smog is a type
- 12. Activities caused smog Transport of materials, equipments
- 13. Smog can cause Like air pollutants and
- 14. 2.3. Ecological Toxicity Toxic materials can
- 15. What materials pose toxic risks to people?
- 16. 3. Impact of Building Materials on Ecological
- 17. 3.1 Global Climate Change Global warming
- 18. Three-quarter of anthropogenic greenhouse-gas emission are generated
- 19. 3.2 Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Human caused emissions
- 20. 3.3 Acidification Acidification occurs in surface waters
- 21. Acid rain also accelerates weathering of building
- 22. 3.4 Eutrophication “Eutrophication is the addition of
- 23. 3.5 Deforestation, Desertification, and Soil Erosion Table
- 24. loss of bio-diversity, global warming,
- 25. agriculture, mining, new
- 26. 3.6 Habitat Alteration Habitat alteration is
- 27. 3.7 Loss of Biodiversity Global climate change,
- 28. 3.8 Water Resource Depletion Product manufacturing activities
- 29. 4. Building Materials Impacts on Energy Consumption
- 30. 4.1 Energy Consumption during the Production of
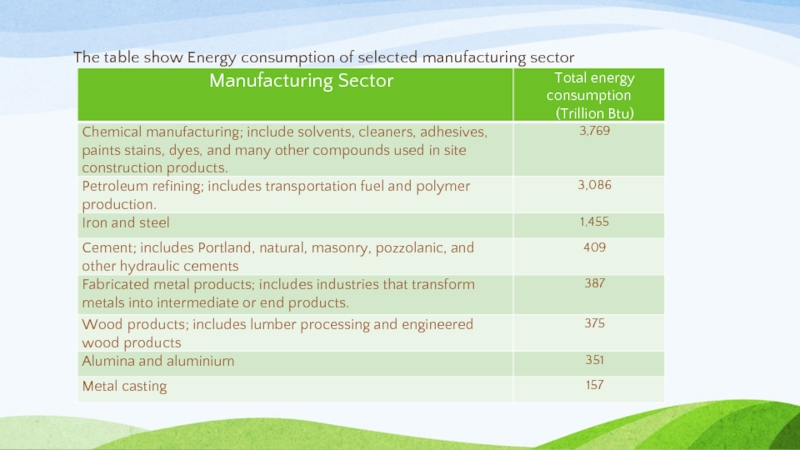
- 31. The table show Energy consumption of selected manufacturing sector
- 32. 4.2 Energy Consumption during Building, Use, and
- 33. 4. 3 Fossil-fuel Depletion Fossil-fuels are used
- 34. 4. 3 Fossil-fuel Depletion Fossil-fuels are used
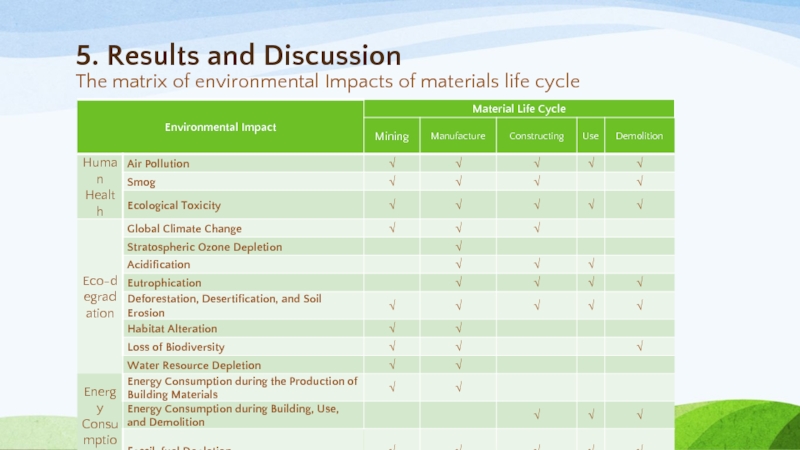
- 35. 5. Results and Discussion The matrix of environmental Impacts of materials life cycle
- 36. 6.Conclusions In order to select green building
- 37. Conclusions created that in order to reduce
- 38. Thank you
Слайд 1The Role of
Environmental Impact in Building Material’s Selection
Hafedh Abed Yahyaa*,
a&b School of Housing, Building and Planning,
University of Science Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia
Слайд 2Titles Content
Introduction
Impact of Building Materials on Human Health
Impact of Building Materials
Building Materials Impacts on Energy Consumption
Results and Discussion
Conclusions
Слайд 3Annually three billion metric tons of raw materials are consumed to
The building industry is the second largest consumer of raw materials, after the food industry.
