- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Mendelelian Genetics презентация
Содержание
- 1. Mendelelian Genetics
- 2. Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) Responsible for the Laws governing Inheritance of Traits. copyright cmassengale
- 3. Gregor Johann Mendel Austrian monk Studied the
- 4. Gregor Johann Mendel Between 1856 and 1863,
- 5. Site of Gregor Mendel’s experimental garden in the Czech Republic. copyright cmassengale
- 6. Mendel stated that physical traits are inherited
- 7. Genetic Terminology Trait - any characteristic that
- 8. Types of Genetic Crosses Monohybrid cross -
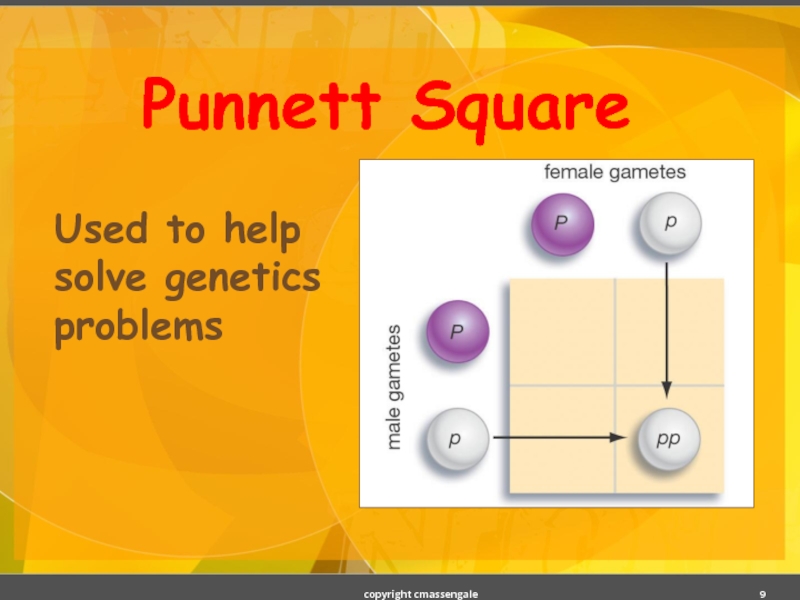
- 9. Punnett Square Used to help solve genetics problems copyright cmassengale
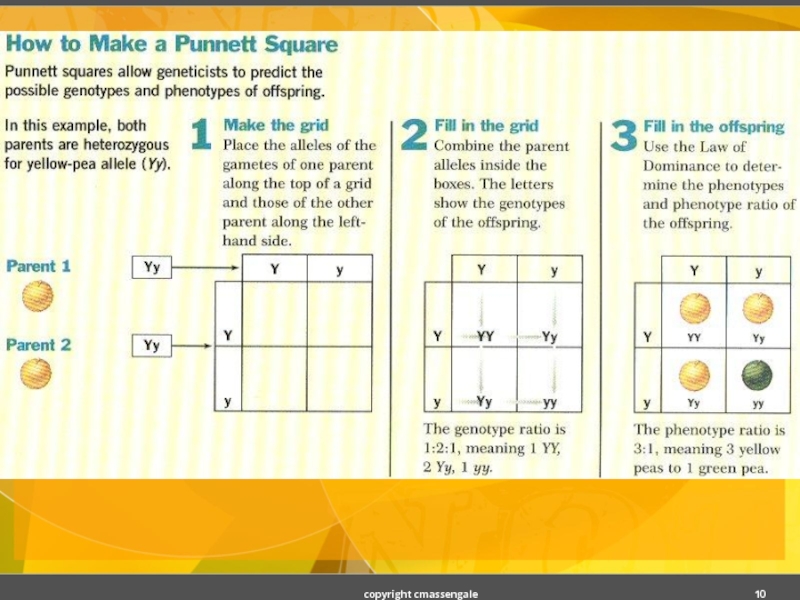
- 10. copyright cmassengale
- 11. Designers - “Genes” Alleles - two forms
- 12. Genotype - gene combination for a trait.
- 13. Genotype & Phenotype in Flowers Genotype of
- 14. Genotypes Homozygous genotype - gene combination involving
- 15. Genes and Environment Determine Characteristics copyright cmassengale
- 16. Mendel’s Pea Plant Experiments copyright cmassengale
- 17. Why peas, Pisum sativum? Can be grown
- 18. Reproduction in Flowering Plants Pollen contains sperm
