- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
GREEN HOUSE EFFECT & ITS GASSES презентация
Содержание
- 1. GREEN HOUSE EFFECT & ITS GASSES
- 2. What is Green House? What is the
- 3. A Greenhouse (also called a Glasshouse) is
- 8. The idea of growing plants
- 10. What is Green House Effect?
- 12. Sun energy passes through atmosphere 26% is
- 14. Water is the most important/potent of
- 15. Deforestation Burning of Fossils Electrical
- 17. Water vapor(H2O) Carbon-dioxide(CO2) Nitrous Oxide(N2O) Methane (CH4) Example of Heat Trapping Gases:
- 18. Greenhouse gas works like a
- 19. Most scientists agree that CO2 plays a
- 21. The figure shows that the concentration of
- 23. A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is
- 25. The Ice at the north
- 27. Result of Green House effect!!!
- 28. Reforestation Personal action Climate policy What Can We Do To Help?
Слайд 2What is Green House?
What is the pre-history of Green House?
What is
What is the causes of Green House effect?
Selective Absorbers & the Green House Effect!
What does a greenhouse gas do?
What happens when more and more greenhouse gases go into the atmosphere?
What happens when the Earth gets warmer?
Result of Green House effect!!!
OUTLINE
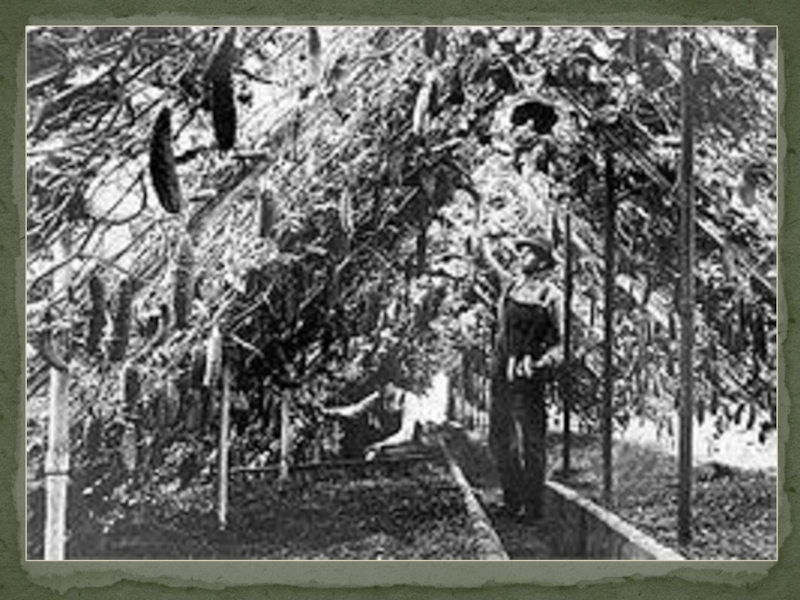
Слайд 3 A Greenhouse (also called a Glasshouse) is
a building in
plants are grown. These structures range in size from small sheds to very large buildings. A miniature greenhouse is known as a cold frame.
What is Green House?
Слайд 8 The idea of growing plants in environmentally controlled areas
Giant greenhouses in the Netherlands
But the first modern greenhouses were built in Italy in the 13th century.