1.Introduction
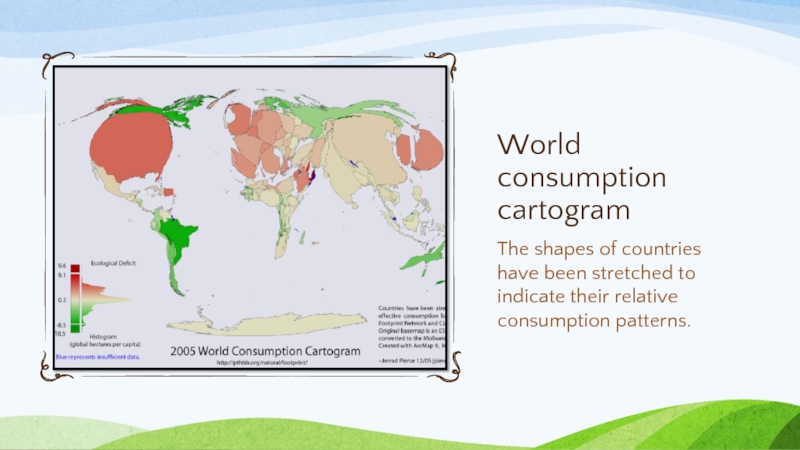
Слайд 4The shapes of countries have been stretched to indicate their relative
World consumption cartogram
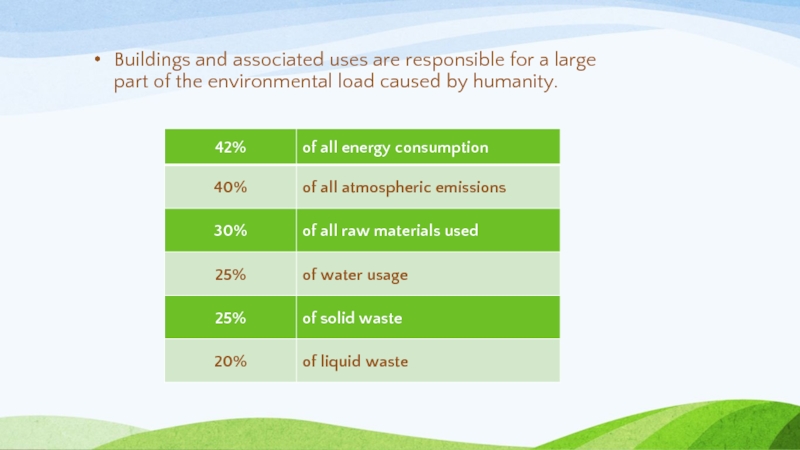
Слайд 5Buildings and associated uses are responsible for a large part of
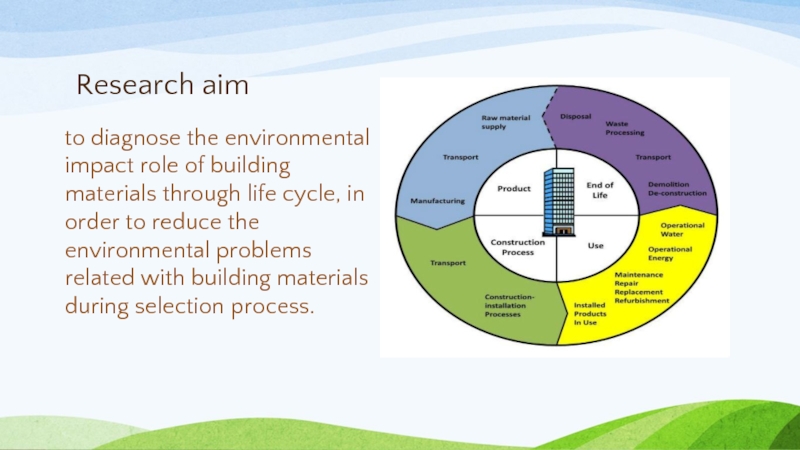
Слайд 7Research aim
to diagnose the environmental impact role of building materials through
Слайд 82. Impact of Building Materials on Human Health
2.1. Air Pollution
“Air pollutants
Слайд 9Activities caused air pollution
Production of electricity
Operation of equipment used in
Manufacturing processes, mining and crushing of materials
Слайд 10Air pollutants can cause
cancer
reproductive effects
birth defects
damage to the immune
damage to the developmental
damage to the respiratory
neurological problems in humans and other species
Слайд 11 2.2. Smog
“Smog is a type of air pollution, resulting when
Beijing China air on a day after rain (left) and a sunny but smoggy day (right) August 2005.