- 19. Mendel’s Experimental Methods Mendel hand-pollinated flowers using
- 20. How Mendel Began Mendel produced pure strains
- 21. EightTraits of Pea Plant Seed shape ---
- 22. copyright cmassengale
- 23. copyright cmassengale
- 24. Mendel’s Experimental Results copyright cmassengale
- 25. Did the observed ratio match the theoretical
- 26. Generation “Gap” Parental P1 Generation = the
- 27. Following the Generations Cross 2 Pure
- 28. Monohybrid Crosses copyright cmassengale
- 29. Trait: Seed Shape Alleles: R – Round r
- 30. P1 Monohybrid Cross Review Homozygous dominant x
- 31. Trait: Seed Shape Alleles: R – Round r
- 32. F1 Monohybrid Cross Review Heterozygous x heterozygous
- 33. What Do the Peas Look Like? copyright cmassengale
- 34. …And Now the Test Cross Mendel then
- 35. Trait: Seed Shape Alleles: R – Round r
- 36. Trait: Seed Shape Alleles: R – Round r
- 37. F2 Monohybrid Cross Review Homozygous x heterozygous
- 38. Practice Your Crosses Work the P1, F1,
- 39. Mendel’s Laws copyright cmassengale
- 40. Results of Monohybrid Crosses Inheritable factors or
- 41. Law of Dominance In
- 42. Law of Dominance copyright cmassengale
- 43. Law of Segregation During the formation of
- 44. Applying the Law of Segregation copyright cmassengale
