- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Cells and Organelles презентация
Содержание
- 1. Cells and Organelles
- 4. Discussion in groups of three Look at
- 14. 1 Organelle Function the substance that fills
- 15. 2 Organelle Function Control center of the
- 16. 3 Type of cellular transport Requires ATP Includes Endocytosis &Exocytosis
- 17. 4 Organelle Function Boundary of the cell
- 18. 5 Vocabulary Word
- 19. 6 Organelle Function Highway of the cell
- 20. 7 Organelle Function Stores, modifies and packages
- 21. 8 Organelle Function Site of protein synthesis
- 22. 9 Vocabulary Word Only allows only some
- 23. 10 Organelle Function Site of food (glucose)
- 24. 11 Organelle Function Highway of the cell
- 25. 12 Function “Powerhouse of the cell” Cellular
- 26. 13 Organelle Function Provides shape and structure
- 27. 14 Organelle Function Cleans the cell ”Garbage
- 28. 15 Organelle Function Aids in cell division
- 29. 16 Phosphate head hydrophilic – attracted
- 30. Vocabulary Word These cells are larger and
- 31. 18 Organelle Function Storage container for water,
- 32. Vocabulary Word A eukaryotic cell in which
- 33. 20 Organelle Function Rigid, protective barrier
- 34. 21 Vocabulary Word Genetic material. Encodes the genetic
- 35. 22 Vocabulary Word (2 words) The cell
- 36. 23 Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis
- 37. Example: (Bacteria)
- 38. Unique parts of the plant cell Cell
- 39. 26 having or consisting of a single cell.
- 40. 27 A round body located inside the
- 41. Answers Cytoplasm Nucleus Active Transport
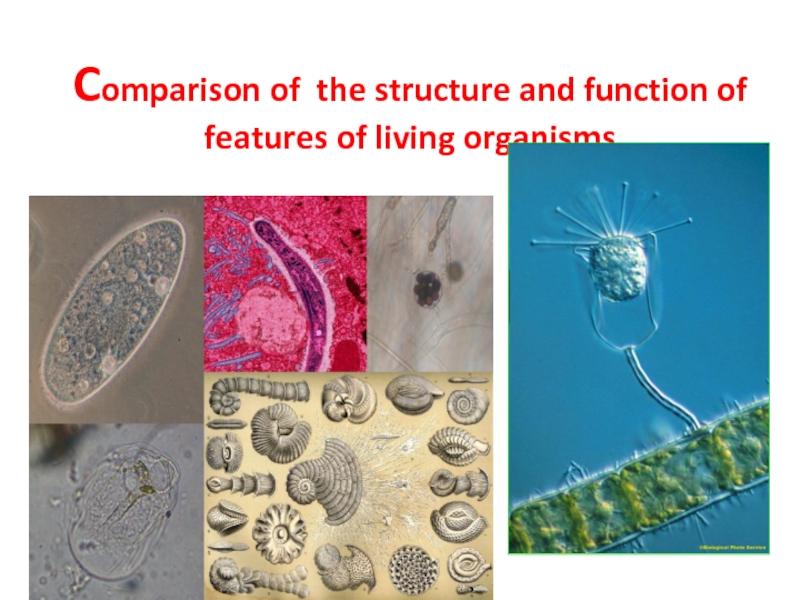
- 44. Comparison of the structure and function of features of living organisms
- 45. Lesson objective/ Learning outcomes 1 - Describe
- 46. KEY CONCEPTS Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms, most of which are microscopic
- 47. Protista Not a really valid “Kingdom”
