- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
IMPRS workshop Comparative Genomics презентация
Содержание
- 1. IMPRS workshop Comparative Genomics
- 2. What is positive selection?
- 3. Positive selection is selection on a particular
- 4. Woolhouse et al, 2002. Nat. Genet Directional
- 5. Species A Diversifying positive selection Interspecific level Positive selection driving divergence
- 6. Why is it interesting to identify traits
- 7. How can we detect positive selection?
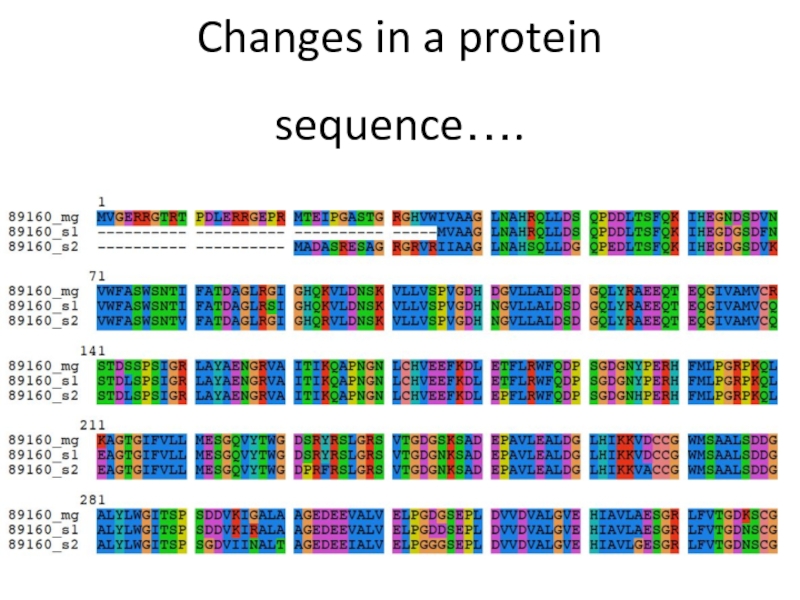
- 8. Changes in a protein sequence….
- 9. Come from changes in the nucleotide sequence
- 10. Quantifying non-synonymous variation - an estimate of
- 11. Rate of synonymous mutations Rate of non-synonymous mutations To measure positive selection:
- 12. Positive selection between species Ks or dS Ka or dN
- 13. Positive selection in a population PS PN
- 14. Species A Species B Species C PN
- 15. Species A Species B Species C PN
- 16. Nei and Gojobori, 1986 Counts of
- 17. Calculate potential synonymous sites (S) for each
- 18. Calculate Sd and Nd for each codon.
- 19. Positive selection between species ds dN
- 20. Species A Species B Species C PN
- 21. McDonald Kreitman (MK) test to contrast within and between species variation
- 22. Repl: Nonsynonymous, Syn: Synonymous Fixed: Substitution, Poly: Polymorphisms Drosophila dataset alcohol dehydrogenase
- 23. MK test contrasts within and between species