- 45. Law of Independent Assortment Alleles
- 46. Dihybrid Cross A breeding experiment that tracks
- 47. Question: How many gametes will be produced
- 48. Answer: 1. RrYy: 2n = 22 =
- 49. Dihybrid Cross Traits: Seed shape & Seed
- 50. Dihybrid Cross copyright cmassengale
- 51. Dihybrid Cross copyright cmassengale
- 52. Dihybrid Cross Round/Yellow: 9 Round/green: 3 wrinkled/Yellow: 3 wrinkled/green: 1 9:3:3:1 copyright cmassengale
- 53. Test Cross A mating between an individual
- 54. Test Cross Possible results: copyright cmassengale
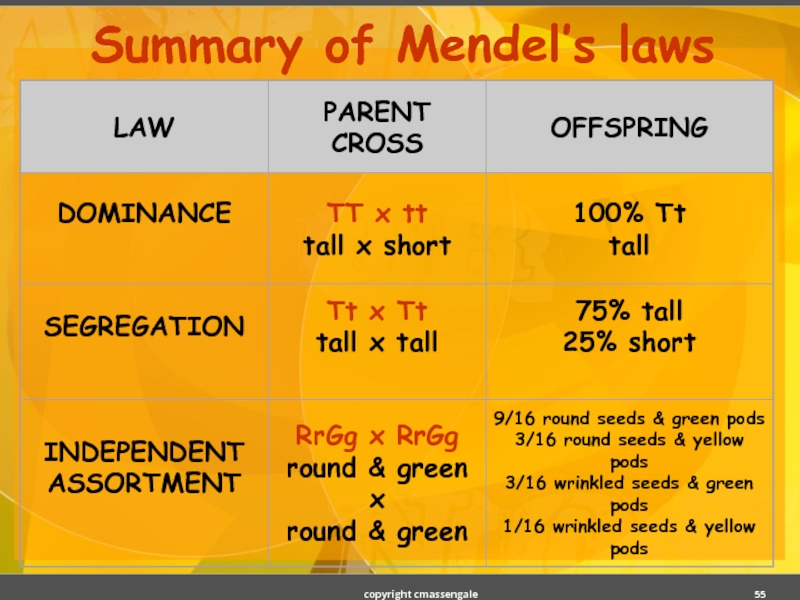
- 55. Summary of Mendel’s laws copyright cmassengale
- 56. Incomplete Dominance and Codominance copyright cmassengale
- 57. Incomplete Dominance F1 hybrids have an appearance
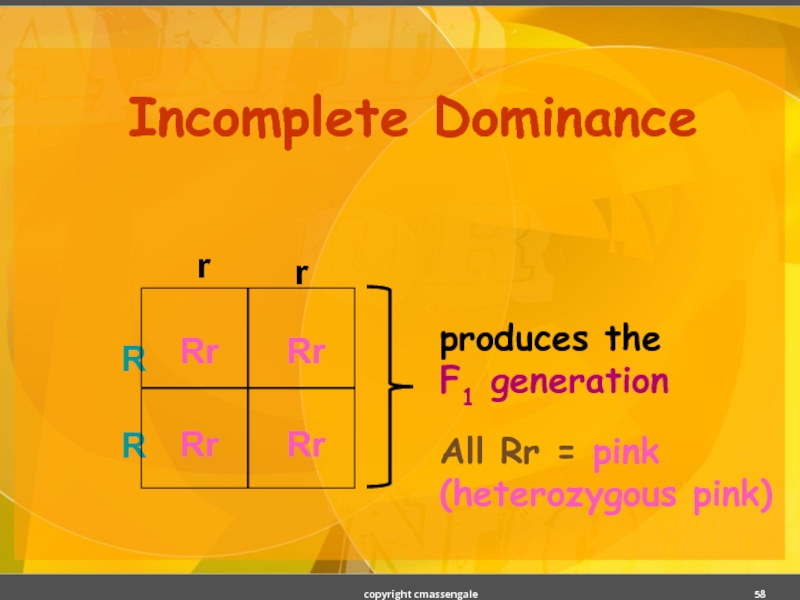
- 58. Incomplete Dominance r copyright cmassengale
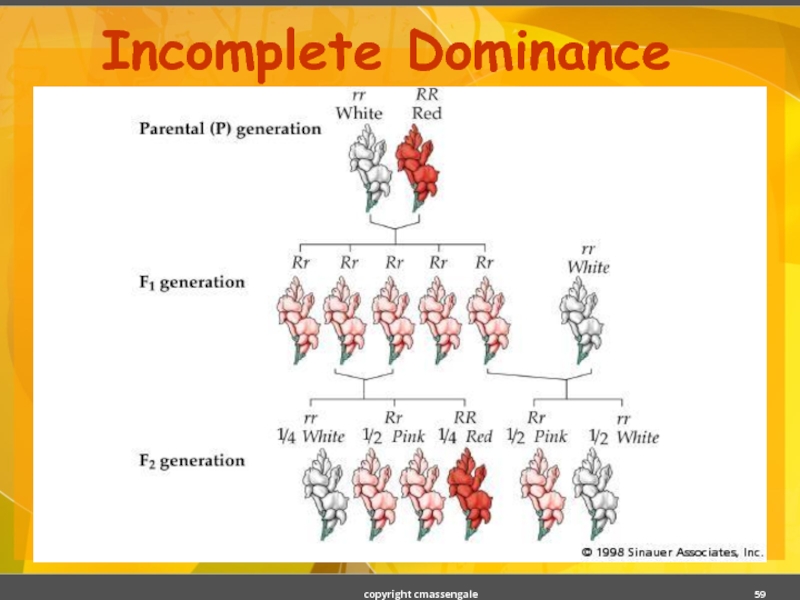
- 59. Incomplete Dominance copyright cmassengale
- 60. Codominance Two alleles are expressed (multiple alleles)
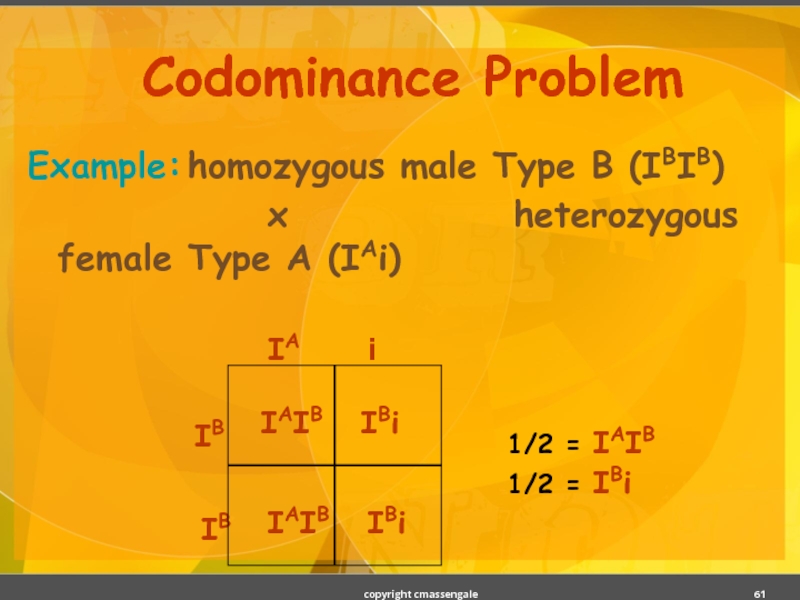
- 61. Codominance Problem Example: homozygous male Type B (IBIB)
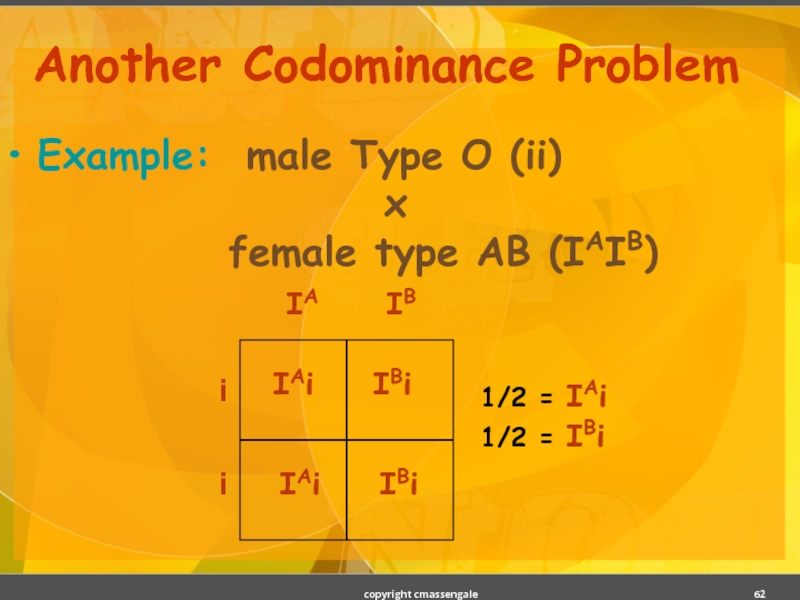
- 62. Another Codominance Problem Example: male Type O
- 63. Codominance Question: If a boy has a