- 48. What Are Protists? “Dumping ground” kingdom Eukaryotic
- 49. Investigation of four different unicells. Prepare a
- 50. Presentation criteria may include: Clear
- 51. Fill the table
Слайд 1Topic: Cells & Organelles
Learning Objectives
Explain the features of the structure
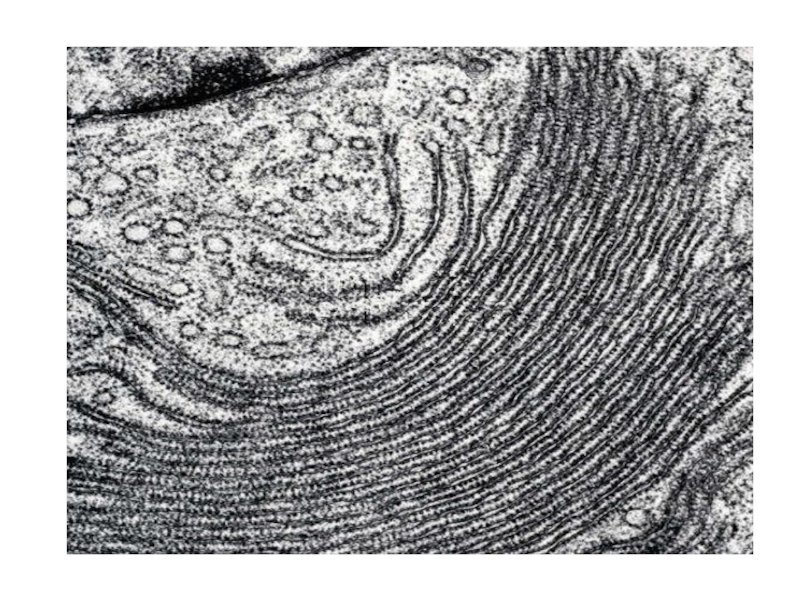
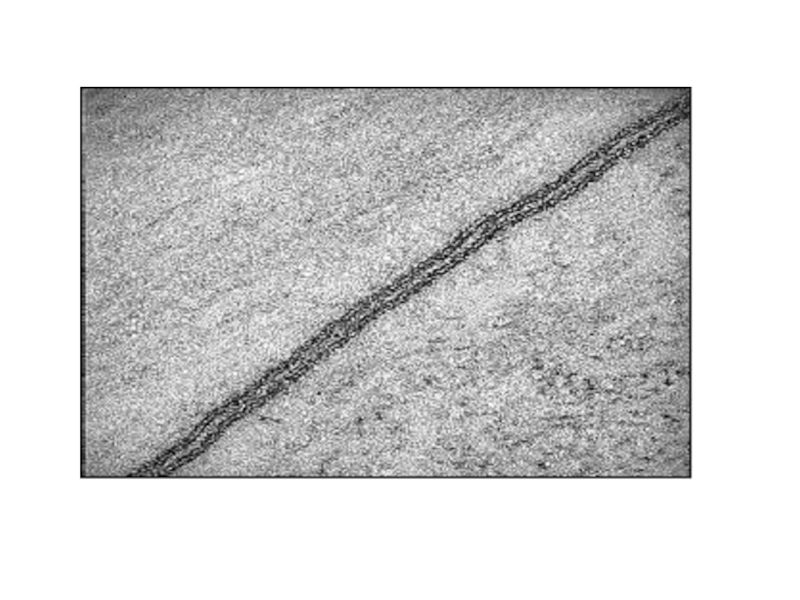
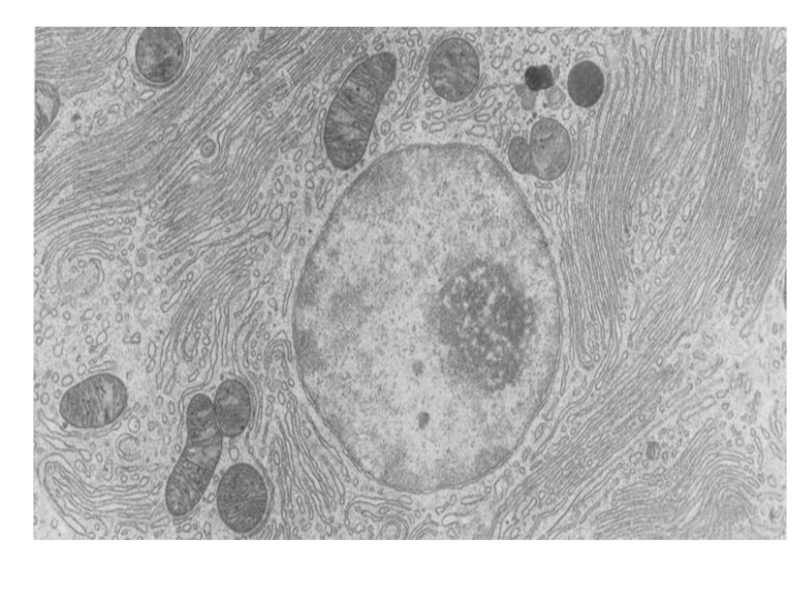
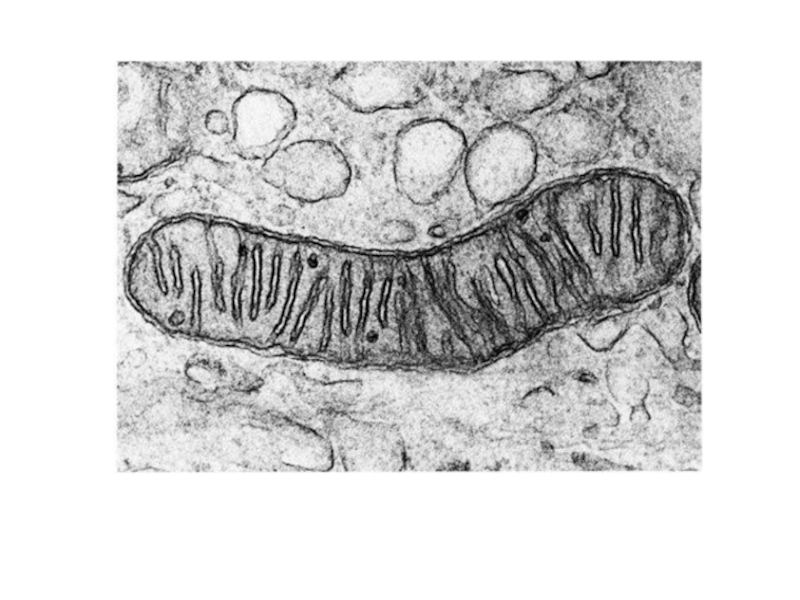
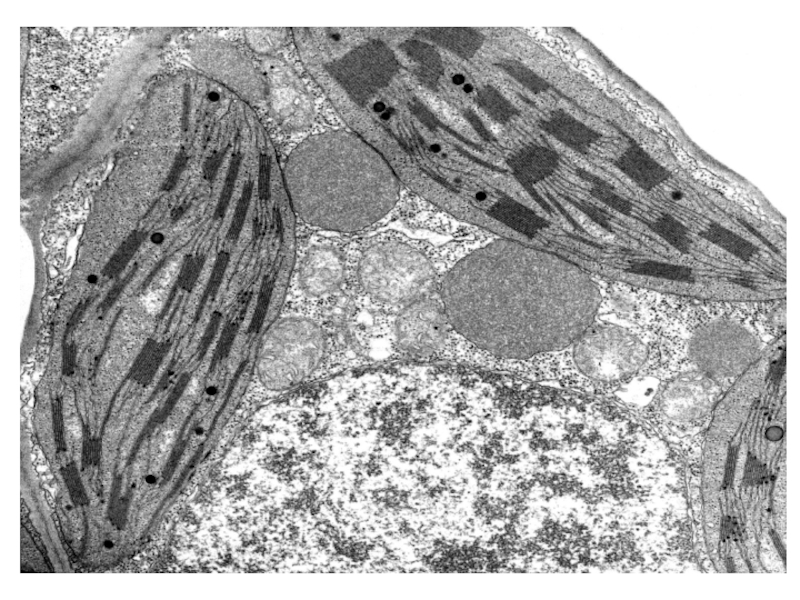
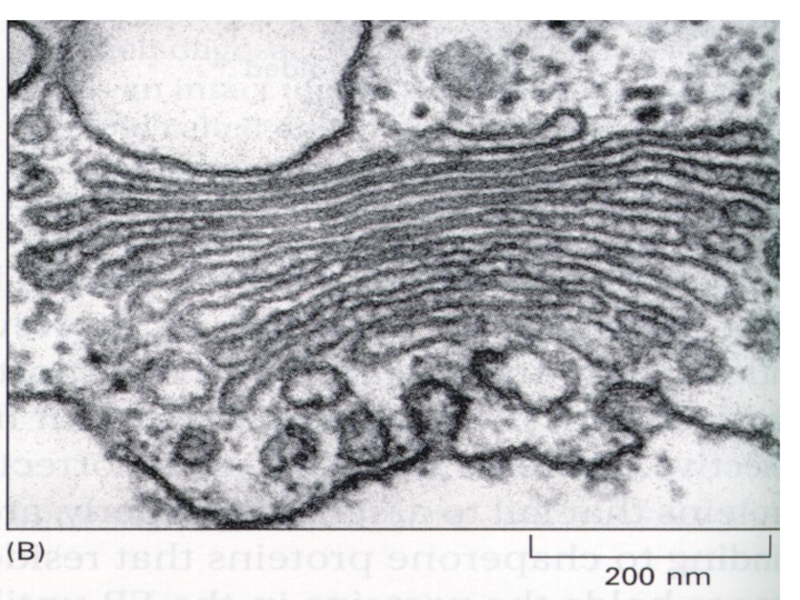
Слайд 4Discussion in groups of three
Look at each of the following electron
Answer these questions to achieve success criteria
What organelle is it?
Where is mostly found in the cell?
List as many functions as possible.
Relate its function to its structure
Any unique or interesting fact.
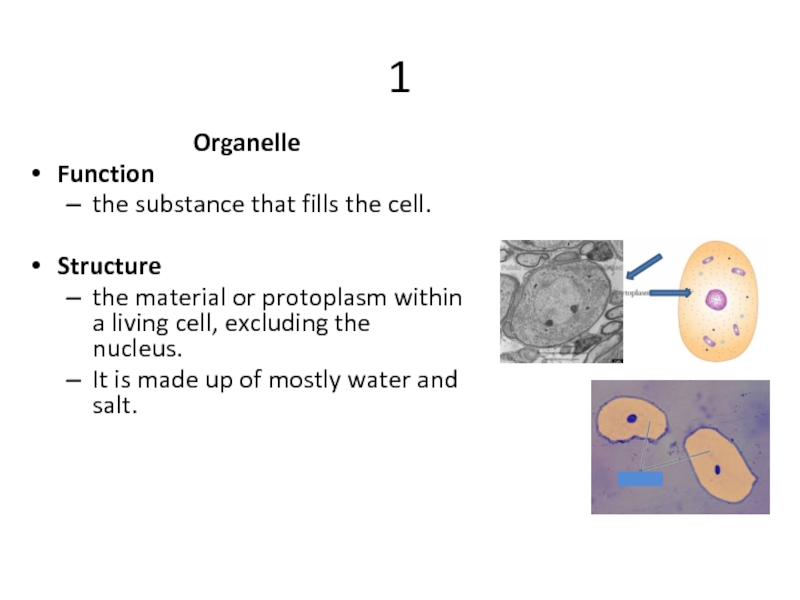
Слайд 141
Organelle
Function
the substance that fills the cell.
