- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Mobile genetic elements презентация
Содержание
- 1. Mobile genetic elements
- 2. Site-specific recombination Moves specialized nucleotide sequence (mobile
- 3. Transpositional site-specific recombination Modest target site selectivity
- 4. Three of the many types of mobile
- 6. Cut and Paste Transposition DNA-only
- 7. The structure of the central intermediate formed by transposase (integrase)
- 8. Replicative Transposition
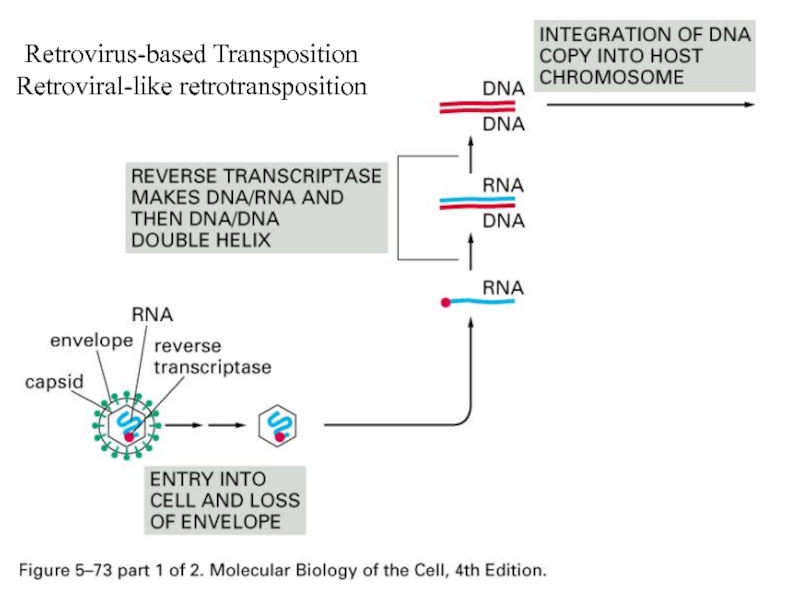
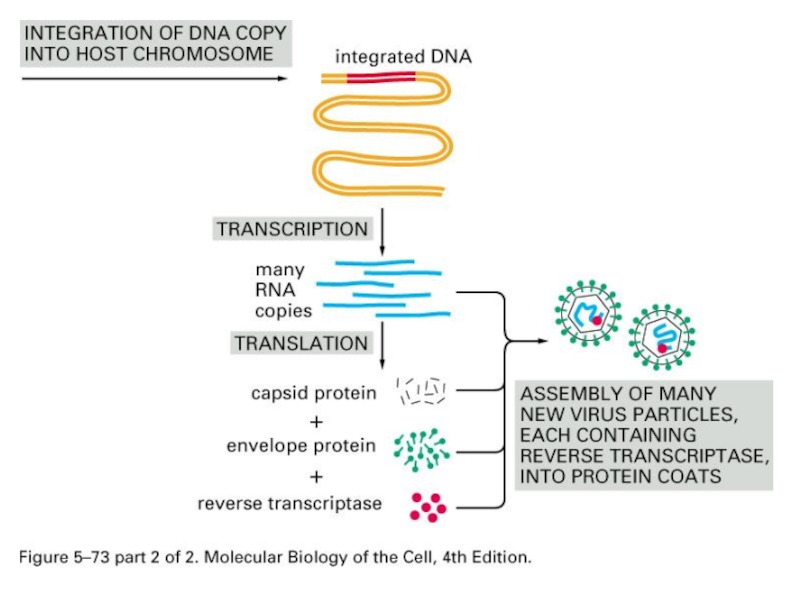
- 9. Retrovirus-based Transposition Retroviral-like retrotransposition
- 11. Reverse Transcriptase From RNA to DNA
- 12. Non-retroviral retrotransposition L1 Element
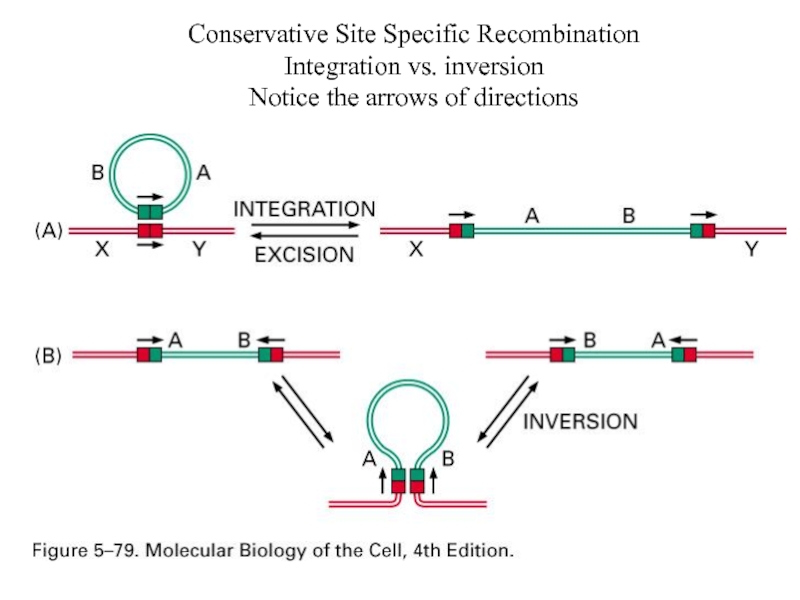
- 13. Conservative Site Specific Recombination Integration vs. inversion Notice the arrows of directions
- 14. Bacteriophase Lambda
- 15. Genetic Engineering to control Gene expression
- 16. Summary DNA site-specific recombination transpositional; conservative
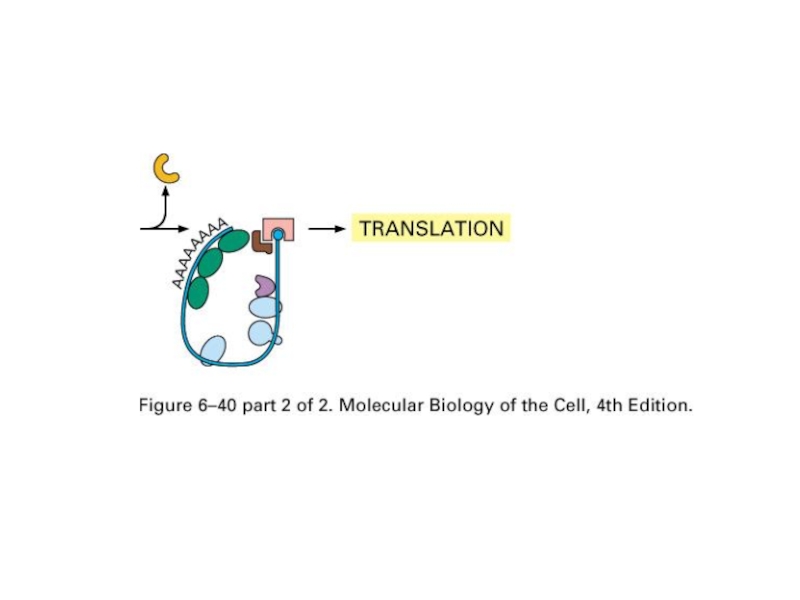
- 17. How Cells Read the Genome: From DNA
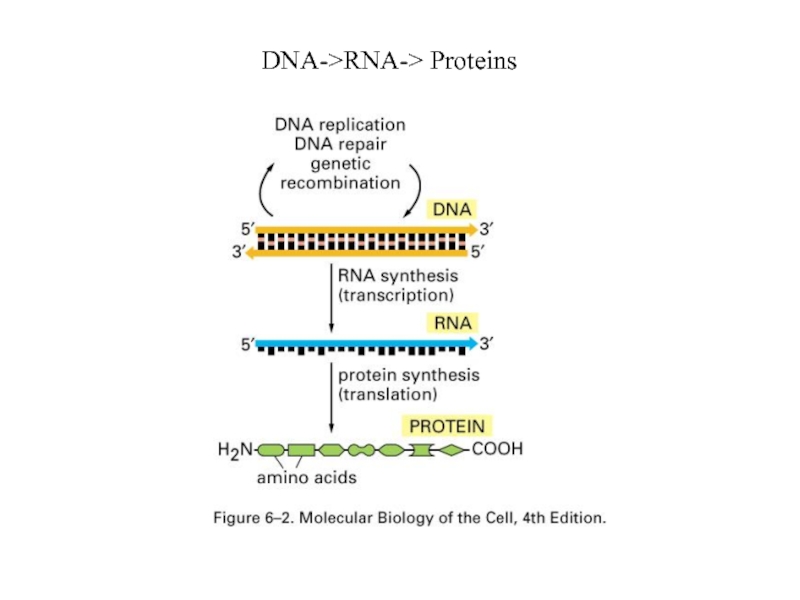