- 64. Codominance Answer: Parents: genotypes = IAi
- 65. Sex-linked Traits Traits (genes) located on the
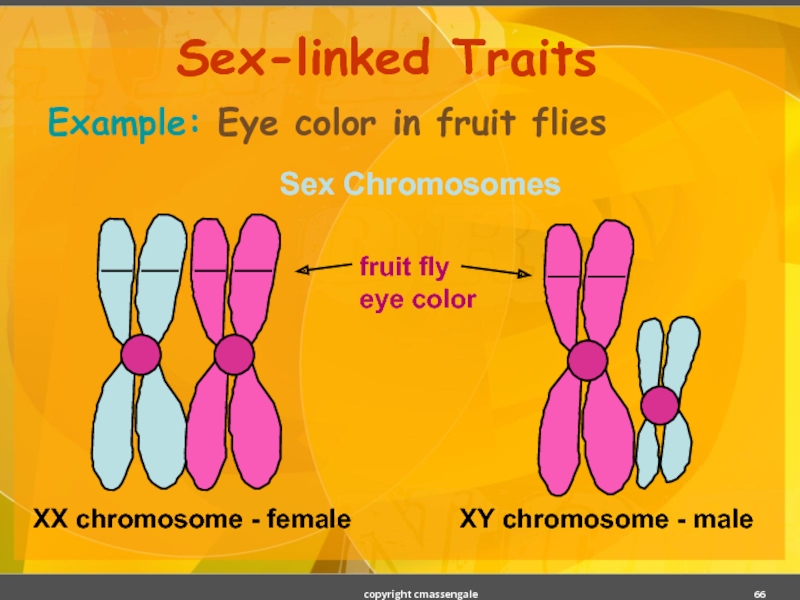
- 66. Sex-linked Traits Sex Chromosomes Example: Eye color in fruit flies copyright cmassengale
- 67. Sex-linked Trait Problem Example: Eye color in
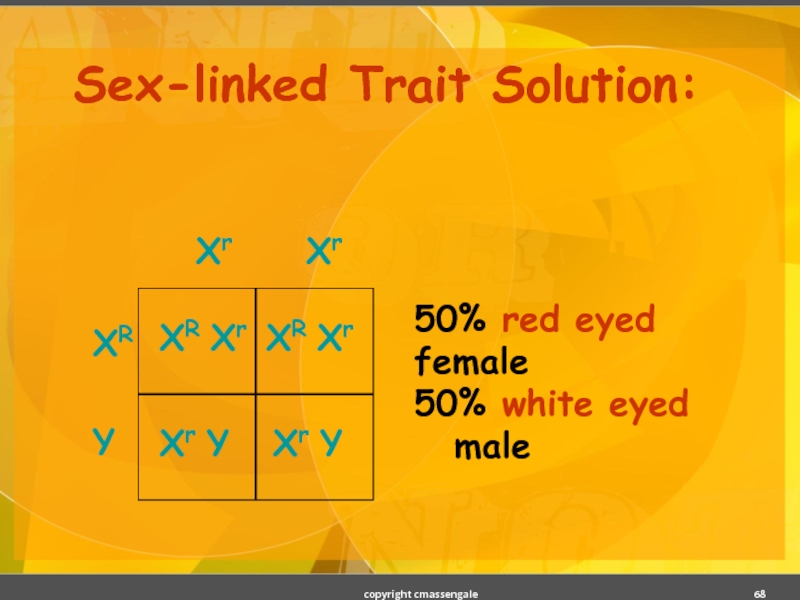
- 68. Sex-linked Trait Solution: 50% red eyed female 50% white eyed male copyright cmassengale
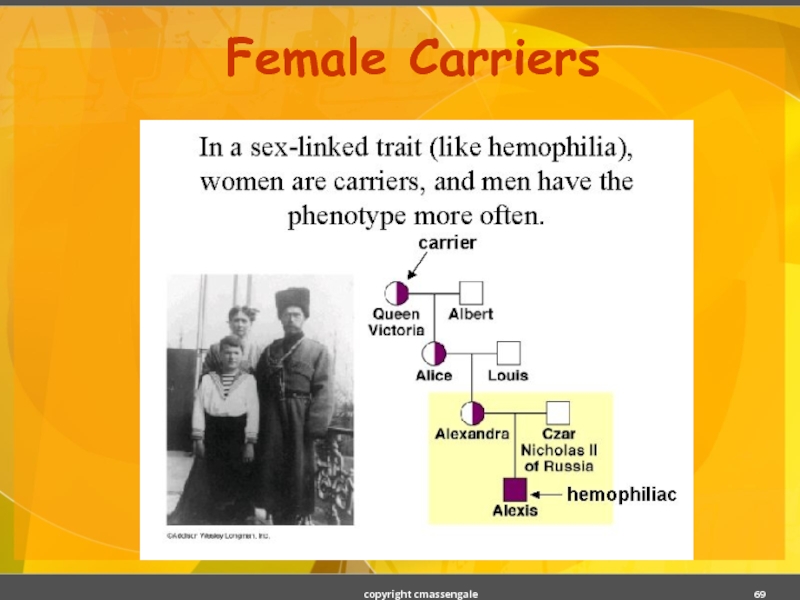
- 69. Female Carriers copyright cmassengale
- 70. Genetic Practice Problems copyright cmassengale
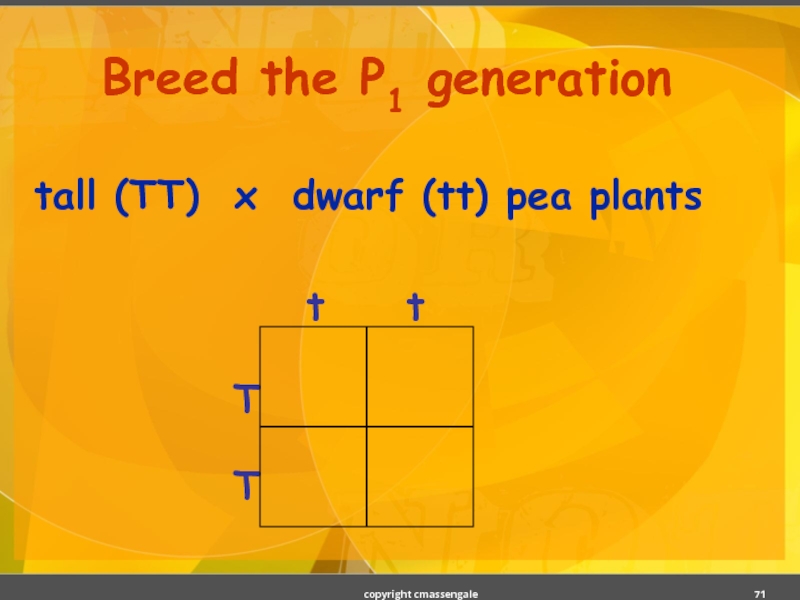
- 71. Breed the P1 generation tall (TT) x dwarf (tt) pea plants copyright cmassengale
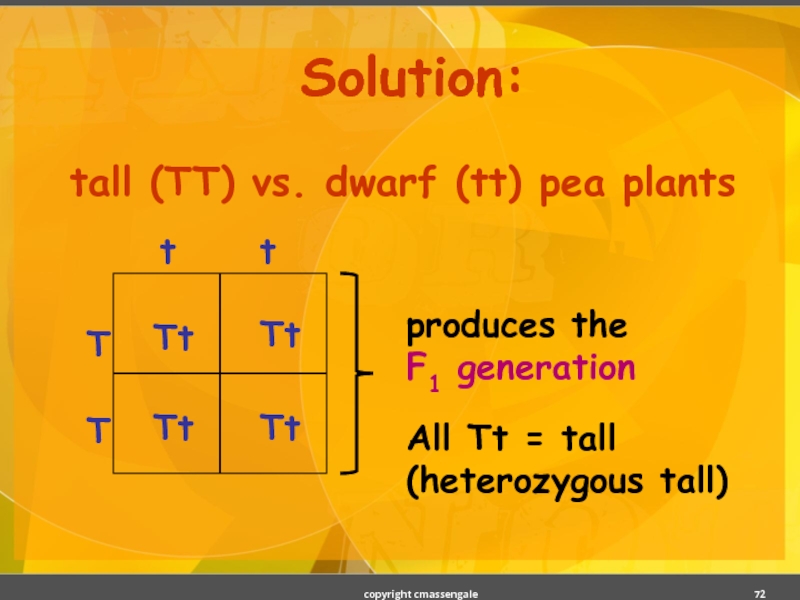
- 72. Solution: tall (TT) vs. dwarf (tt) pea plants copyright cmassengale
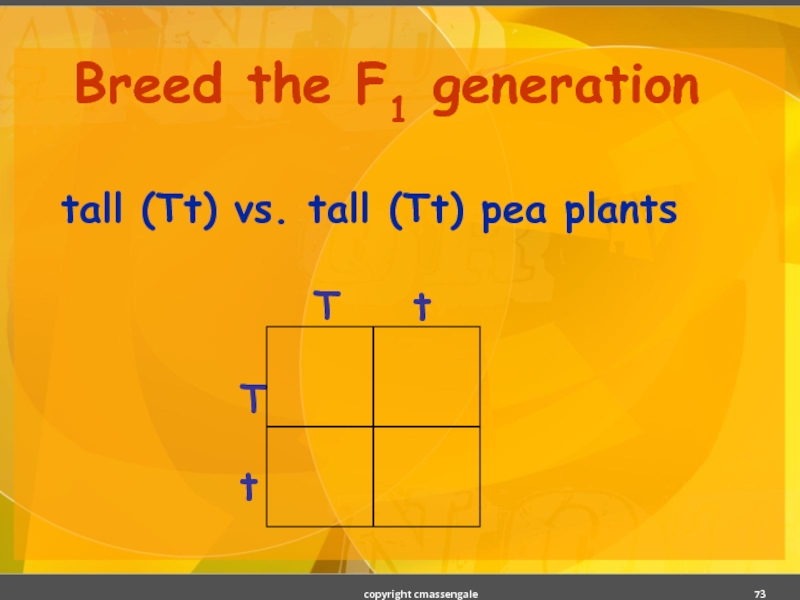
- 73. Breed the F1 generation tall (Tt) vs. tall (Tt) pea plants copyright cmassengale
- 74. Solution: tall (Tt) x tall (Tt) pea plants copyright cmassengale
Слайд 2Gregor Mendel
(1822-1884)
Responsible for the Laws governing Inheritance of Traits.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 3Gregor Johann Mendel
Austrian monk
Studied the inheritance of traits in pea plants.