Pre-History Of Green House :
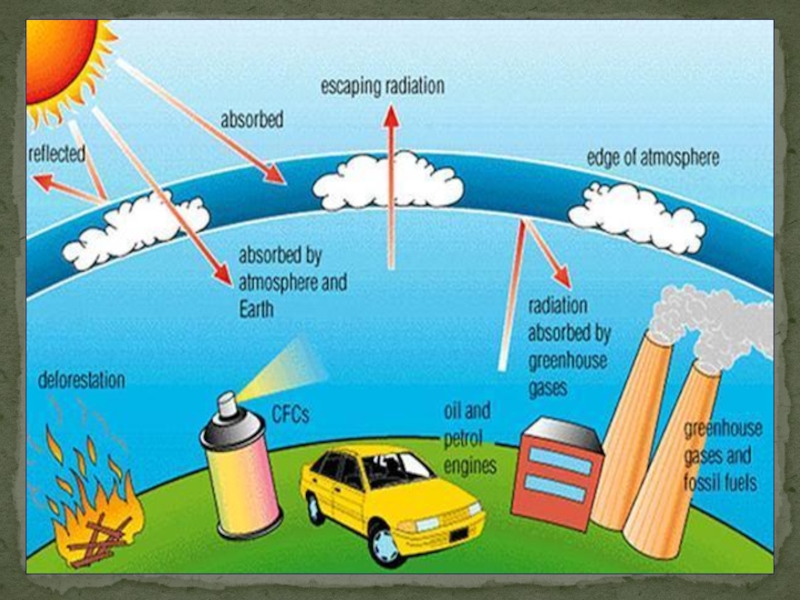
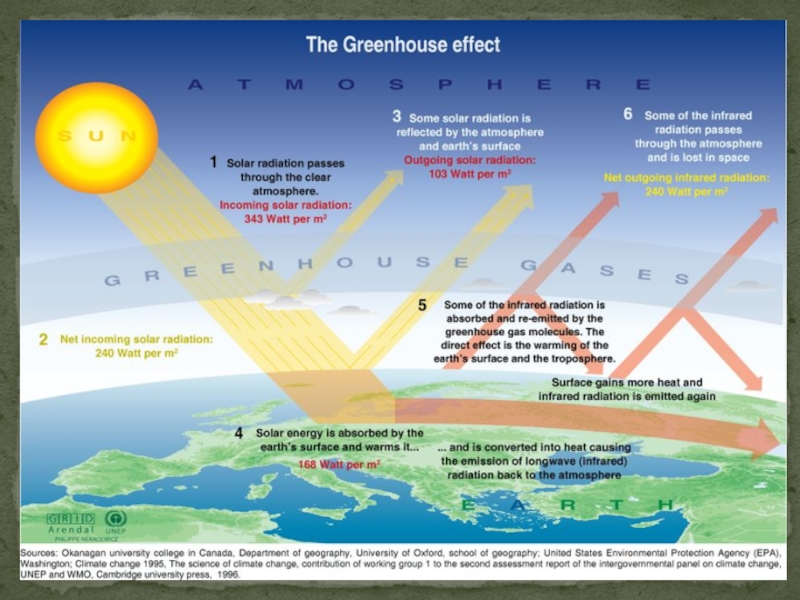
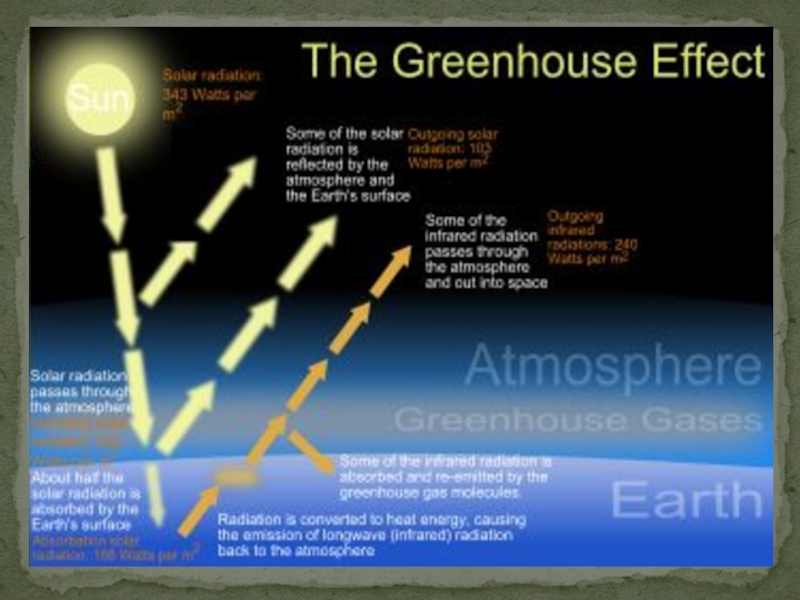
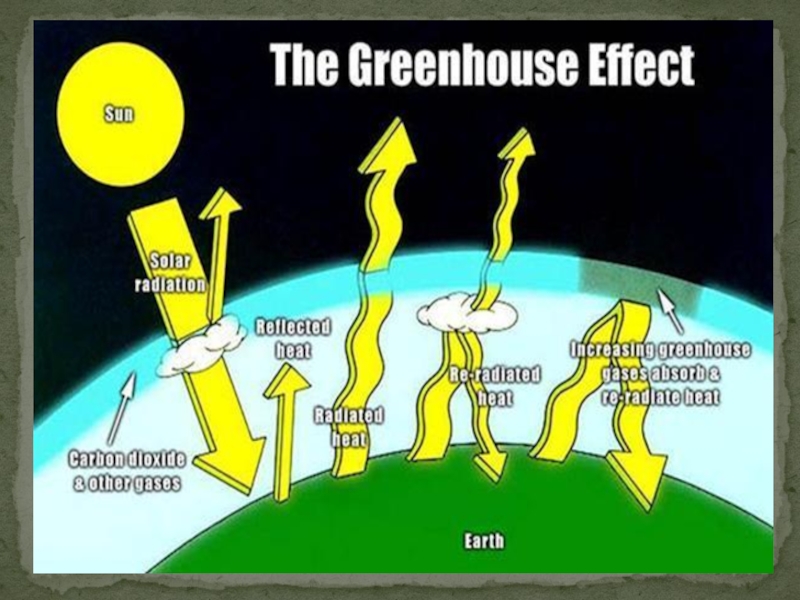
Слайд 10What is Green House Effect?