- 24. Conclusion from MK-test: Adh locus in Drosophila
- 25. One problem with the “counting methods”
- 26. Positive selection on one or few particular
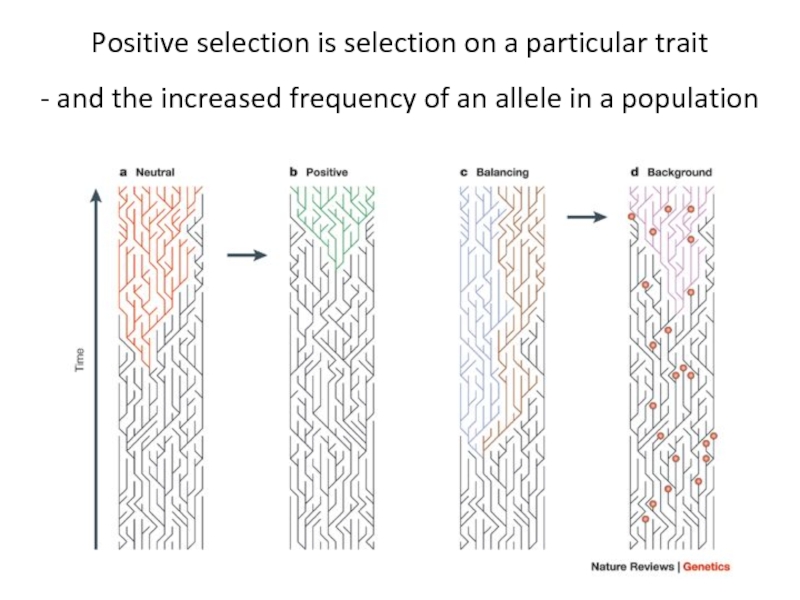
Слайд 3Positive selection is selection on a particular trait
- and the increased
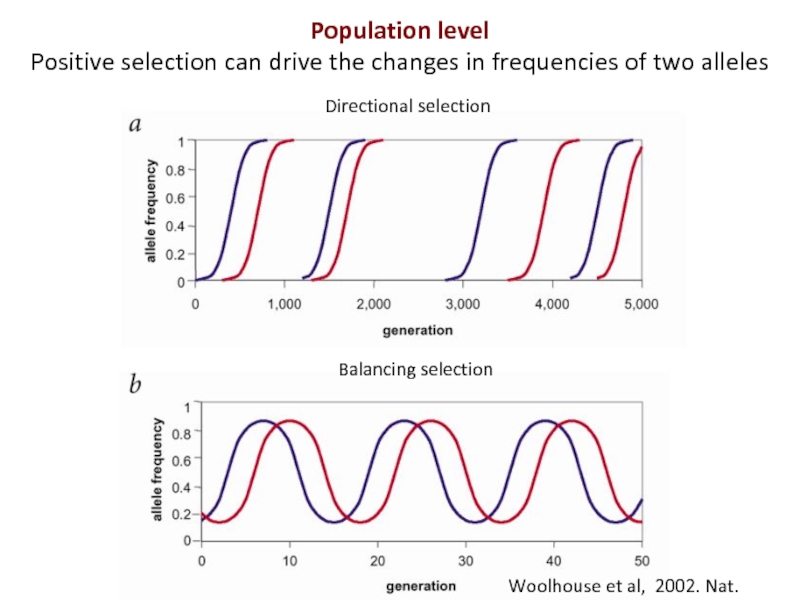
Слайд 4Woolhouse et al, 2002. Nat. Genet
Directional selection
Balancing selection
Population level
Positive selection can
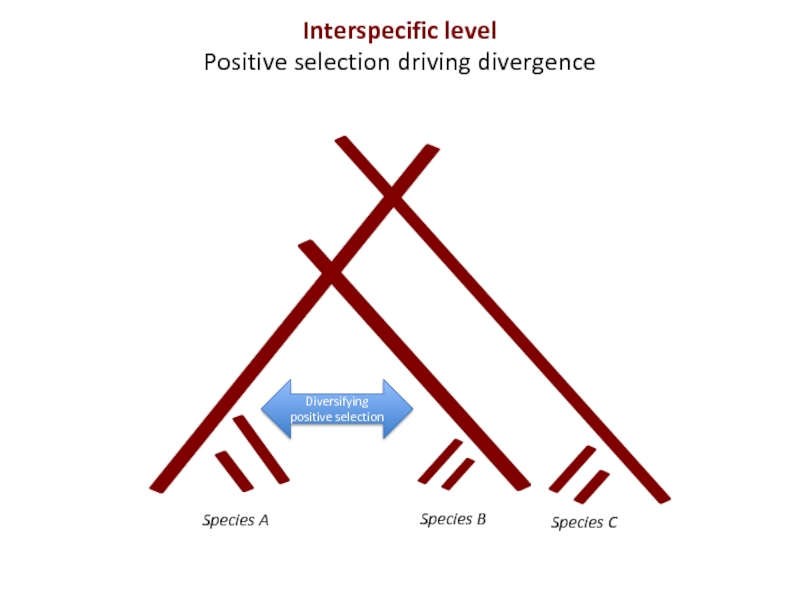
Слайд 5Species A
Diversifying positive selection
Interspecific level
Positive selection driving divergence
Слайд 6Why is it interesting to identify traits which
have undergone or
Function
Evolution
Environment
……
Слайд 10Quantifying non-synonymous variation
- an estimate of positive selection
Synonymous mutations: neutral mutations
Non-synonymous
Слайд 14Species A
Species B
Species C
PN / Ps
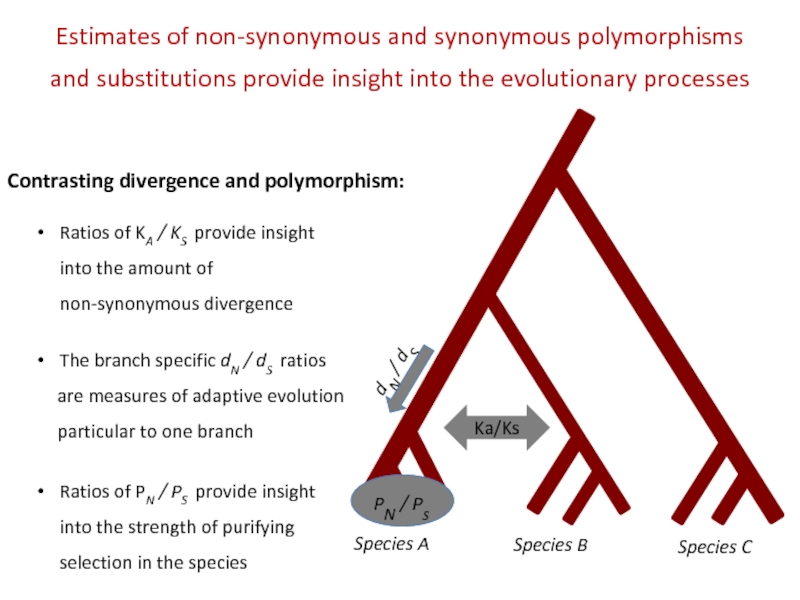
Estimates of non-synonymous and synonymous polymorphisms
Analysing divergence and polymorphism:
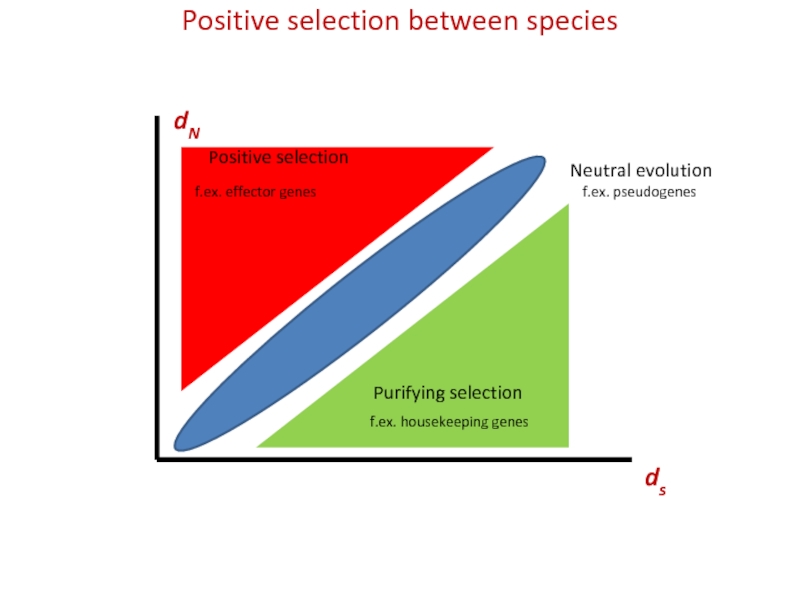
KA / KS ratios > 1 indicate positive selection
KA / KS ratios < 1 indicate negative selection
KA / KS ratios = 1 indicates neutral evolution
KA and dN: rate of non-synonymous substitutions
KS and dS: rate of synonymous substitutions
PN: Amount of non-synonymous polymorphisms
PS: Amount of synonymous polymorphisms
Ka/Ks
branch-specific estimate
Слайд 15Species A
Species B