Developed
Mendel's work was not recognized until the turn of the 20th century.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 4Gregor Johann Mendel
Between 1856 and 1863, Mendel cultivated and tested some
He found that the plants' offspring retained traits of the parents.
Called the “Father of Genetics“.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 6Mendel stated that physical traits are inherited as “particles”.
Mendel did not
Particulate Inheritance
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 7Genetic Terminology
Trait - any characteristic that can be passed from parent
Heredity - passing of traits from parent to offspring.
Genetics - study of heredity.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 8Types of Genetic Crosses
Monohybrid cross - cross involving a single trait
e.g.
Dihybrid cross - cross involving two traits. e.g. flower color & plant height.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 11Designers - “Genes”
Alleles - two forms of a gene (dominant &
Dominant - stronger of two genes expressed in the hybrid; represented by a capital letter (R).
Recessive - gene that shows up less often in a cross; represented by a lowercase letter (r).
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 12Genotype - gene combination for a trait. (e.g. RR, Rr, rr)
Phenotype - the physical feature resulting from a genotype. (e.g. red, white)
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 13Genotype & Phenotype in Flowers
Genotype of alleles:
R = red flower
r =
All genes occur in pairs, so 2 alleles affect a characteristic
Possible combinations are:
Genotypes RR Rr rr
Phenotypes RED RED YELLOW
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 14Genotypes
Homozygous genotype - gene combination involving 2 dominant or 2 recessive
Heterozygous genotype - gene combination of one dominant & one recessive allele. (e.g. Rr); also called hybrid.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 17Why peas, Pisum sativum?
Can be grown in a small area.
Produce
Produce pure plants when allowed to self-pollinate. several generations
Can be artificially cross-pollinated.
copyright cmassengale
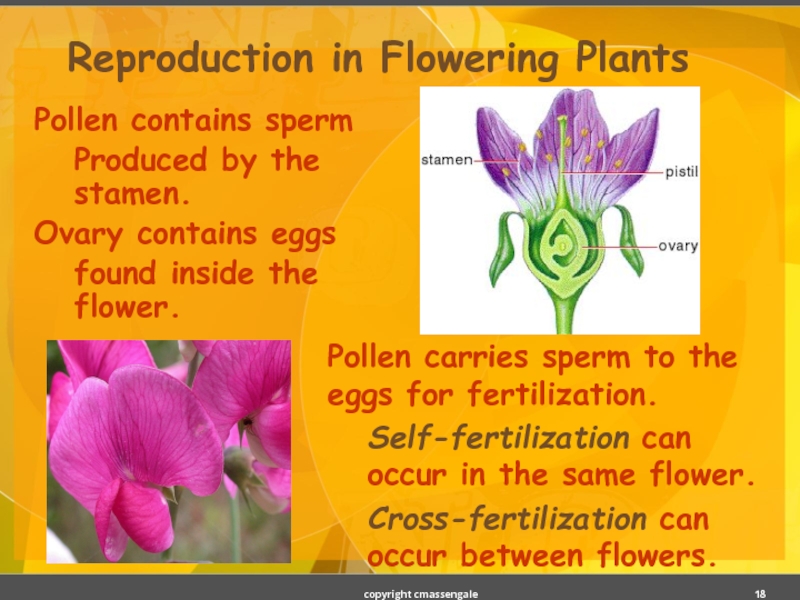
Слайд 18Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Pollen contains sperm
Produced by the stamen.
Ovary contains eggs
found
Pollen carries sperm to the eggs for fertilization.
Self-fertilization can occur in the same flower.
Cross-fertilization can occur between flowers.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 19Mendel’s Experimental Methods
Mendel hand-pollinated flowers using a paintbrush
He could snip the
Covered each flower with a cloth bag.