- 18. DNA->RNA-> Proteins
- 19. Genes expressed with different efficiency
- 20. The chemical structure differences between DNAs and RNAs ribose, deoxyribose Uracil and thymine
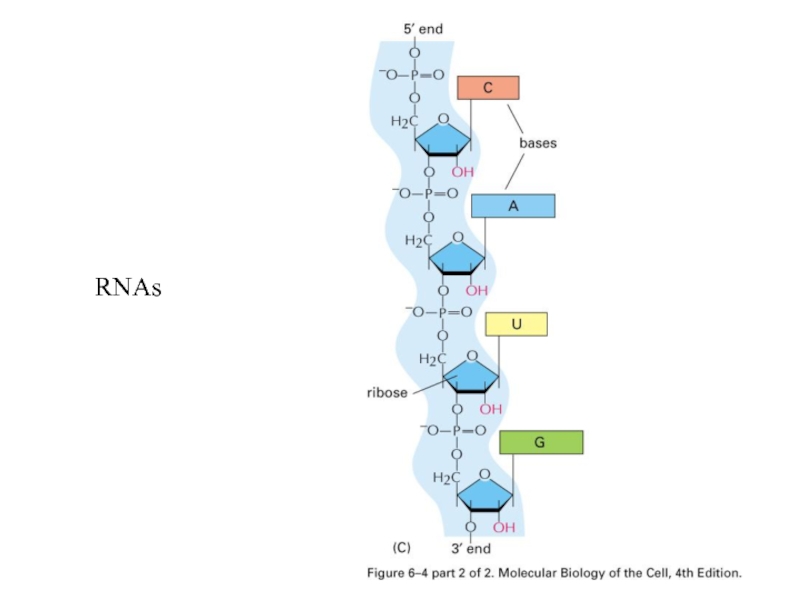
- 21. RNAs
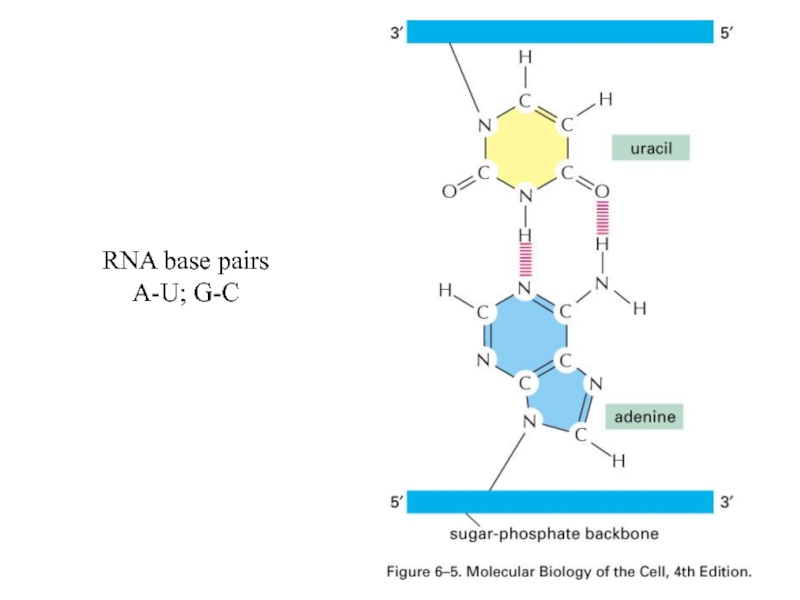
- 22. RNA base pairs A-U; G-C
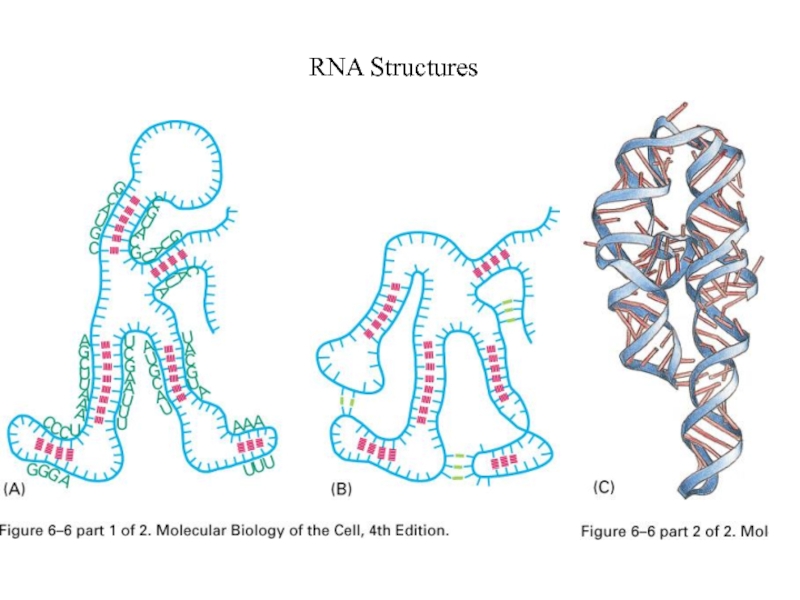
- 23. RNA Structures
- 24. DNA transcription to RNA No need
- 25. RNA Polymerases RNA polymerase I: rRNA RNA polymerase II: mRNA RNA polymerase III: tRNA
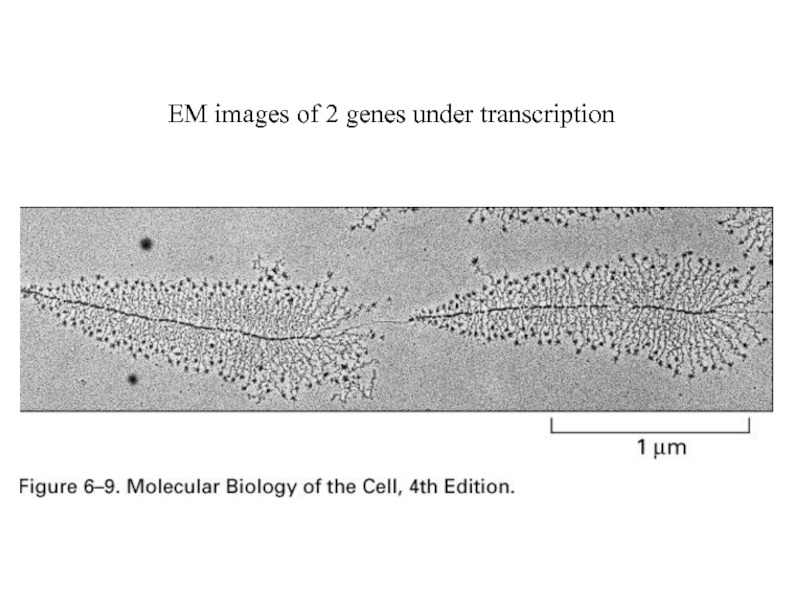
- 26. EM images of 2 genes under transcription
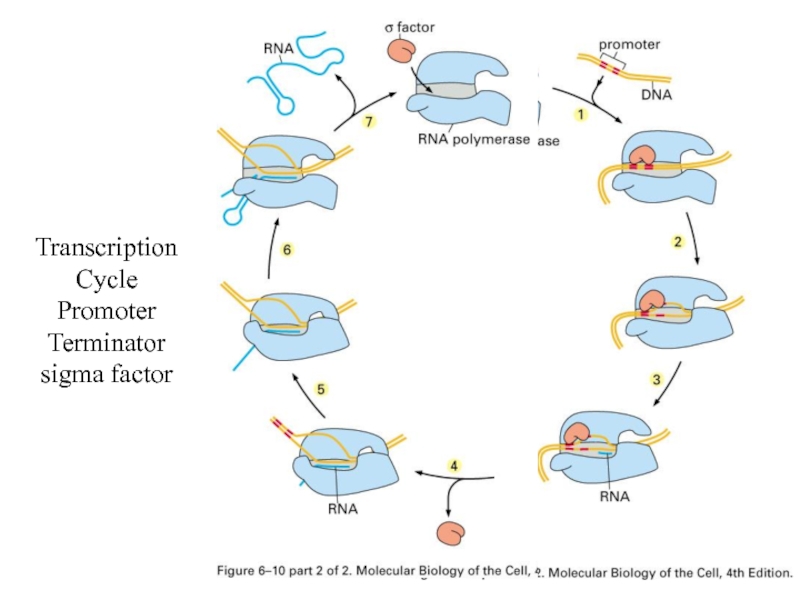
- 27. Transcription Cycle Promoter Terminator sigma factor
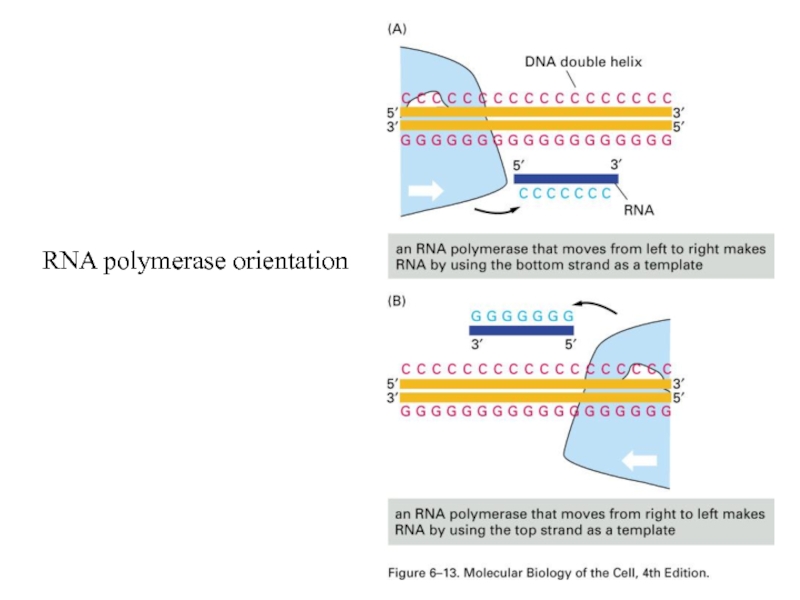
- 28. RNA polymerase orientation
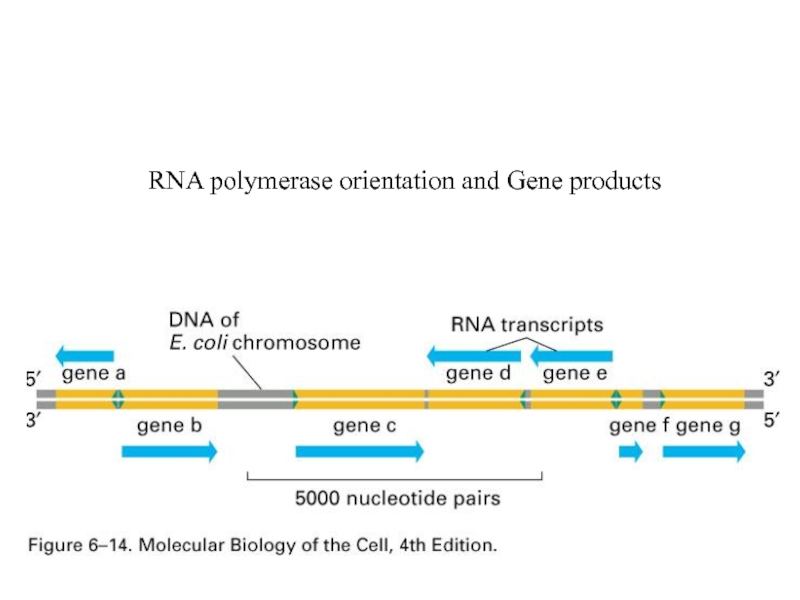
- 29. RNA polymerase orientation and Gene products
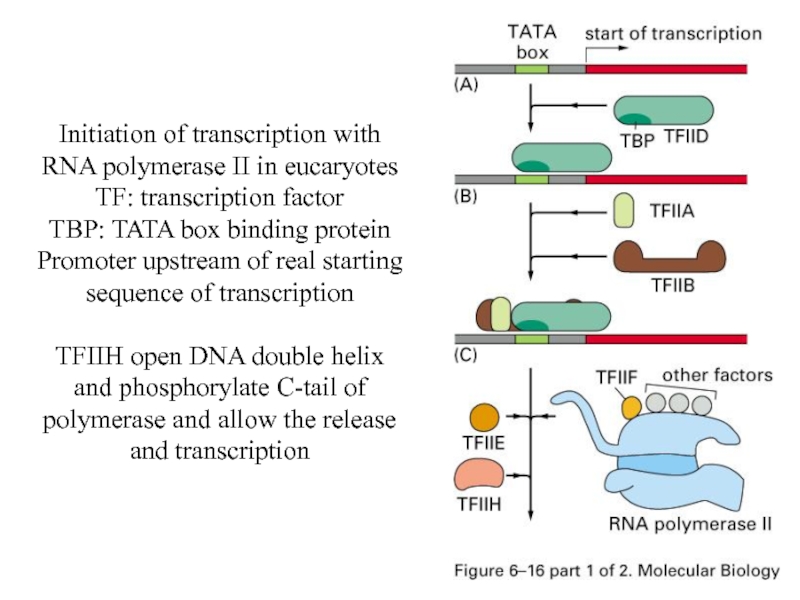
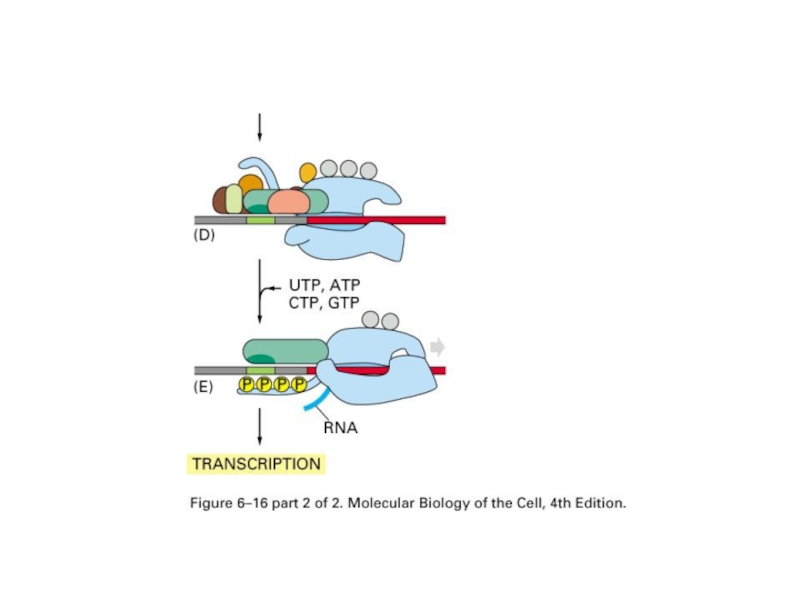
- 30. Initiation of transcription with RNA polymerase II
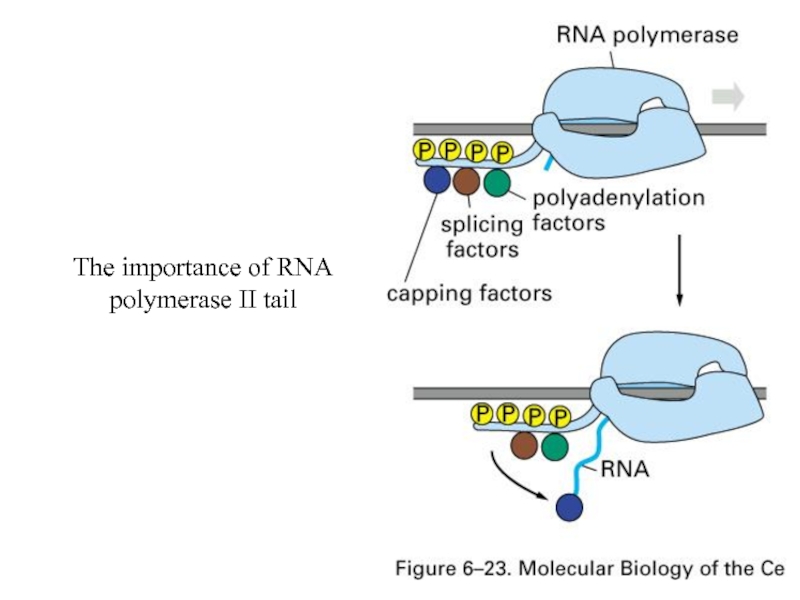
- 32. The importance of RNA polymerase II tail
- 33. Initiation of transcription with RNA polymerase II