Species C
PN / Ps
Estimates of non-synonymous and synonymous polymorphisms
Contrasting divergence and polymorphism:
Ka/Ks
The branch specific dN / dS ratios
are measures of adaptive evolution
particular to one branch
Ratios of PN / PS provide insight into the strength of purifying selection in the species
Ratios of KA / KS provide insight into the amount of non-synonymous divergence
Слайд 16Nei and Gojobori, 1986
Counts of non-synonymous mutations for each gene
Counts of synonymous mutations for each gene (Sd)
Counts of potential non-synonymous sites for each gene (N)
Counts of potential synonymous sites for each gene (S)
Non-synonymous substitution rate: KA = Nd / N
Synonymous substitution rate: KS = Sd / S
Ratio KA/KS as an inidicator of evolutionary
mode in each gene
Basic analyses of the proportion of non-synonymous to synonymous divergence KA/KS
Слайд 17Calculate potential synonymous sites (S) for each codon
A fourfold degenerate
A non-degenerate site counts as S = 0 (N = 1)
A two fold degenerate site counts as S = 1/3 (N = 2/3)
Proline S = 0 + 0 + 1 = 1
Phenylalanine S = 0 + 0 + 1/3 = 1/3
For Glycine S = 0 + 0 + 1 = 1, for Alanine S = 0 + 0 + 1 = Take the average: S=1
Leucine for UUA, S = 1/3 + 0 + 1/3 = 2/3
for CUA, S = 1/3 + 0 + 1 = 4/3
Take the average of these: S = 1 for codon 4
Phenylalanine for UUU, S = 1/3
for guanine, S = 1
Take average: S = 2/3
For whole sequence, S = 1 + 1/3 + 1 + 1 + 2/3 = 4