He traced traits through the several generations.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 20How Mendel Began
Mendel produced pure strains by allowing the plants to
copyright cmassengale
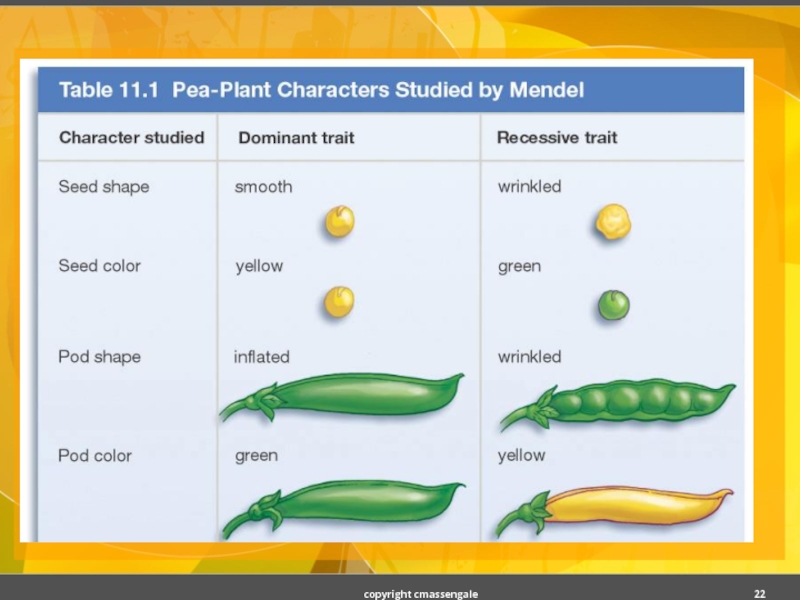
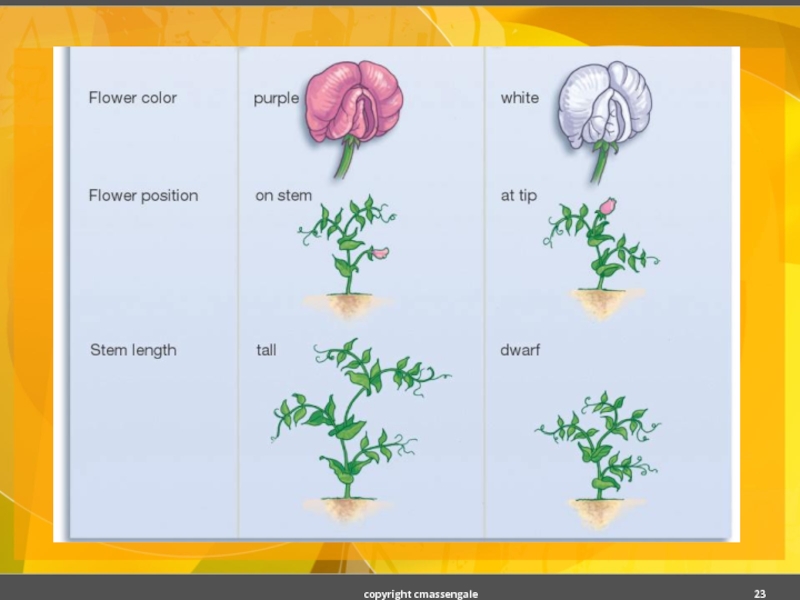
Слайд 21EightTraits of Pea Plant
Seed shape --- Round (R) or Wrinkled (r)
Seed
Pod Shape --- Smooth (S) or Wrinkled (s)
Pod Color --- Green (G) or Yellow (g)
Seed Coat Color --- Gray (G) or White (g)
Flower position---Axial (A) or Terminal (a)
Plant Height --- Tall (T) or Short (t)
Flower color --- Purple (P) or White (p)
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 25Did the observed ratio match the theoretical ratio?
The theoretical or expected
Mendel’s observed ratio was 2.96:1
The discrepancy is due to statistical error.
The larger the sample the more nearly the results approximate to the theoretical ratio.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 26Generation “Gap”
Parental P1 Generation = the parental generation in a breeding
F1 generation = the first-generation offspring in a breeding experiment. (1st filial generation)
From breeding individuals from the P1 generation.
F2 generation = the second-generation offspring in a breeding experiment. (2nd filial generation)
From breeding individuals from the F1 generation.
copyright cmassengale
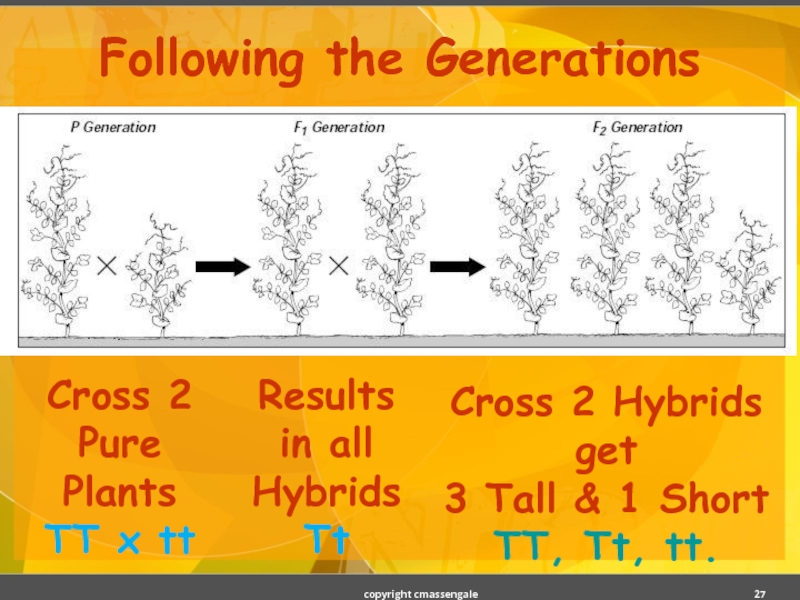
Слайд 27Following the Generations
Cross 2 Pure Plants
TT x tt
Results in all Hybrids
Tt
Cross
copyright cmassengale
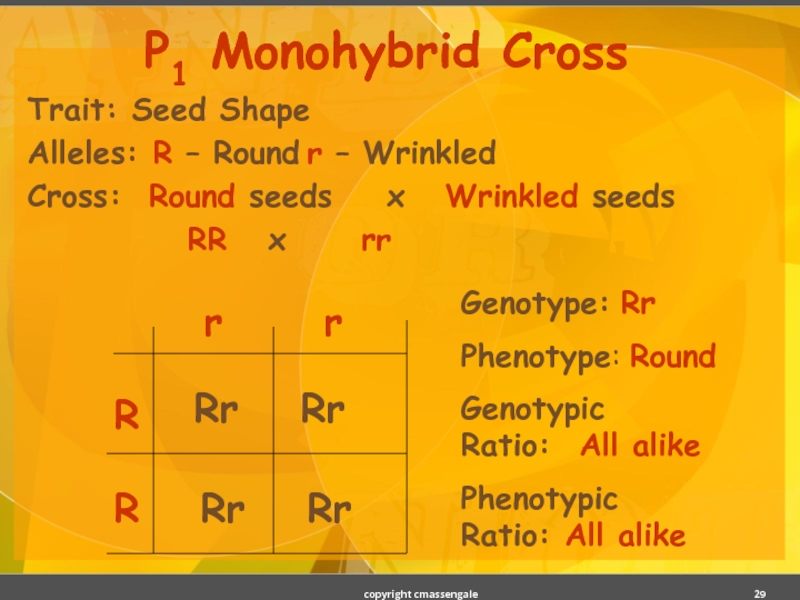
Слайд 29Trait: Seed Shape
Alleles: R – Round r – Wrinkled
Cross: Round seeds
RR x rr
P1 Monohybrid Cross
R
R
r
r
Rr
Rr
Rr
Rr
Genotype: Rr
Phenotype: Round
Genotypic
Ratio: All alike
Phenotypic
Ratio: All alike
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 30P1 Monohybrid Cross Review
Homozygous dominant x Homozygous recessive
Offspring all Heterozygous (hybrids)
Offspring
Genotypic & Phenotypic ratio is ALL ALIKE
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 31Trait: Seed Shape
Alleles: R – Round r – Wrinkled
Cross: Round seeds
Rr x Rr
F1 Monohybrid Cross
R
r
r
R
RR
rr
Rr
Rr
Genotype: RR, Rr, rr
Phenotype: Round &
wrinkled
Gen. Ratio: 1:2:1
Phen. Ratio: 3:1
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 32F1 Monohybrid Cross Review
Heterozygous x heterozygous
Offspring:
25% Homozygous dominant RR
50% Heterozygous Rr
25%
Offspring called F2 generation
Genotypic ratio is 1:2:1
Phenotypic Ratio is 3:1