- 34. Genes to proteins The comparison between eucaryotes (substantially complex) and procaryotes (simple)
- 35. mRNA between procaryotic and eucaryotic cells 5’ capping and 3’ polyadenylation
- 36. 5’ capping
- 37. Splicing effects on gene products RNA splicing Exons: expressed sequences Introns: intervening sequences
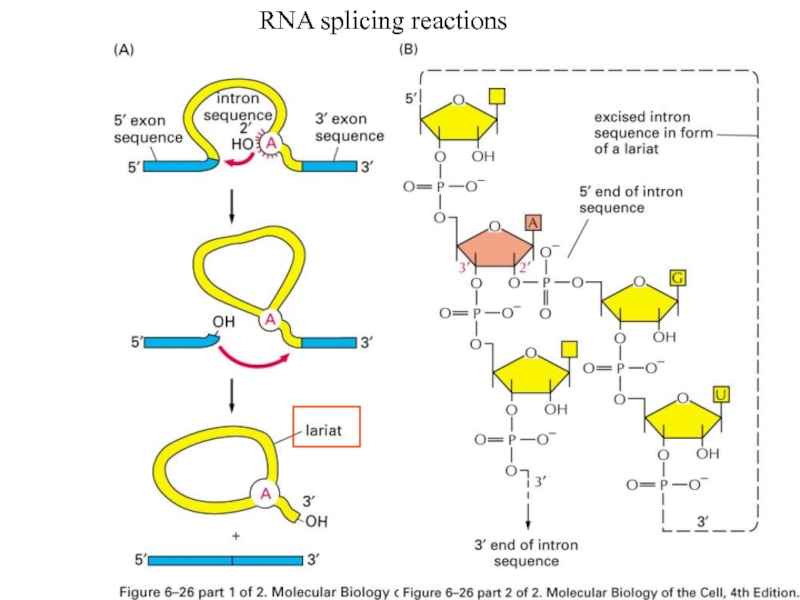
- 38. RNA splicing reactions
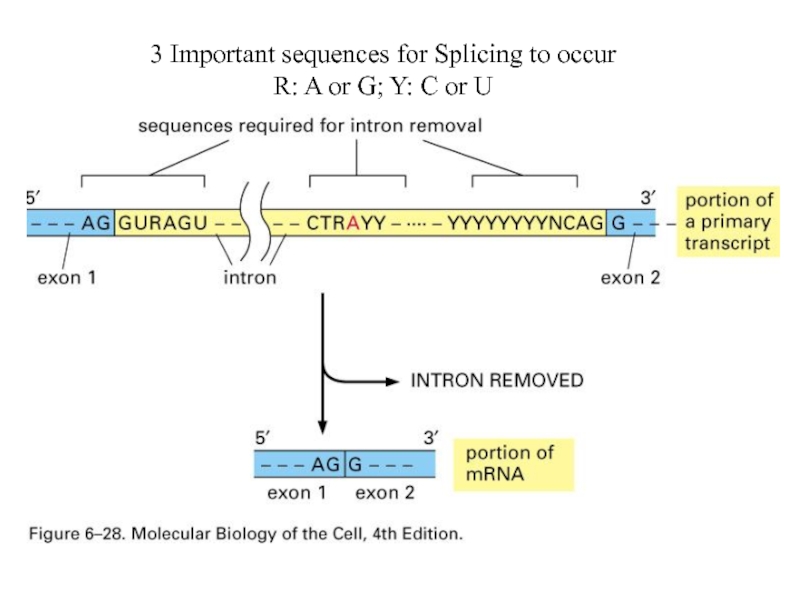
- 39. 3 Important sequences for Splicing to occur R: A or G; Y: C or U
- 40. RNA Splicing mechanism BBP: branch-point binding protein
- 42. Further mechanism to mark Exon and Intron
- 43. Consensus sequence for 3’ process AAUAAA: CstF
- 44. Major steps for 3’ end of eucaryotic mRNA
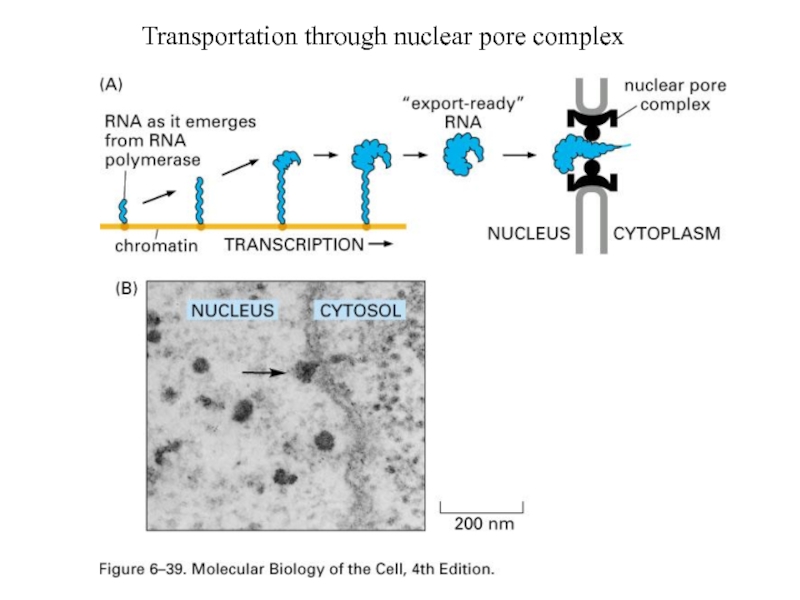
- 46. Transportation through nuclear pore complex
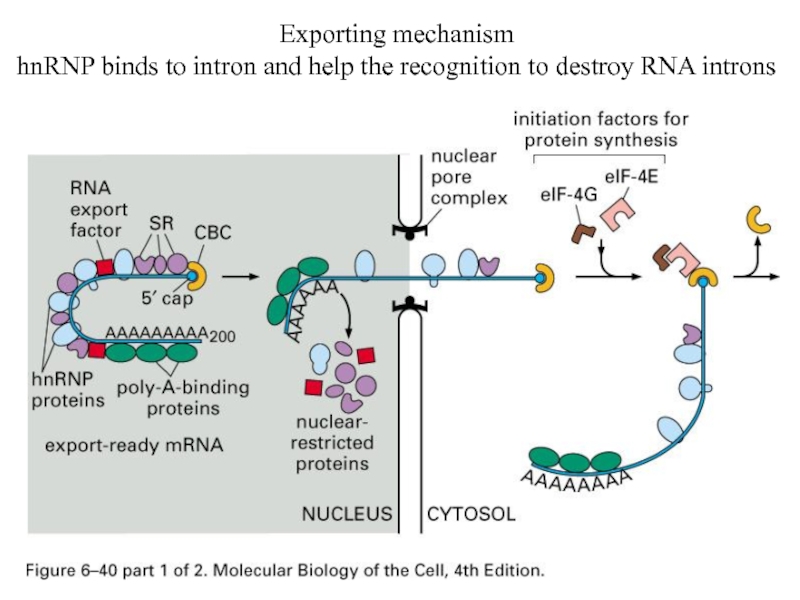
- 47. Exporting mechanism hnRNP binds to intron and help the recognition to destroy RNA introns
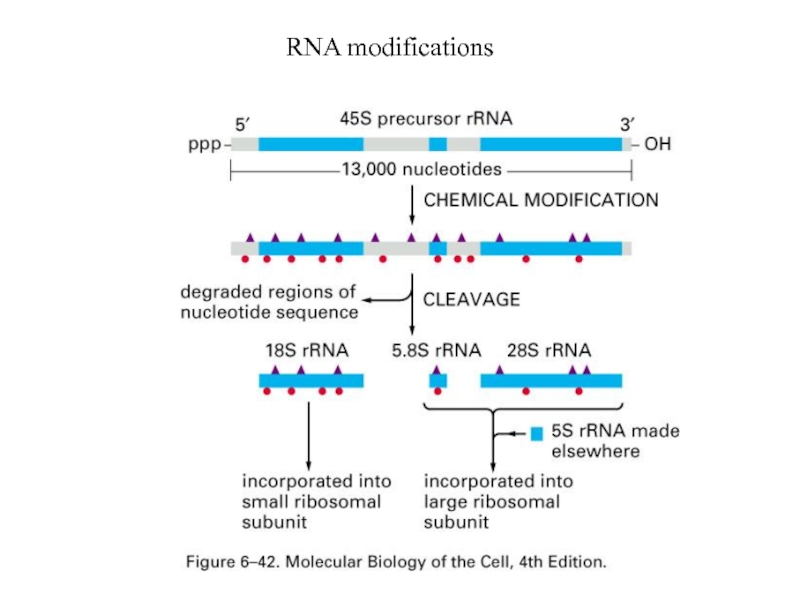
- 49. RNA modifications
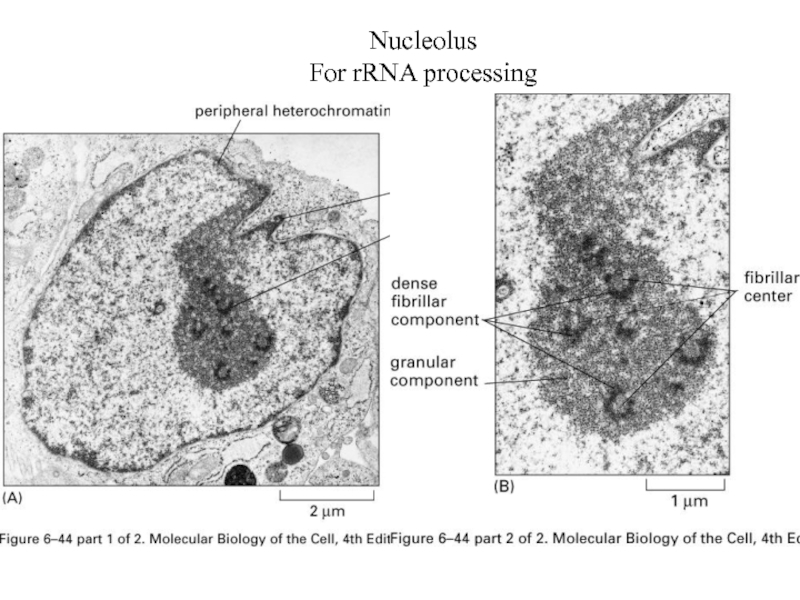
- 50. Nucleolus For rRNA processing
- 51. Nucleolus and other subcompartments Cajal bodies, GEMS (Gemini of coiled bodies), interchromatin granule clusters