Structure
the material or protoplasm within a
It is made up of mostly water and salt.
Слайд 152
Organelle
Function
Control center of the cell
Contains DNA
Structure
Surrounded by a double membrane
Usually the
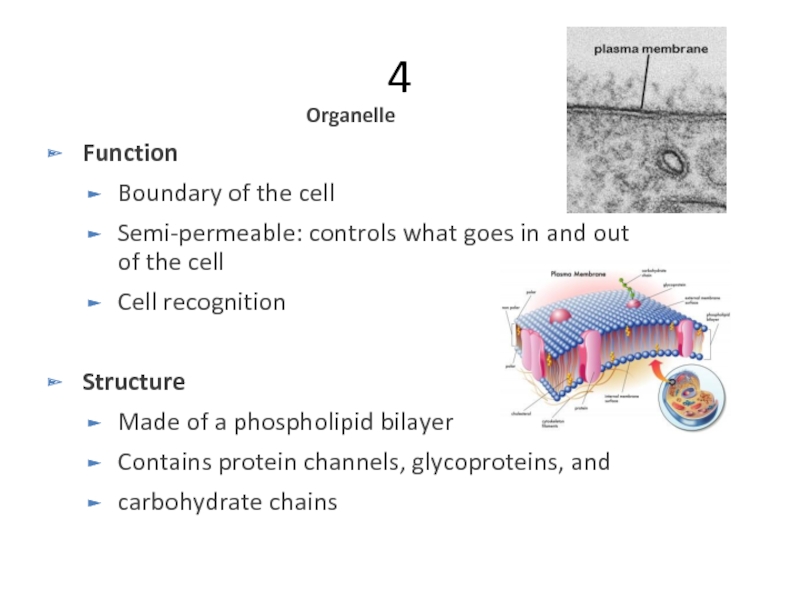
Слайд 174
Organelle
Function
Boundary of the cell
Semi-permeable: controls what goes in and out of
Cell recognition
Structure
Made of a phospholipid bilayer
Contains protein channels, glycoproteins, and
carbohydrate chains
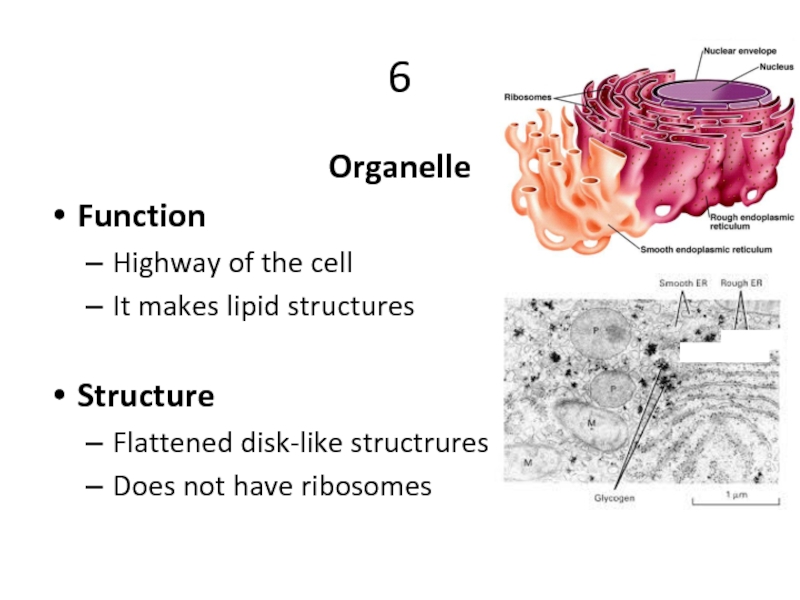
Слайд 196
Organelle
Function
Highway of the cell
It makes lipid structures
Structure
Flattened disk-like structrures
Does not have
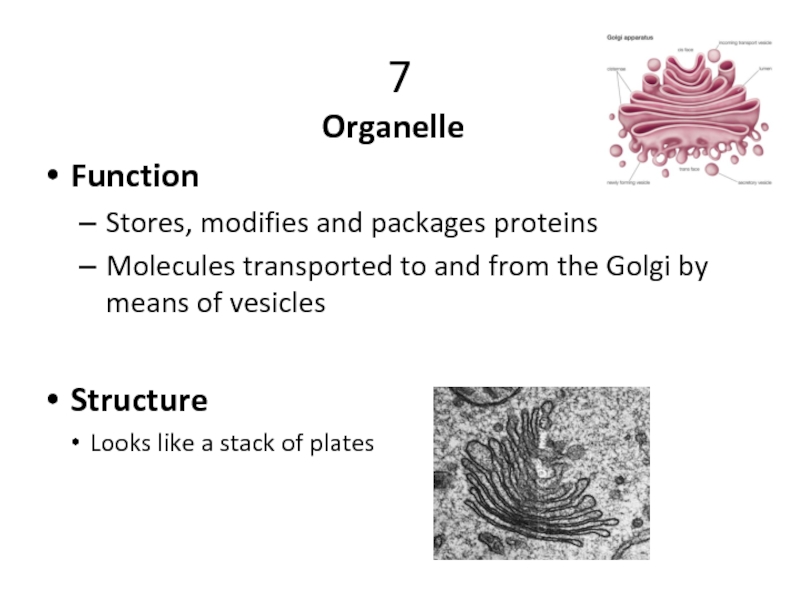
Слайд 207
Organelle
Function
Stores, modifies and packages proteins
Molecules transported to and from the Golgi
Structure
Looks like a stack of plates