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 34…And Now the Test Cross
Mendel then crossed a pure & a
This is known as an F2 or test cross
There are two possible testcrosses: Homozygous dominant x Hybrid Homozygous recessive x Hybrid
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 35Trait: Seed Shape
Alleles: R – Round r – Wrinkled
Cross: Round seeds
RR x Rr
F2 Monohybrid Cross (1st)
R
R
r
R
RR
Rr
RR
Rr
Genotype: RR, Rr
Phenotype: Round
Genotypic
Ratio: 1:1
Phenotypic
Ratio: All alike
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 36Trait: Seed Shape
Alleles: R – Round r – Wrinkled
Cross: Wrinkled seeds x
rr x Rr
F2 Monohybrid Cross (2nd)
r
r
r
R
Rr
rr
Rr
rr
Genotype: Rr, rr
Phenotype: Round & Wrinkled
G. Ratio: 1:1
P.Ratio: 1:1
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 37F2 Monohybrid Cross Review
Homozygous x heterozygous (hybrid)
Offspring:
50% Homozygous RR or rr
50%
Phenotypic Ratio is 1:1
Called Test Cross because the offspring have SAME genotype as parents.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 38Practice Your Crosses
Work the P1, F1, and both F2 Crosses for
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 40Results of Monohybrid Crosses
Inheritable factors or genes are responsible for all
Phenotype is based on Genotype.
Each trait is based on two genes, one from the mother and the other from the father.
True-breeding individuals are homozygous ( both alleles) are the same.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 41Law of Dominance
In a cross of parents that are pure
All the offspring will be heterozygous and express only the dominant trait.
RR x rr yields all Rr (round seeds)
copyright cmassengale
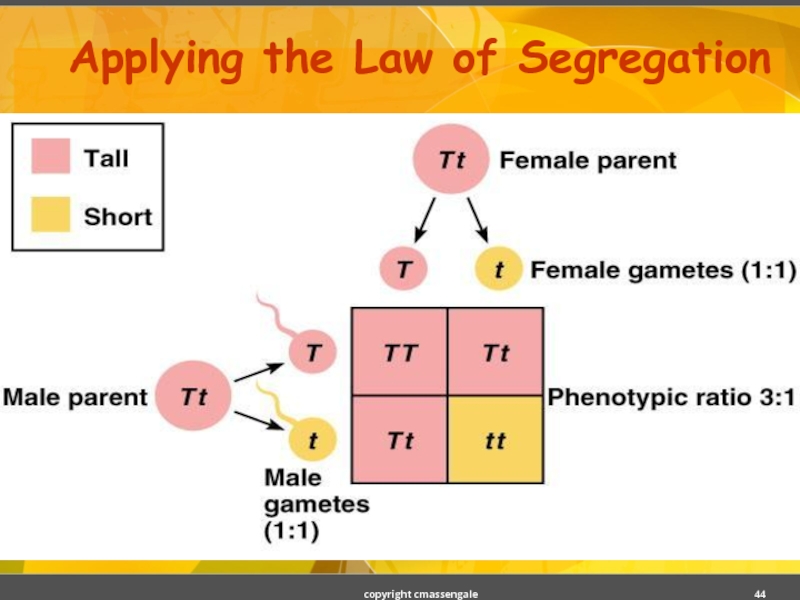
Слайд 43Law of Segregation
During the formation of gametes (eggs or sperm), the
Alleles for a trait are then "recombined" at fertilization, producing the genotype for the traits of the offspring.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 45Law of Independent Assortment
Alleles for different traits are distributed to
This law can be illustrated using dihybrid crosses.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 46Dihybrid Cross
A breeding experiment that tracks the inheritance of two traits.
Mendel’s
a. Each pair of alleles segregates independently during gamete formation
b. Formula: 2n (n = # of heterozygotes)
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 47Question:
How many gametes will be produced for the following allele arrangements?