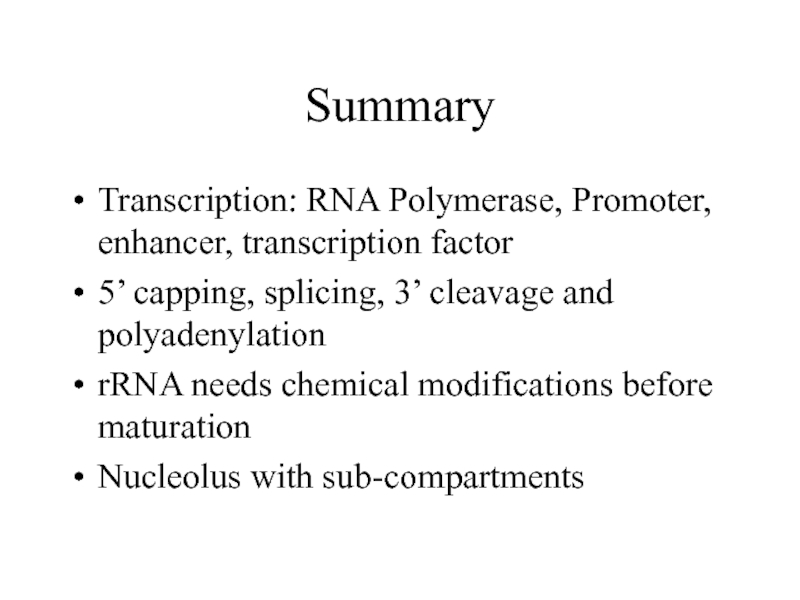
- 52. Summary Transcription: RNA Polymerase, Promoter, enhancer, transcription
- 53. From RNA to Protein Protein synthesis Protein Folding and regulation
- 54. The Genetic Code
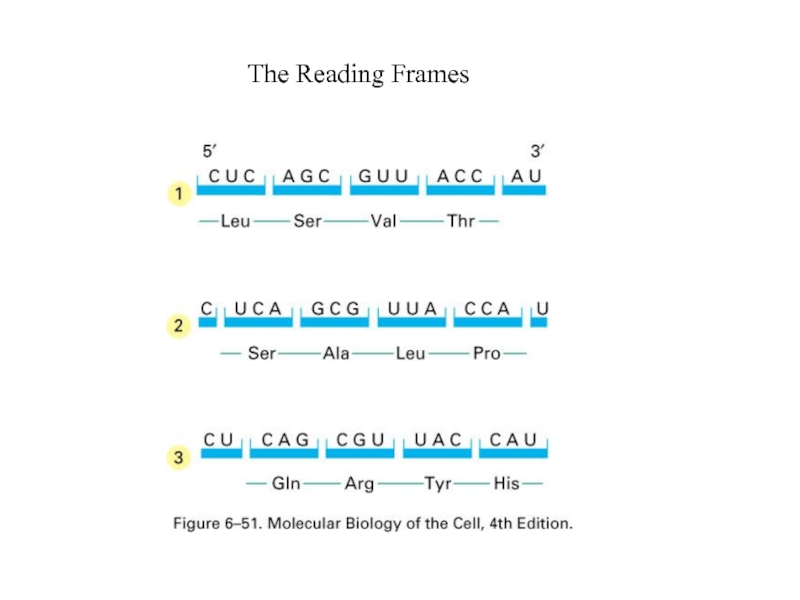
- 55. The Reading Frames
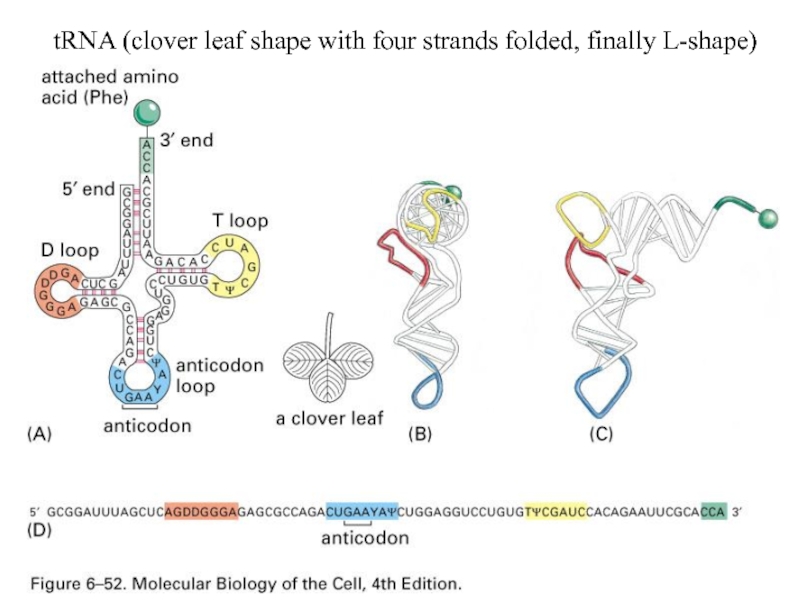
- 56. tRNA (clover leaf shape with four strands folded, finally L-shape)
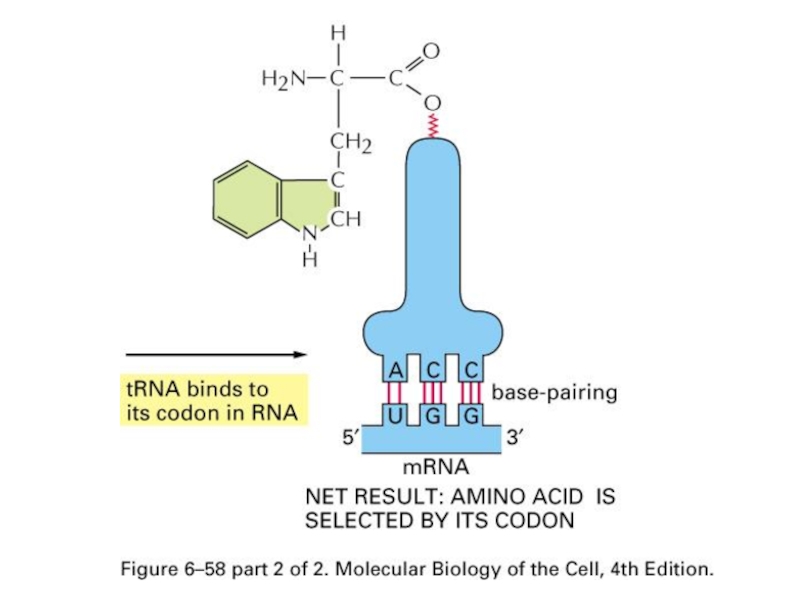
- 57. tRNA and mRNA pairing
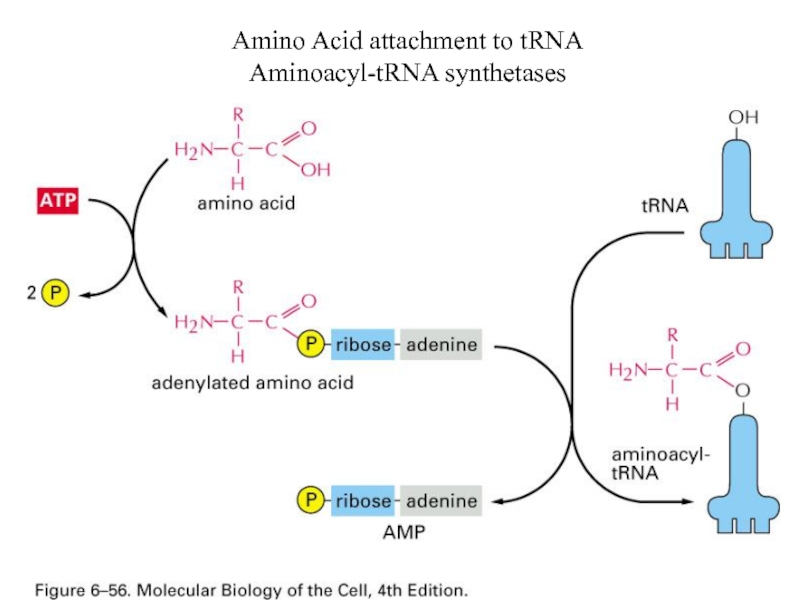
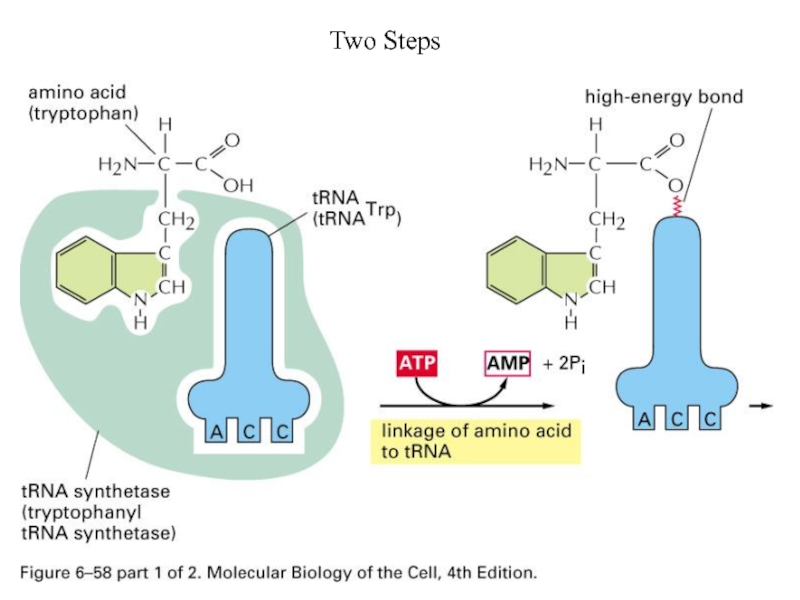
- 58. Amino Acid attachment to tRNA Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
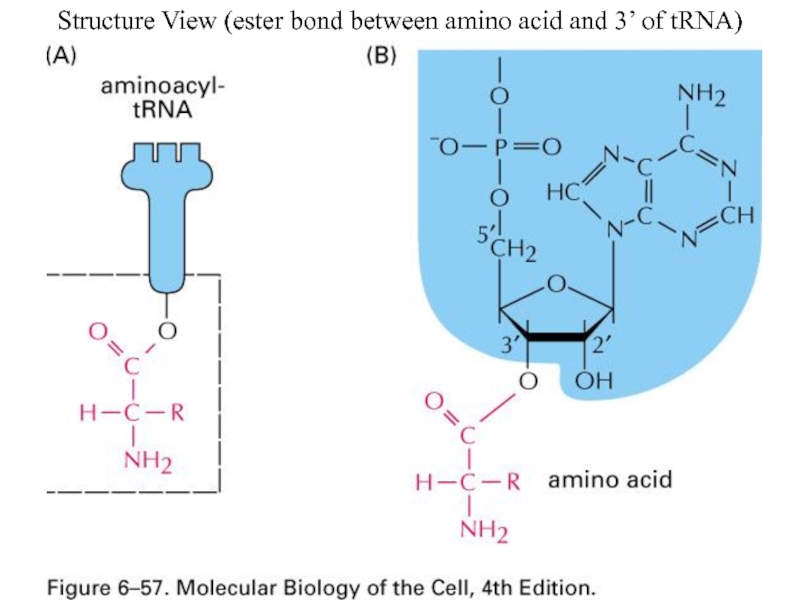
- 59. Structure View (ester bond between amino acid and 3’ of tRNA)
- 60. Two Steps
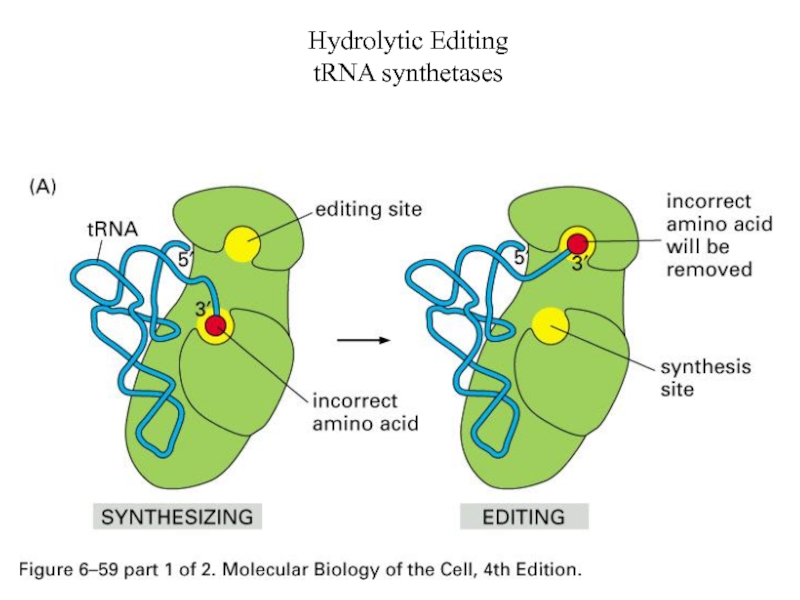
- 62. Hydrolytic Editing tRNA synthetases
- 63. Hydrolytic Editing DNA polymerase
- 64. Protein synthesis
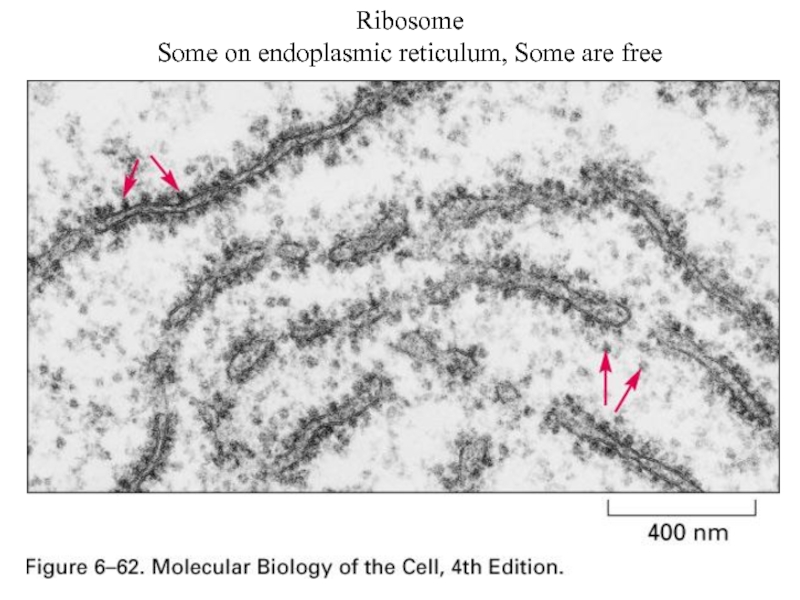
- 66. Ribosome Some on endoplasmic reticulum, Some are free
- 67. Ribosome binding sites 2 subunits: large and
- 68. Translation: Position at A Peptidyl transferase to
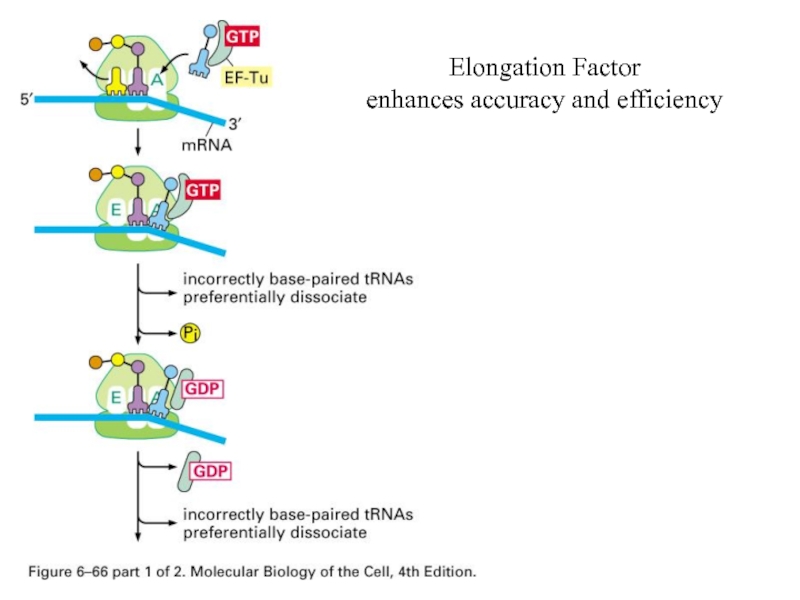