Photo taken by Bobak Ha'Eri
Слайд 12Activities caused smog
Transport of materials,
equipments used on the construction site,
equipments
Слайд 13Smog can cause
Like air pollutants and acidification compounds, smog can have
Слайд 14 2.3. Ecological Toxicity
Toxic materials can be released into ecosystems
As
fossil-fuel combustion
from the direct environmental application of toxic pesticides.
Слайд 15What materials pose toxic risks to people?
asphalt sealants
CCA-treated lumber
substances resulting
substances resulting from the using process
disposing of plastics, metals, metal finishes, solvents, and adhesives.
Слайд 163. Impact of Building Materials on Ecological Degradation
The following are the
As the source materials resources and
As a sink for emissions As by-products of manufacturing processes .
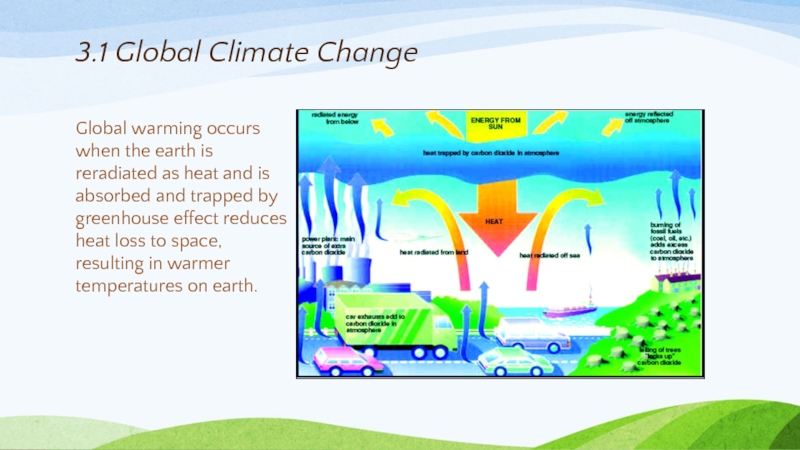
Слайд 173.1 Global Climate Change
Global warming occurs when the earth is reradiated