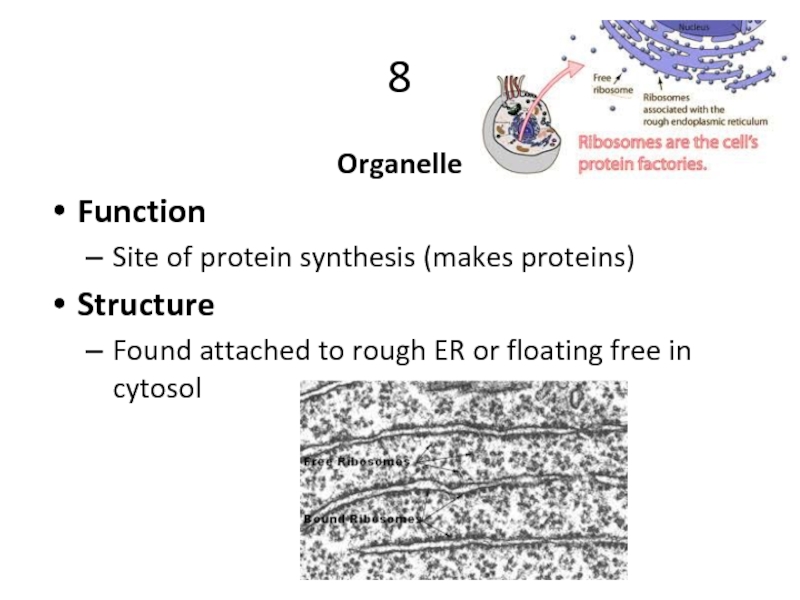
Слайд 218
Organelle
Function
Site of protein synthesis (makes proteins)
Structure
Found attached to rough ER or
Слайд 229
Vocabulary Word
Only allows only some materials through
Can cross membrane freely
Small nonpolar
Cannot cross membrane freely
Large Polar molecules, such as sugars, do not cross the membrane easily
Слайд 2310
Organelle
Function
Site of food (glucose) production
Photosynthesis
Structure
Found only in plant cells
Contains the green
Bound by a double membrane
Слайд 2411
Organelle
Function
Highway of the cell
it makes proteins structures
Structure
Connected to nuclear membrane
Studded with
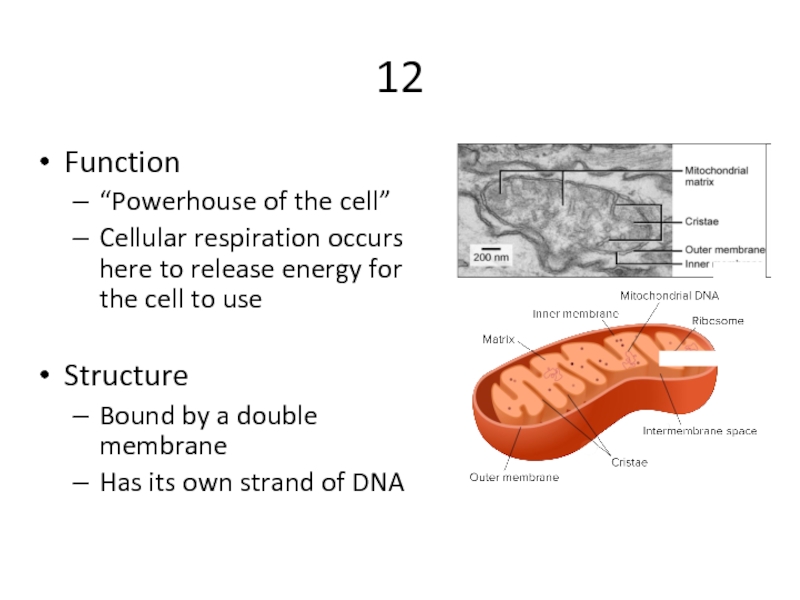
Слайд 2512
Function
“Powerhouse of the cell”
Cellular respiration occurs here to release energy for
Structure
Bound by a double membrane
Has its own strand of DNA