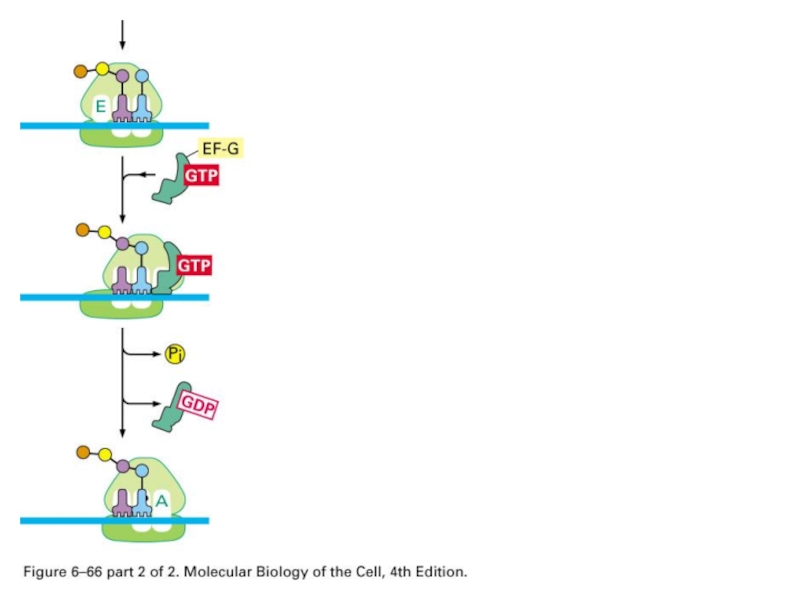
- 70. Elongation Factor enhances accuracy and efficiency
- 72. The Initiation of protein synthesis in eucaryotes Eucaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) AUG encodes Met
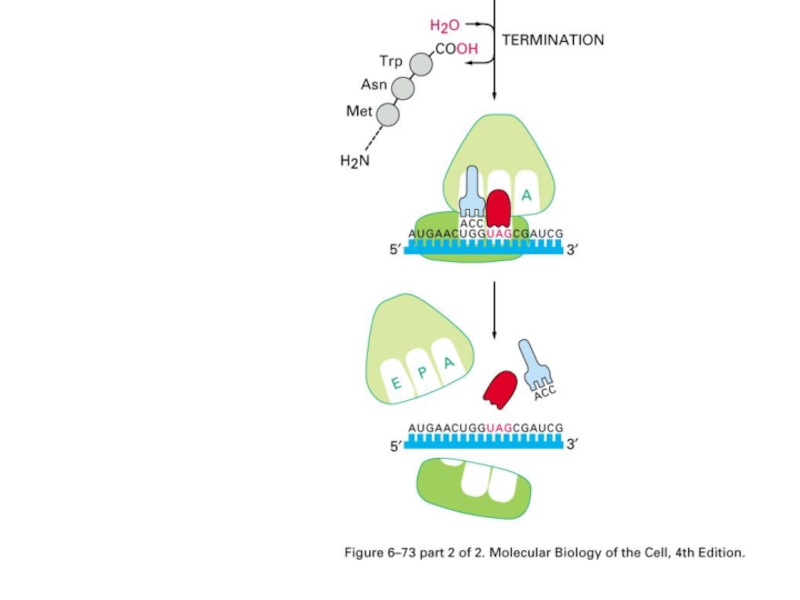
- 74. Stop codons UAA, UAG, UGA Releasing factor, coupling a water molecule
- 76. Multiple Copies on the Same mRNA (polysomes)
Слайд 2Site-specific recombination
Moves specialized nucleotide sequence (mobile genetic elements) between non-homologous sites
within a genome.
Transpositional site-specific recombination
Conservative site-specific recombinatinon
Transpositional site-specific recombination
Conservative site-specific recombinatinon
Слайд 3Transpositional site-specific recombination
Modest target site selectivity and insert mobile genetic elements
into many sites
Transposase enzyme cuts out mobile genetic elements and insert them into specific sites.
Transposase enzyme cuts out mobile genetic elements and insert them into specific sites.
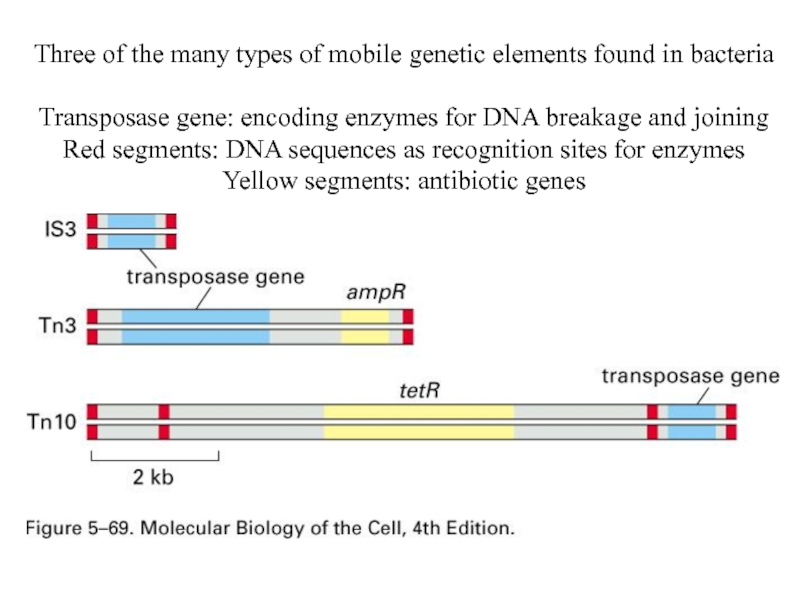
Слайд 4Three of the many types of mobile genetic elements found in
bacteria