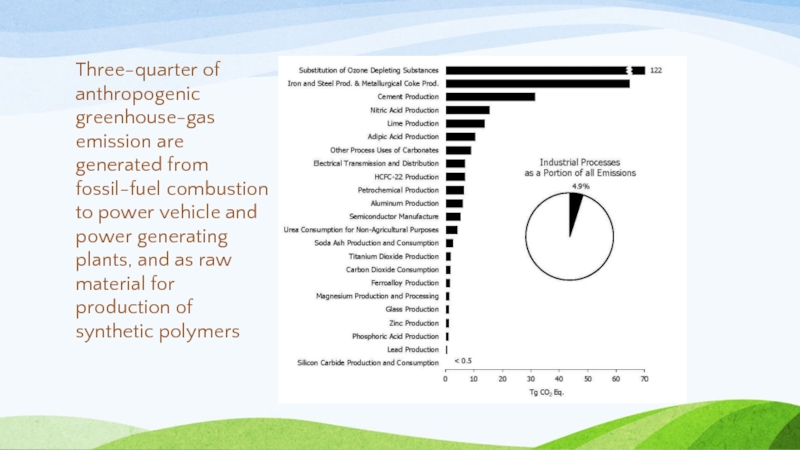
Слайд 18Three-quarter of anthropogenic greenhouse-gas emission are generated from fossil-fuel combustion to
Слайд 193.2 Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
Human caused emissions of Ozone-depleting substances, such as
This has a number of potentially negative consequences, such as impacts on plants and agriculture, and increases in cancer and cataracts in people
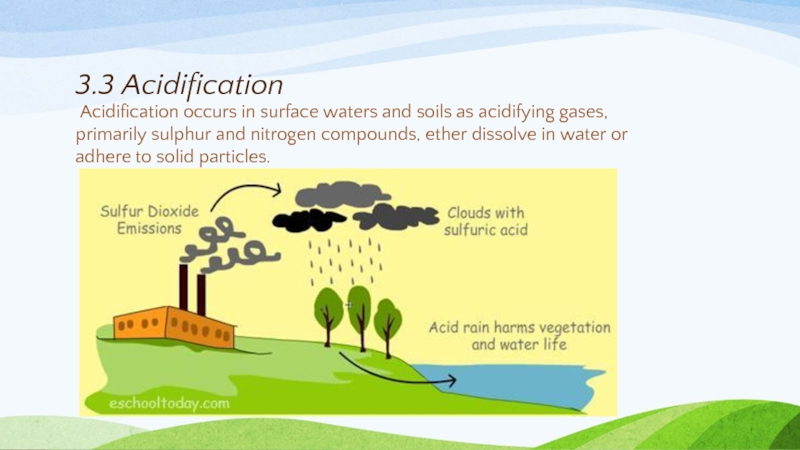
Слайд 203.3 Acidification
Acidification occurs in surface waters and soils as acidifying gases,
Слайд 21Acid rain also accelerates weathering of building materials such as granite,
Слайд 223.4 Eutrophication
“Eutrophication is the addition of nutrients, such as nitrogen and
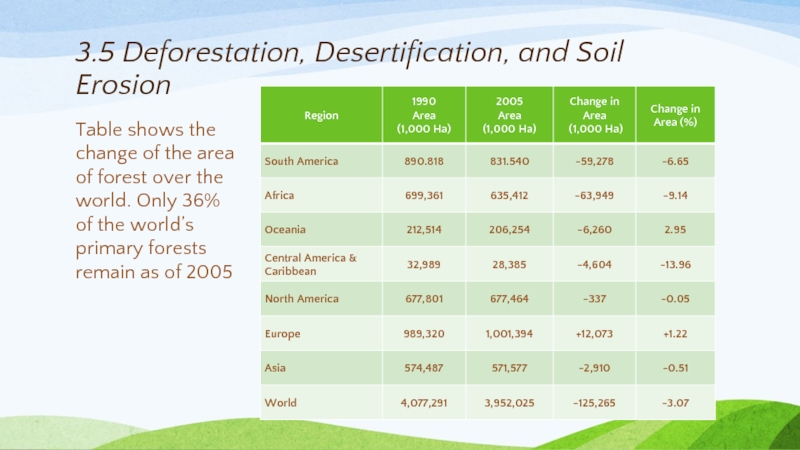
Слайд 233.5 Deforestation, Desertification, and Soil Erosion
Table shows the change of the
Слайд 24loss of bio-diversity,
global warming,
soil erosion,
and desertification..