The Greenhouse effect is a
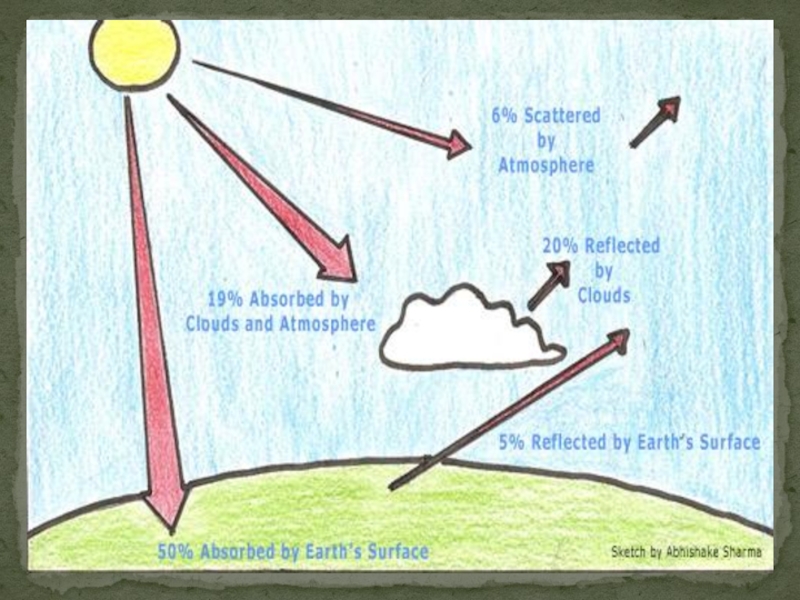
Слайд 12Sun energy passes through atmosphere
26% is reflected or scattered
19% absorbed by
4% reflected to space by Sun
51% reaches the surface
Process of the Green House Effect
Слайд 14 Water is the most important/potent of greenhouse gas.
Water vapor
Selective Absorbers & the G.H.e
CO2 is not very abundant but it is a potent greenhouse gas that we are able to increase in the atmosphere . By contrast, H2O is already saturated and its amount in the atmosphere cannot be increased.
Increasing CO2 content in the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels is thought to result in global warming.
Global warming results in more atmospheric water thus increasing the greenhouse effect — feedback
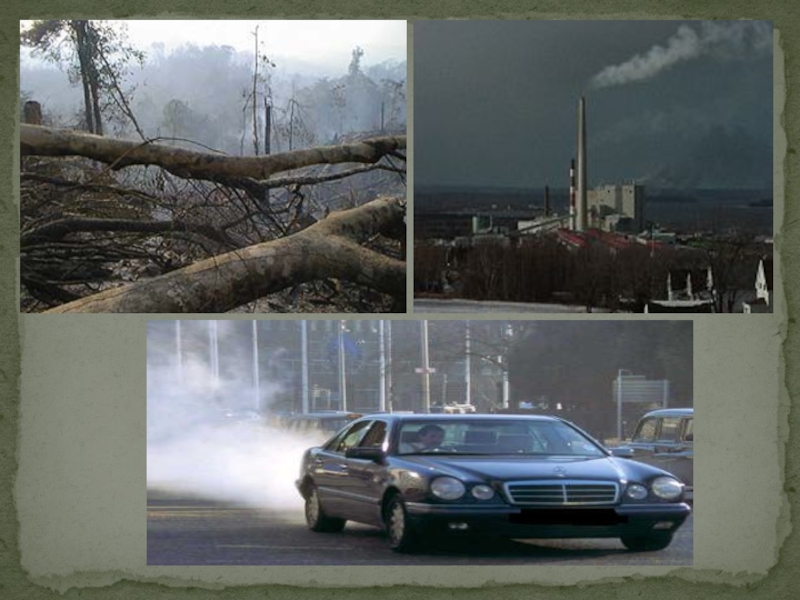
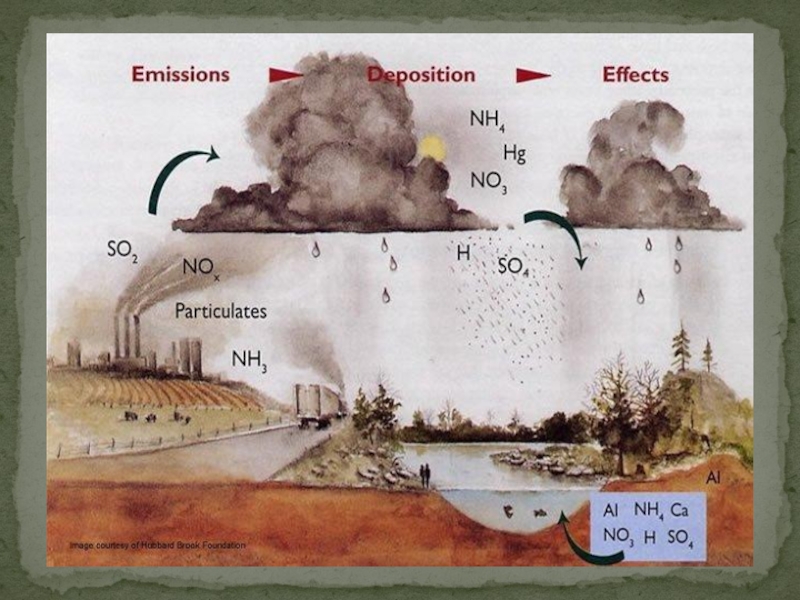
Слайд 15Deforestation
Burning of Fossils
Electrical Appliances
Population Growth
Causes of Green House Effect:
Слайд 17Water vapor(H2O)
Carbon-dioxide(CO2)
Nitrous Oxide(N2O)