Transposase gene: encoding enzymes for DNA breakage and joining
Red segments: DNA sequences as recognition sites for enzymes
Yellow segments: antibiotic genes
Transposase gene: encoding enzymes for DNA breakage and joining
Red segments: DNA sequences as recognition sites for enzymes
Yellow segments: antibiotic genes
Слайд 13Conservative Site Specific Recombination
Integration vs. inversion
Notice the arrows of directions
Слайд 16Summary
DNA site-specific recombination
transpositional; conservative
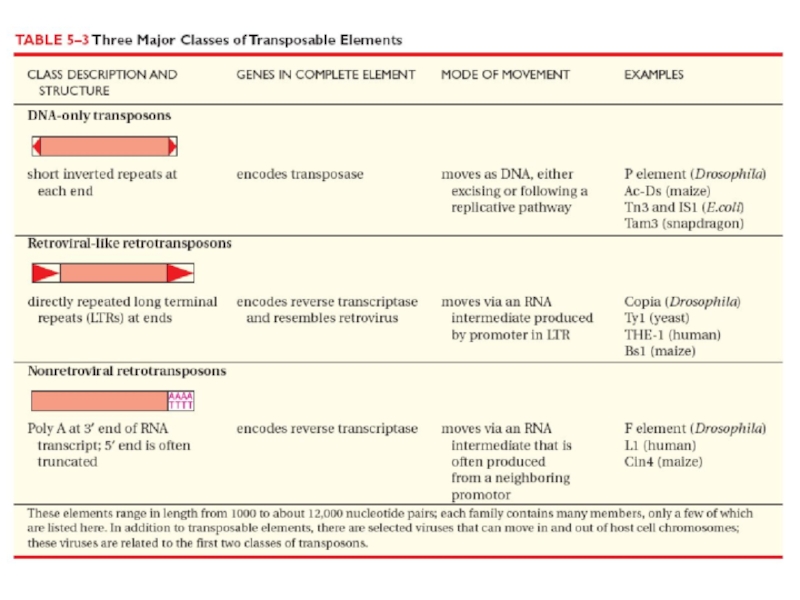
Transposons: mobile genetic elements
Transpositional: DNA only transposons, retroviral-like
retrotransposons, nonretroviral retrotransposons
Слайд 17How Cells Read the Genome: From DNA to Protein
1. Transcription
2. RNA
Modification and Splicing
3. RNA transportation
4. Translation
5. Protein Modification and Folding
3. RNA transportation
4. Translation
5. Protein Modification and Folding
Слайд 20The chemical structure differences between DNAs and RNAs
ribose, deoxyribose
Uracil and thymine
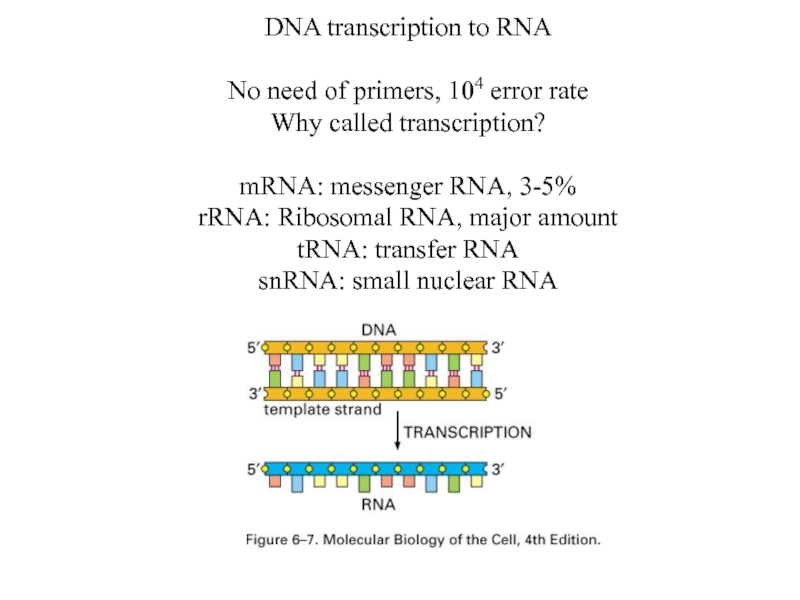
Слайд 24DNA transcription to RNA
No need of primers, 104 error rate
Why called
transcription?