Deforestation, the large-scale
Слайд 25 agriculture,
mining,
new construction of buildings, or roads,
when trees
Lumber For building materials
Deforestation occurs when forested land is cleared for
Слайд 263.6 Habitat Alteration
Habitat alteration is the primary impact resulting from
Habitat alteration also can occur as a result of air, water, and land releases from industrial processes that change environmental conditions
Слайд 273.7 Loss of Biodiversity
Global climate change, the destruction of forests and
Biodiversity controls the spread of diseases, provides food and drugs for humans, and provides resources for industrial materials such as fibre, dyes, resins, gums, adhesives, rubber, and oils
Слайд 283.8 Water Resource Depletion
Product manufacturing activities use water, and effluent wastes
In addition, the use of impervious surfaces (such as concrete and asphalt) seriously reduces groundwater recharge
Слайд 294. Building Materials Impacts on Energy Consumption
The other environmental problems of
The industrial sector is the largest end user of energy, greater ever than the transportation sector or building operation
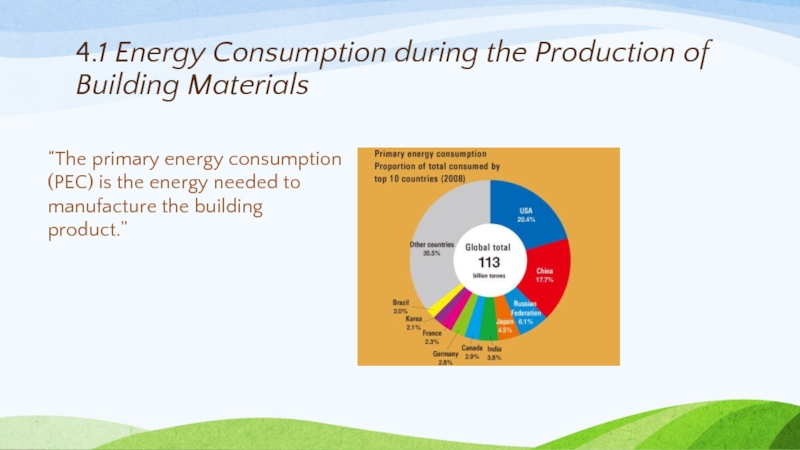
Слайд 304.1 Energy Consumption during the Production of Building Materials
“The primary energy
Слайд 324.2 Energy Consumption during Building, Use, and Demolition
Building materials consume more
Energy consumption for the transport of manufactured products.
Energy consumption on the building site.
Energy consumption during maintenance
Energy consumption of dismantling or removal of materials during demolition
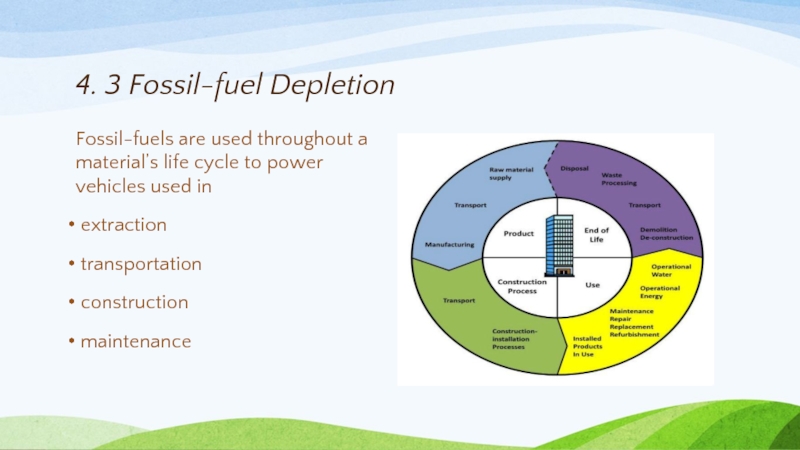
Слайд 334. 3 Fossil-fuel Depletion
Fossil-fuels are used throughout a material’s life cycle
extraction
transportation
construction
maintenance
Слайд 344. 3 Fossil-fuel Depletion
Fossil-fuels are used throughout a material’s life cycle
extraction
transportation
construction
maintenance
Слайд 366.Conclusions
In order to select green building materials, the designer needs to
How is the product mining or harvested, manufactured, and transported?
Is it produced at the factory in another country?
Does that factory release pollution into the environment?
What is the product made of?
Does it contain recycled content or renewable materials?
How much water consumption does it take to create the product?
And, overall, is the material biodegradable or recyclable when use it in the building?
Слайд 37Conclusions created that in order to reduce the environmental impacts, the
Provide resource savings
Provide energy savings
Reduce wastes (be reusable and easily recyclable).
Not be harmful for human health
Provide comfortable and suitable conditions for human health within the covered areas.