Remember:
1. RrYy
2. AaBbCCDd
3. MmNnOoPPQQRrssTtQq
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 48Answer:
1. RrYy: 2n = 22 = 4 gametes
RY Ry
2. AaBbCCDd: 2n = 23 = 8 gametes
ABCD ABCd AbCD AbCd
aBCD aBCd abCD abCD
3. MmNnOoPPQQRrssTtQq: 2n = 26 = 64 gametes
copyright cmassengale
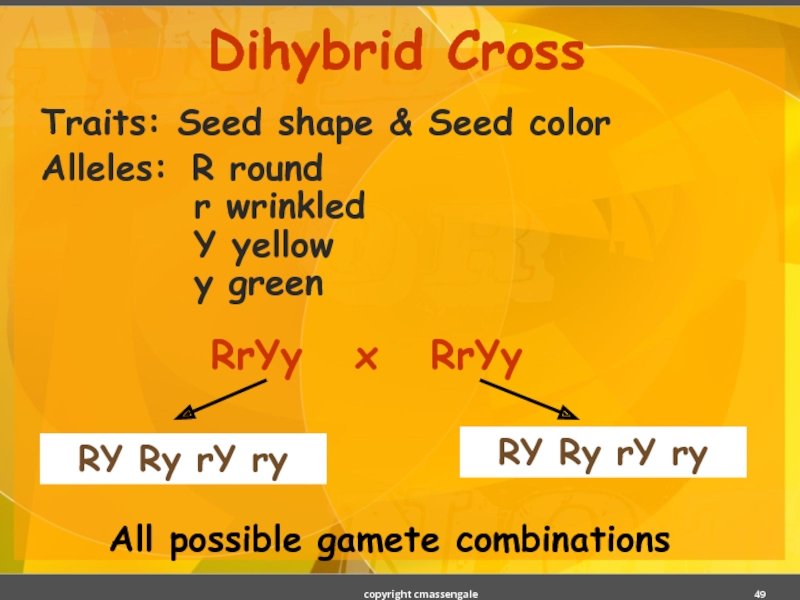
Слайд 49Dihybrid Cross
Traits: Seed shape & Seed color
Alleles: R round
RrYy x RrYy
RY Ry rY ry
RY Ry rY ry
All possible gamete combinations
copyright cmassengale
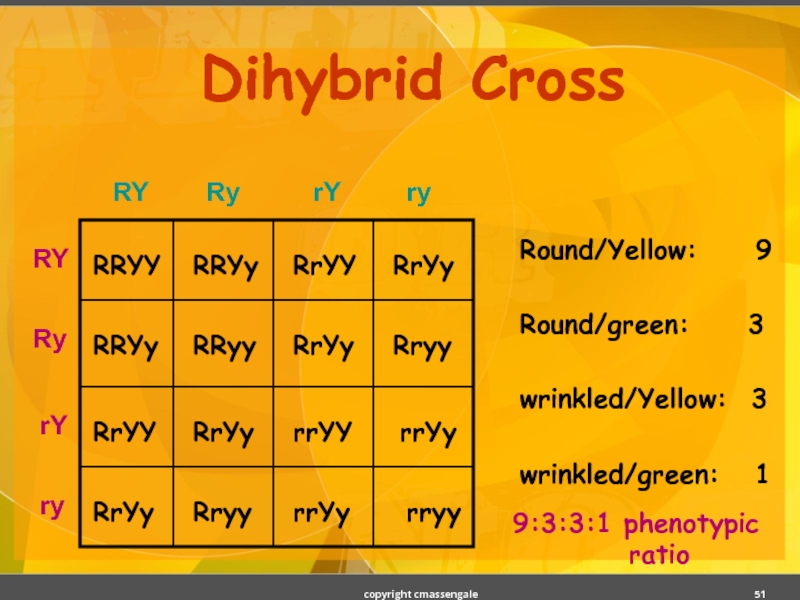
Слайд 52Dihybrid Cross
Round/Yellow: 9
Round/green: 3
wrinkled/Yellow: 3
wrinkled/green: 1
9:3:3:1
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 53Test Cross
A mating between an individual of unknown genotype and a
Example: bbC__ x bbcc
BB = brown eyes
Bb = brown eyes
bb = blue eyes
CC = curly hair
Cc = curly hair
cc = straight hair
copyright cmassengale
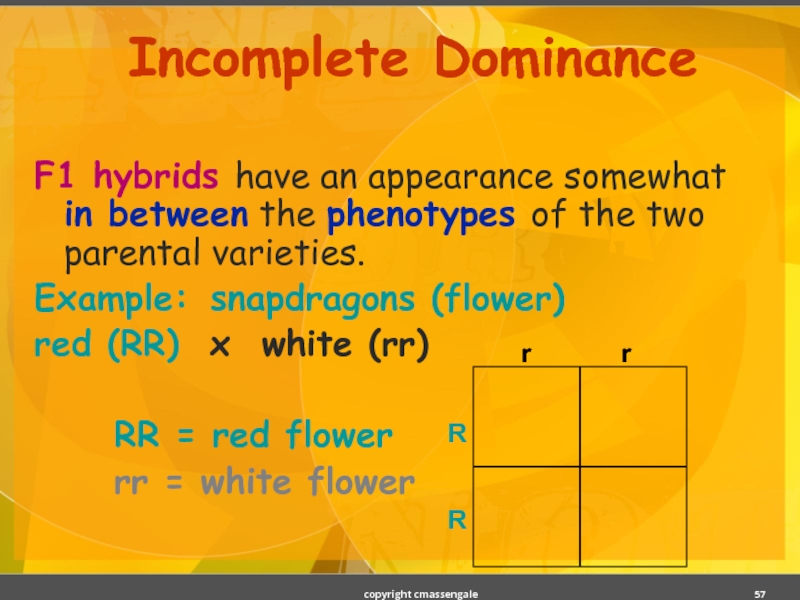
Слайд 57Incomplete Dominance
F1 hybrids have an appearance somewhat in between the phenotypes
Example: snapdragons (flower)
red (RR) x white (rr)
RR = red flower
rr = white flower
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 60Codominance
Two alleles are expressed (multiple alleles) in heterozygous individuals.
Example: blood type
1. type
2. type B = IBIB or IBi
3. type AB = IAIB
4. type O = ii
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 61Codominance Problem
Example: homozygous male Type B (IBIB)
x heterozygous female Type
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 62Another Codominance Problem
Example: male Type O (ii)
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 63Codominance
Question:
If a boy has a blood type O and his sister
type O (ii) X type AB (IAIB)
boy girl
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 65Sex-linked Traits
Traits (genes) located on the sex chromosomes.
Sex chromosomes are X
XX genotype for females
XY genotype for males
Many sex-linked traits carried on X chromosome.
copyright cmassengale
Слайд 67Sex-linked Trait Problem
Example: Eye color in fruit flies
(red-eyed male) x
Remember: the Y chromosome in males does not carry traits.
RR = red eyed
Rr = red eyed
rr = white eyed
XY = male
XX = female
copyright cmassengale