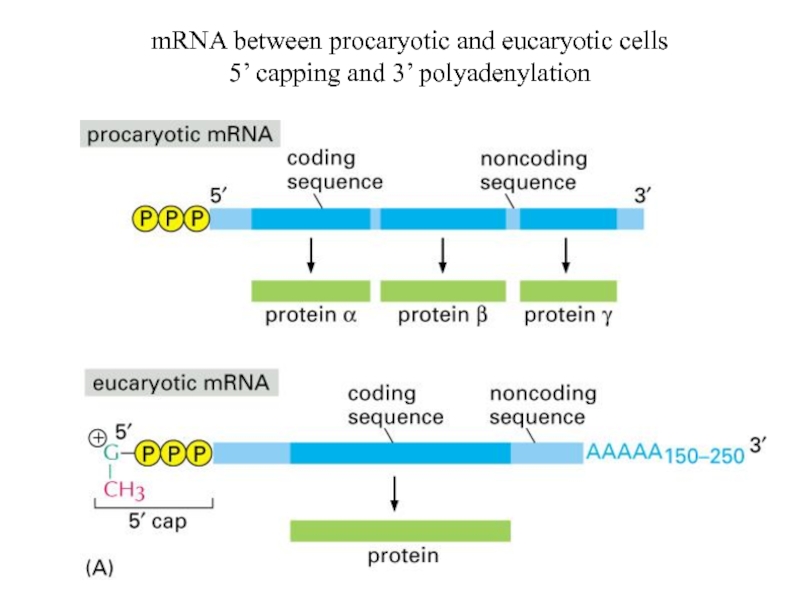
mRNA: messenger RNA, 3-5%
rRNA: Ribosomal RNA, major amount
tRNA: transfer RNA
snRNA: small nuclear RNA
mRNA: messenger RNA, 3-5%
rRNA: Ribosomal RNA, major amount
tRNA: transfer RNA
snRNA: small nuclear RNA
Слайд 30Initiation of transcription with RNA polymerase II in eucaryotes
TF: transcription factor
TBP:
TATA box binding protein
Promoter upstream of real starting sequence of transcription
TFIIH open DNA double helix and phosphorylate C-tail of polymerase and allow the release and transcription
Promoter upstream of real starting sequence of transcription
TFIIH open DNA double helix and phosphorylate C-tail of polymerase and allow the release and transcription
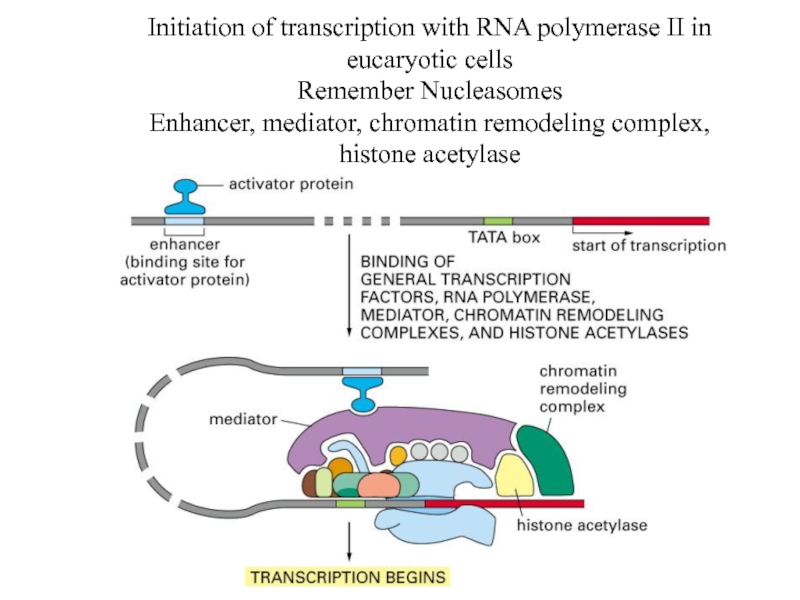
Слайд 33Initiation of transcription with RNA polymerase II in eucaryotic cells
Remember Nucleasomes
Enhancer,
mediator, chromatin remodeling complex, histone acetylase
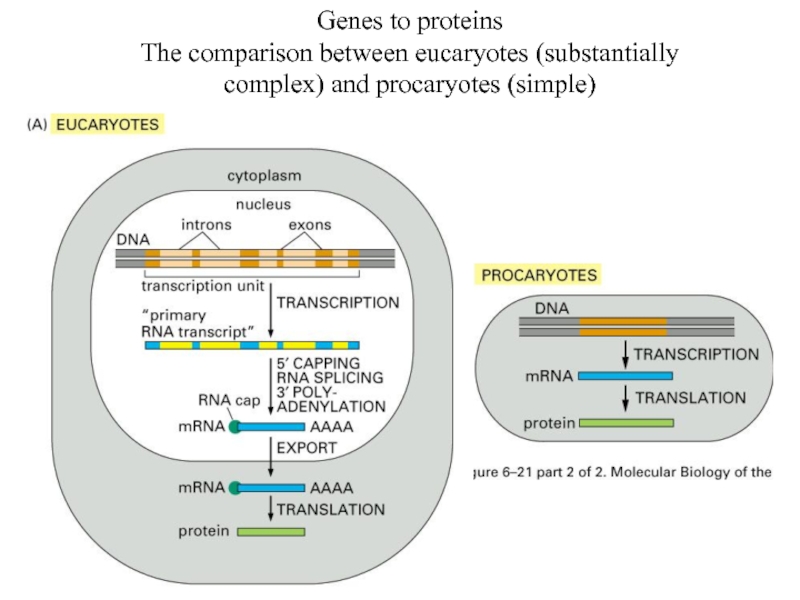
Слайд 34Genes to proteins
The comparison between eucaryotes (substantially complex) and procaryotes (simple)
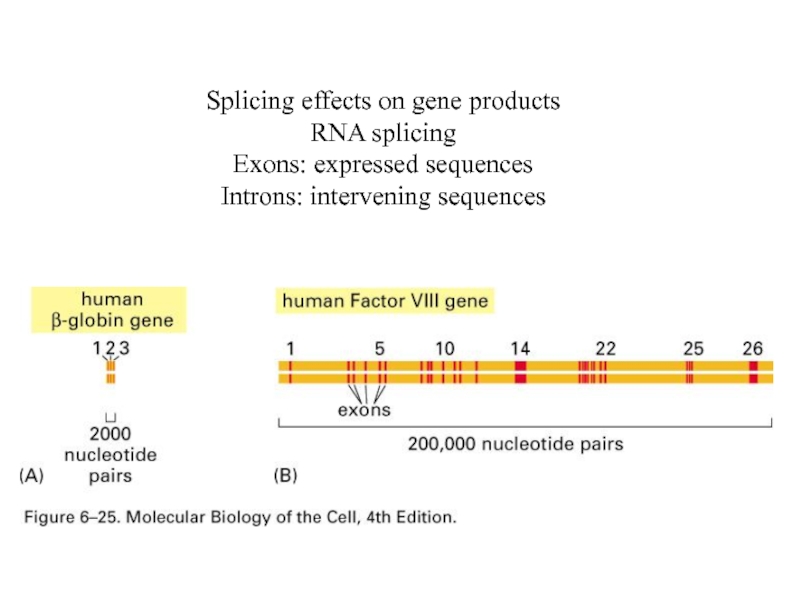
Слайд 37Splicing effects on gene products
RNA splicing
Exons: expressed sequences
Introns: intervening sequences
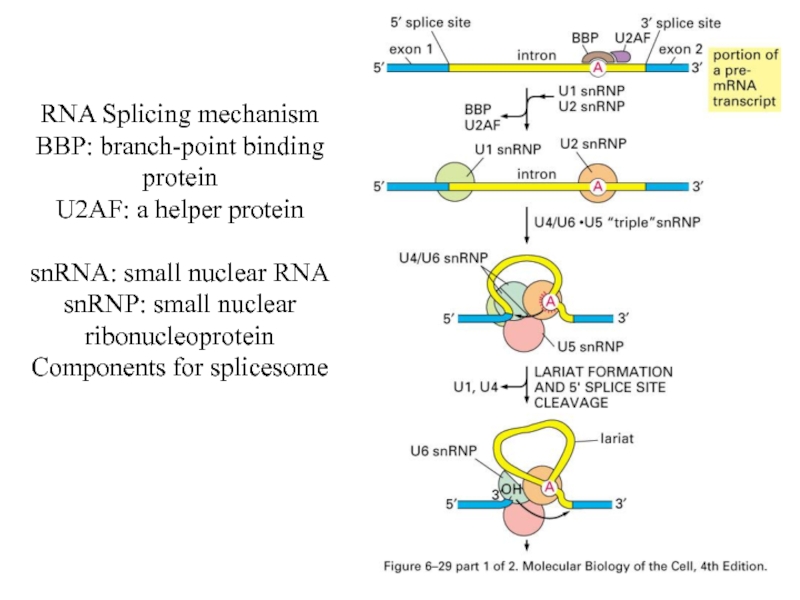
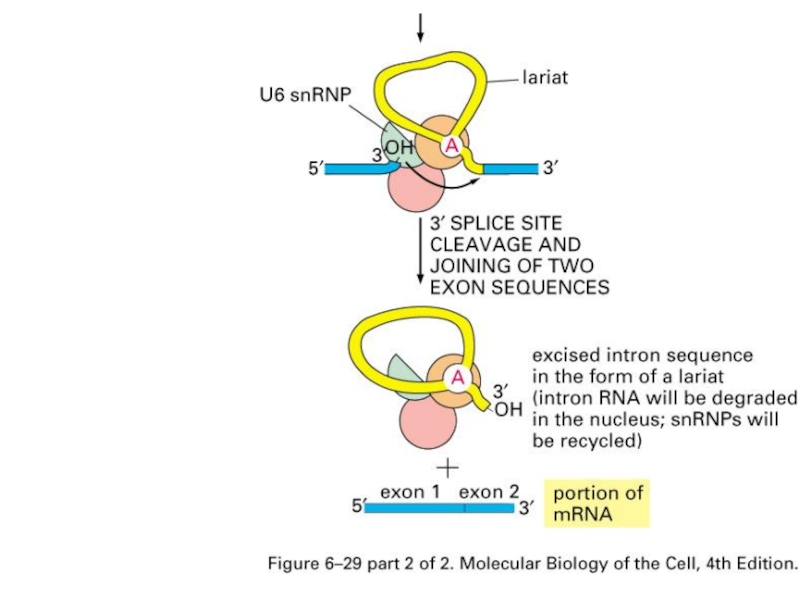
Слайд 40RNA Splicing mechanism
BBP: branch-point binding protein
U2AF: a helper protein
snRNA: small nuclear
RNA
snRNP: small nuclear ribonucleoprotein
Components for splicesome
snRNP: small nuclear ribonucleoprotein
Components for splicesome
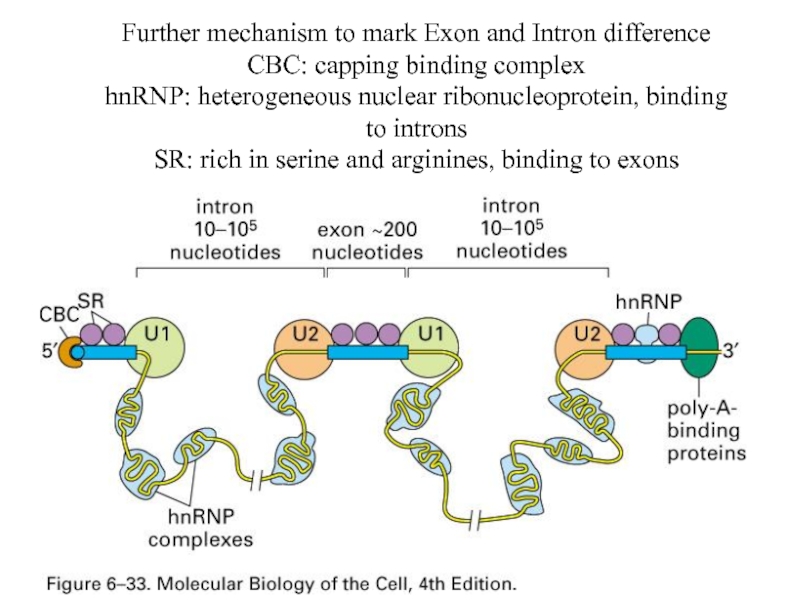
Слайд 42Further mechanism to mark Exon and Intron difference