Methane (CH4)
Example of Heat Trapping Gases:
Слайд 18 Greenhouse gas works like a great space blanket that
What does Green House Gases Do?
Слайд 19Most scientists agree that CO2 plays a role in warming the
However, the somewhat controversial hypothesis is that increased (anthropogenic?) CO2 in the atmosphere may enhance the warming of our planet.
CO2 Plays a Role:
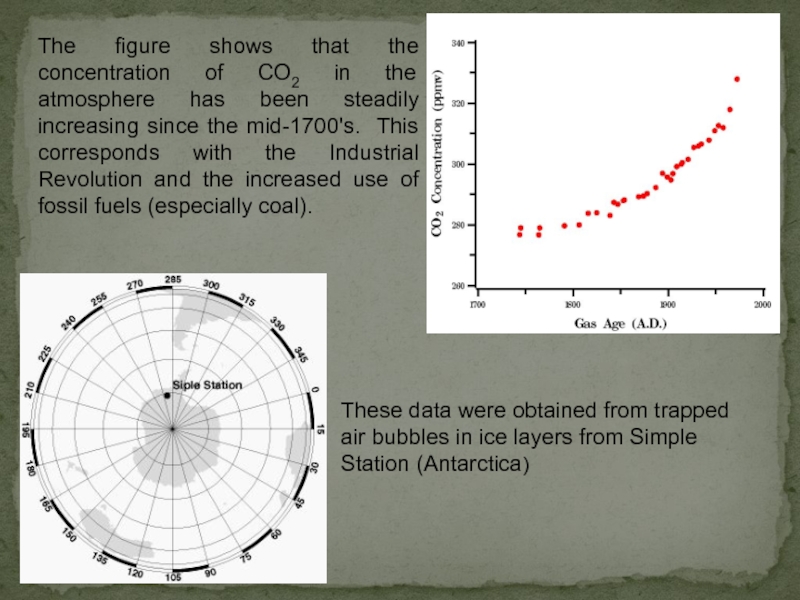
Слайд 21The figure shows that the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere
These data were obtained from trapped air bubbles in ice layers from Simple Station (Antarctica)
Слайд 23
A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere
What happens when more and more greenhouse gases go into the atmosphere?
Слайд 25 The Ice at the north and south poles will
What happens when the Earth gets warmer?
Слайд 27 Result of Green House effect!!!
Global warming
Economic impact
Agricultural impact
Effects on aquatic systems
Effects on hydrological cycles
Health
Direct effects of temperature rise
Spread of disease