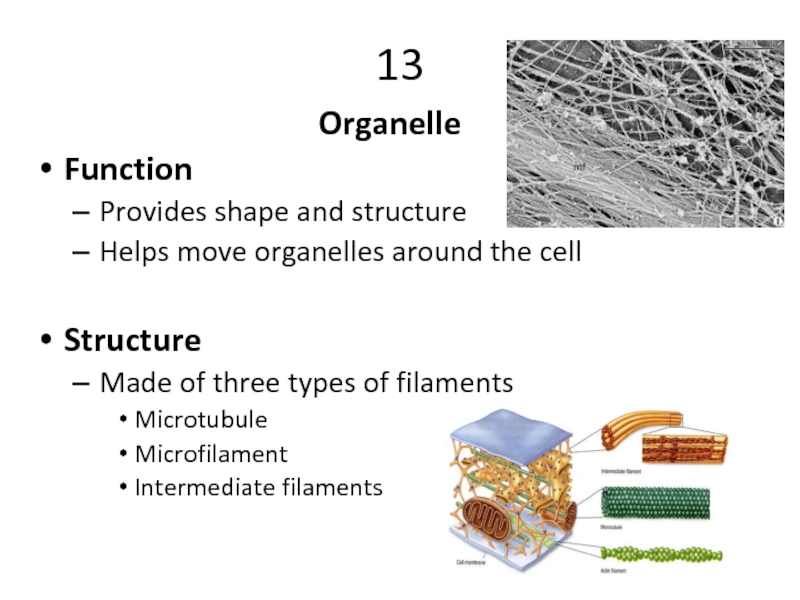
Слайд 2613
Organelle
Function
Provides shape and structure
Helps move organelles around the cell
Structure
Made of three
Microtubule
Microfilament
Intermediate filaments
Слайд 2714
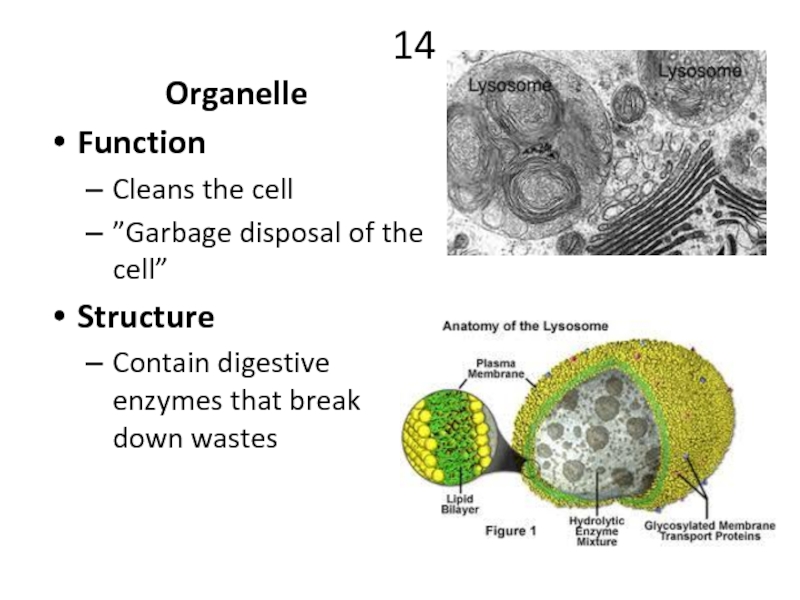
Organelle
Function
Cleans the cell
”Garbage disposal of the cell”
Structure
Contain digestive enzymes that break
Слайд 2815
Organelle
Function
Aids in cell division
Structure
Usually found only in animal cells
Made of microtubules
Слайд 2916
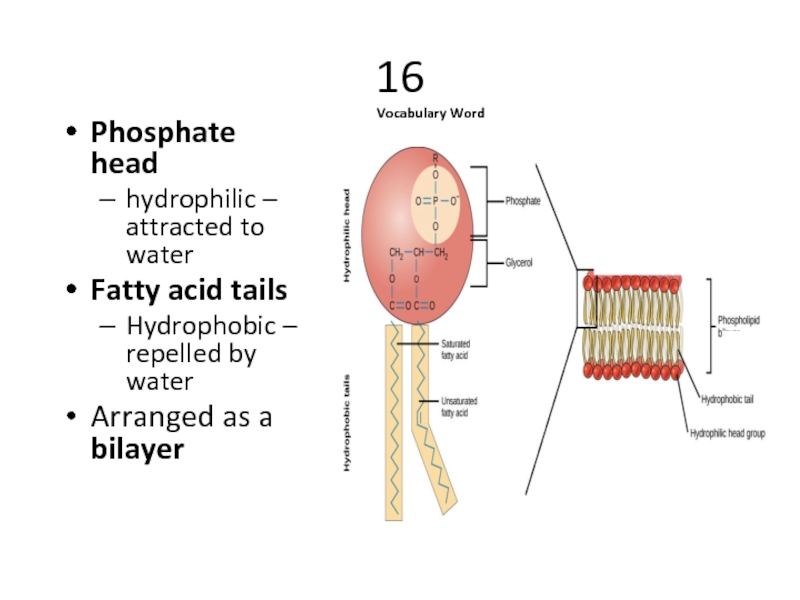
Phosphate head
hydrophilic – attracted to water
Fatty acid tails
Hydrophobic – repelled
Arranged as a bilayer
Vocabulary Word
Слайд 30Vocabulary Word
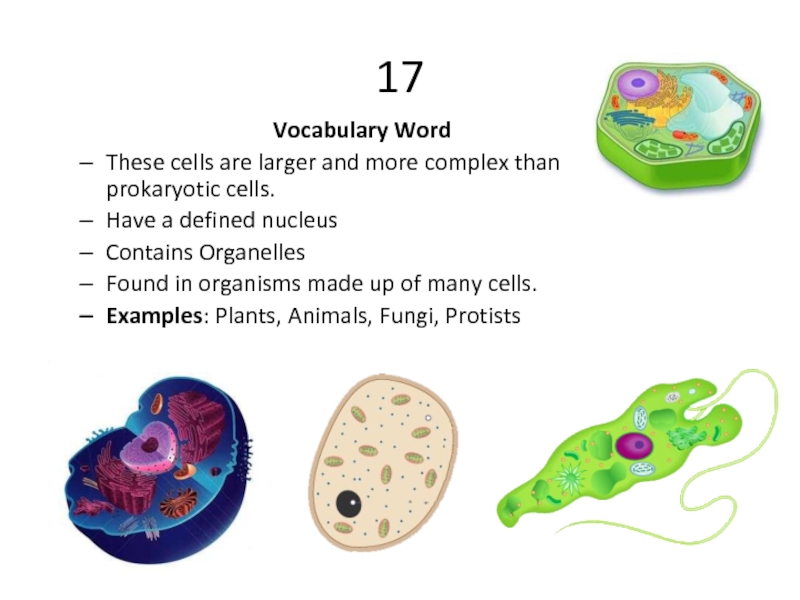
These cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
Have a defined nucleus
Contains Organelles