CBC: capping binding complex
hnRNP:
heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein, binding to introns
SR: rich in serine and arginines, binding to exons
SR: rich in serine and arginines, binding to exons
Слайд 43Consensus sequence for 3’ process
AAUAAA: CstF (cleavage stimulation factor F)
GU-rich sequence:
CPSF (cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor)
Слайд 51Nucleolus and other subcompartments
Cajal bodies, GEMS (Gemini of coiled bodies), interchromatin
granule clusters
Слайд 52Summary
Transcription: RNA Polymerase, Promoter, enhancer, transcription factor
5’ capping, splicing, 3’ cleavage
and polyadenylation
rRNA needs chemical modifications before maturation
Nucleolus with sub-compartments
rRNA needs chemical modifications before maturation
Nucleolus with sub-compartments
Слайд 67Ribosome binding sites
2 subunits: large and small
4 binding sites: 1 for
mRNA at small subunit, 3 for tRNA in large subunit
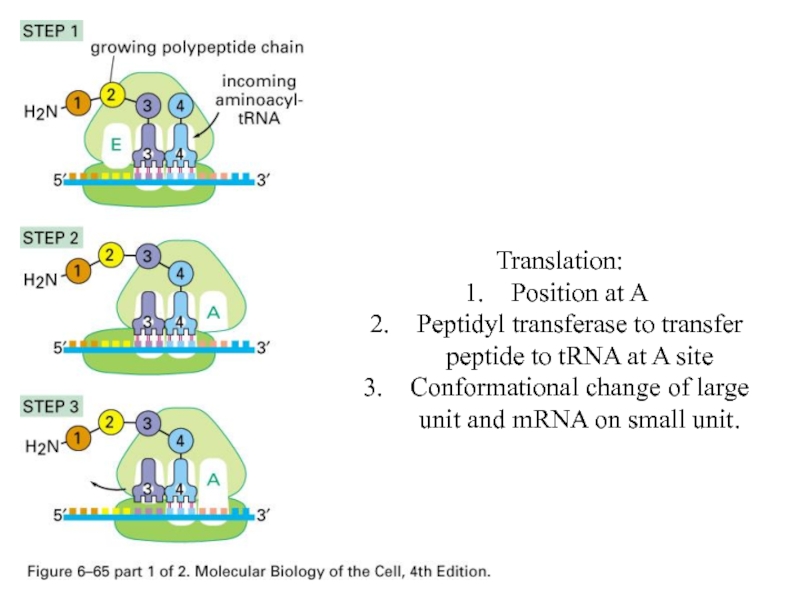
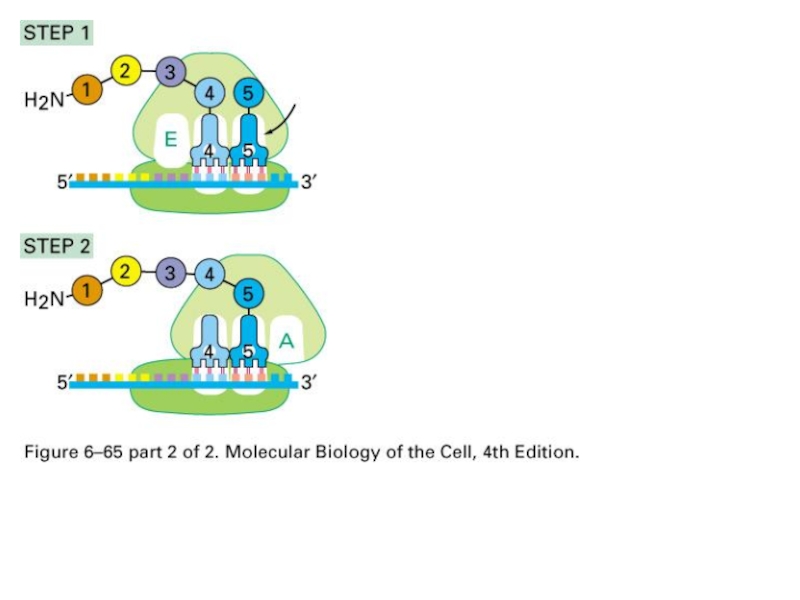
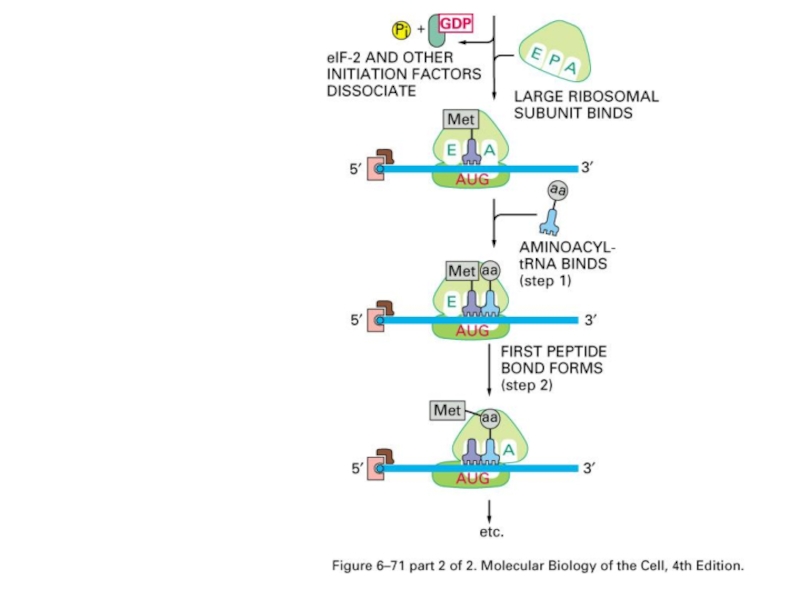
Слайд 68Translation:
Position at A
Peptidyl transferase to transfer peptide to tRNA at A
site
Conformational change of large unit and mRNA on small unit.
Conformational change of large unit and mRNA on small unit.
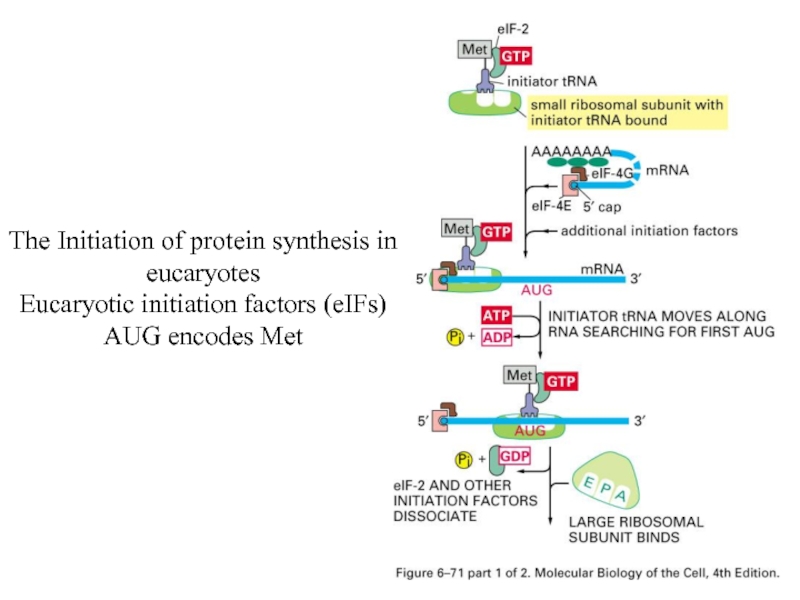
Слайд 72The Initiation of protein synthesis in eucaryotes
Eucaryotic initiation factors (eIFs)
AUG encodes
Met
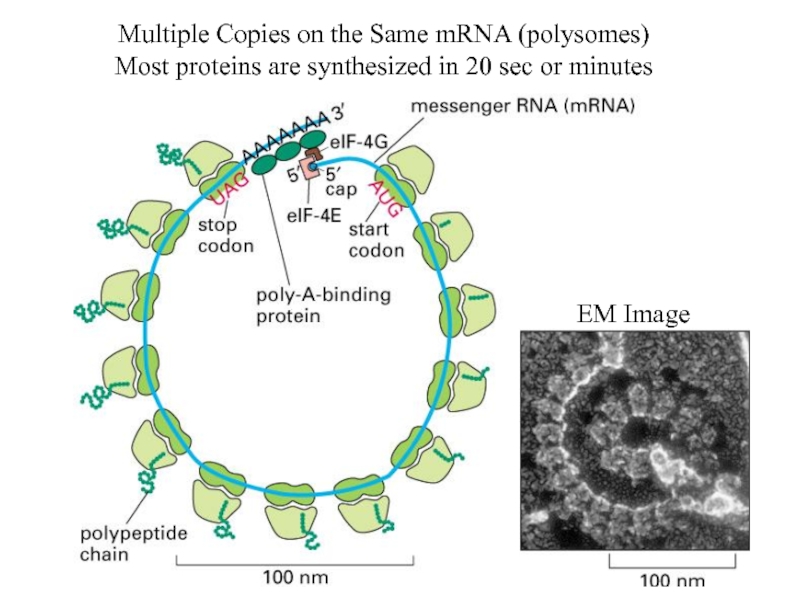
Слайд 76Multiple Copies on the Same mRNA (polysomes)
Most proteins are synthesized in
20 sec or minutes
EM Image