N = total number of sites: S = 15 - 4 = 11
Counts of possible synonymous sites for each gene (S)
1 2 3 4 5
Pro Phe Gly Leu Phe
Seq 1 CCC UUU GGG UUA UUU
Seq 2 CCC UUC GAG CUA GUA
Pro Phe Ala Leu Val
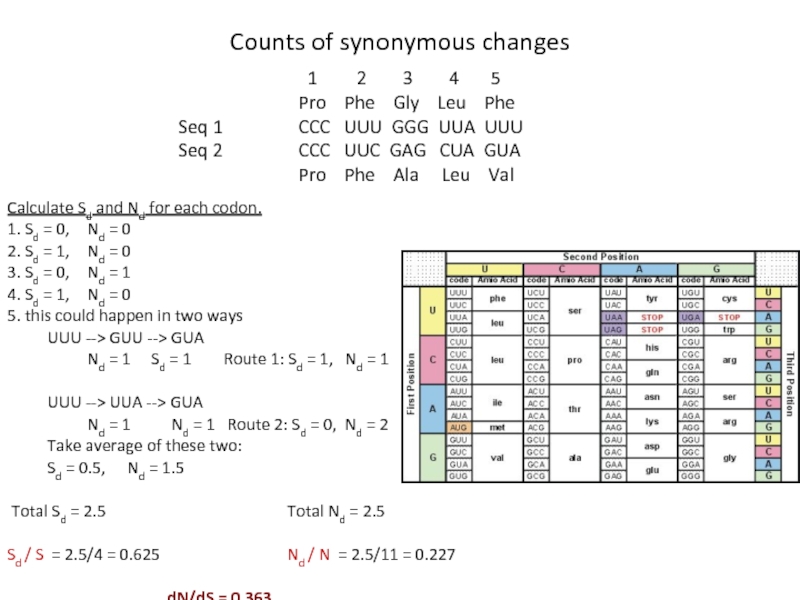
Слайд 18Calculate Sd and Nd for each codon.
1. Sd = 0, Nd
2. Sd = 1, Nd = 0
3. Sd = 0, Nd = 1
4. Sd = 1, Nd = 0
5. this could happen in two ways
UUU --> GUU --> GUA
Nd = 1 Sd = 1 Route 1: Sd = 1, Nd = 1
UUU --> UUA --> GUA
Nd = 1 Nd = 1 Route 2: Sd = 0, Nd = 2
Take average of these two:
Sd = 0.5, Nd = 1.5
Total Sd = 2.5 Total Nd = 2.5
Sd / S = 2.5/4 = 0.625 Nd / N = 2.5/11 = 0.227
dN/dS = 0.363
1 2 3 4 5
Pro Phe Gly Leu Phe
Seq 1 CCC UUU GGG UUA UUU
Seq 2 CCC UUC GAG CUA GUA
Pro Phe Ala Leu Val
Counts of synonymous changes
Слайд 20Species A
Species B
Species C
PN / Ps
When positive selection is related to
Contrasting divergence and polymorphism:
Ka/Ks
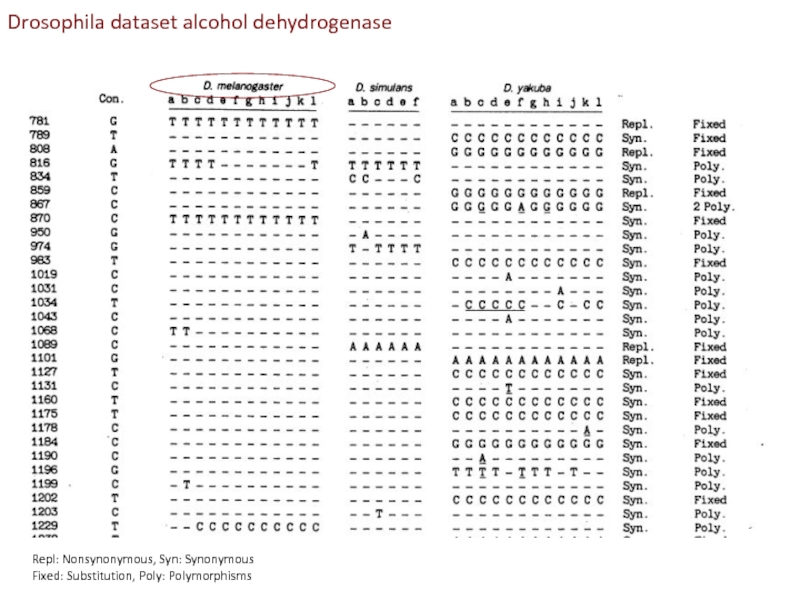
Слайд 22Repl: Nonsynonymous, Syn: Synonymous
Fixed: Substitution, Poly: Polymorphisms
Drosophila dataset alcohol dehydrogenase
Слайд 23MK test contrasts within and between species synonymous
and non-synonymous differences
Contingency
Слайд 24Conclusion from MK-test:
Adh locus in Drosophila has accumulated adaptive mutations (been
Слайд 26Positive selection on one or few particular codons
or in one particular
? Evolutionary model to detect selection in particular codons or branches