Found in organisms made up of many cells.
Examples: Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists
17
Слайд 3118
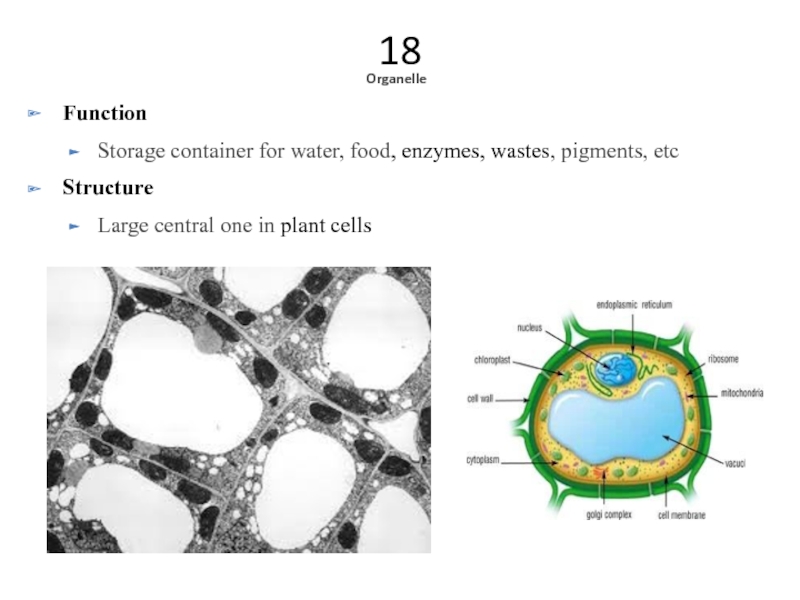
Organelle
Function
Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc
Structure
Large central one
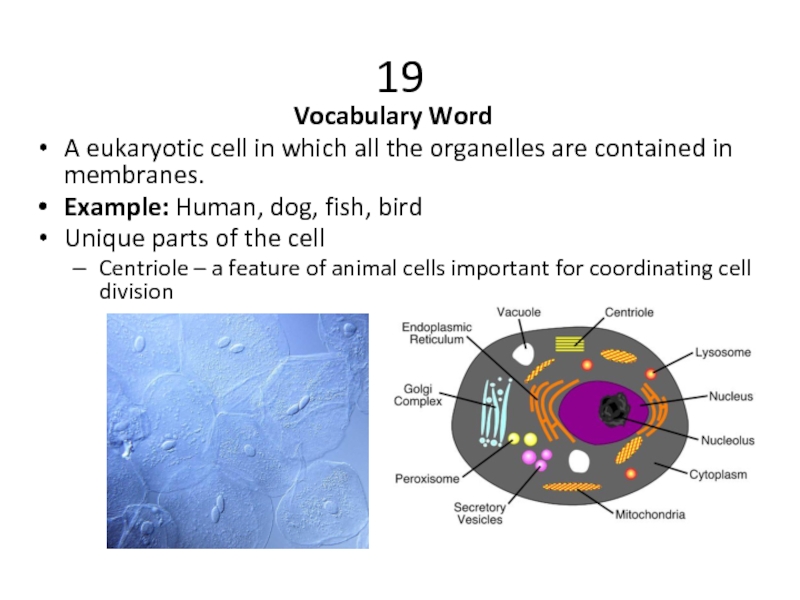
Слайд 32Vocabulary Word
A eukaryotic cell in which all the organelles are contained
Example: Human, dog, fish, bird
Unique parts of the cell
Centriole – a feature of animal cells important for coordinating cell division
19
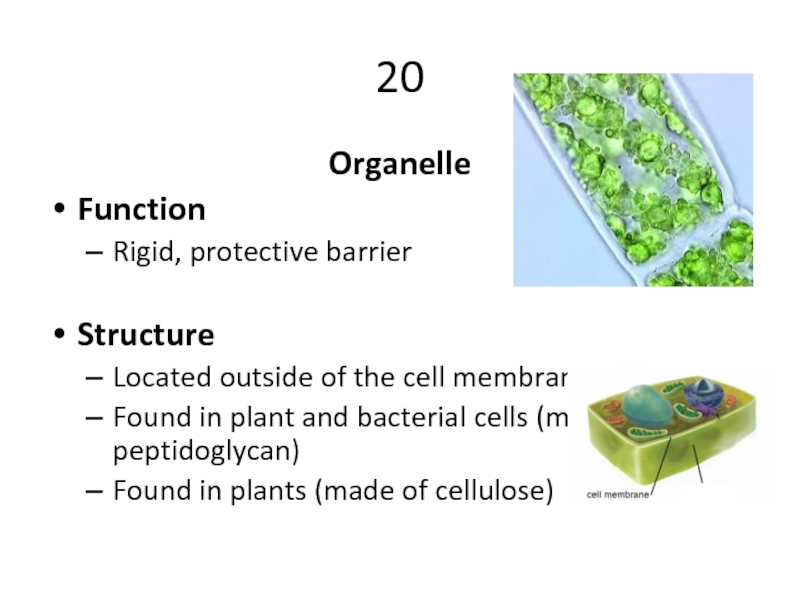
Слайд 3320
Organelle
Function
Rigid, protective barrier
Structure
Located outside of the cell membrane
Found in plant and
Found in plants (made of cellulose)
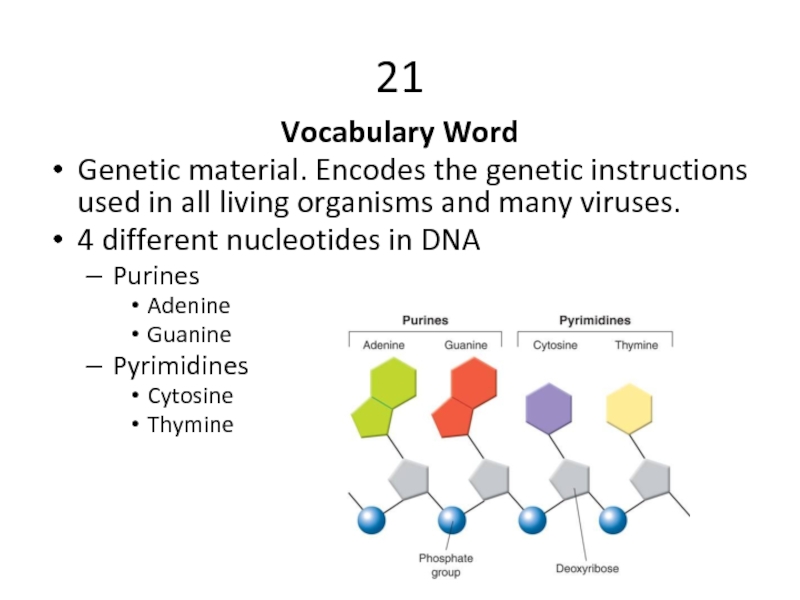
Слайд 3421
Vocabulary Word
Genetic material. Encodes the genetic instructions used in all living organisms and
4 different nucleotides in DNA
Purines
Adenine
Guanine
Pyrimidines
Cytosine
Thymine
Слайд 3522
Vocabulary Word
(2 words)
The cell membrane is described as this as this
1st
2nd Word – a pattern that produces by the scattered protein molecules when the membrane is viewed from above
Слайд 37Example: (Bacteria)
24
These cells are simple in structure
No structured nucleus
Exist as single-celled
Bacteria is both helpful and harmful to us and the environment.
Structure:
Capsule
Cell wall
Chromosomes
Cytoplasm
Flagellum (bacterial cells only)
Inner membrane
Outer membrane
Pili (bacterial cells only)
Ribosomes
Слайд 38Unique parts of the plant cell
Cell wall – a feature that
Chloroplast – a feature that allows cells to do photosynthesis and make their own glucose from sunlight, water and carbon dioxide
25
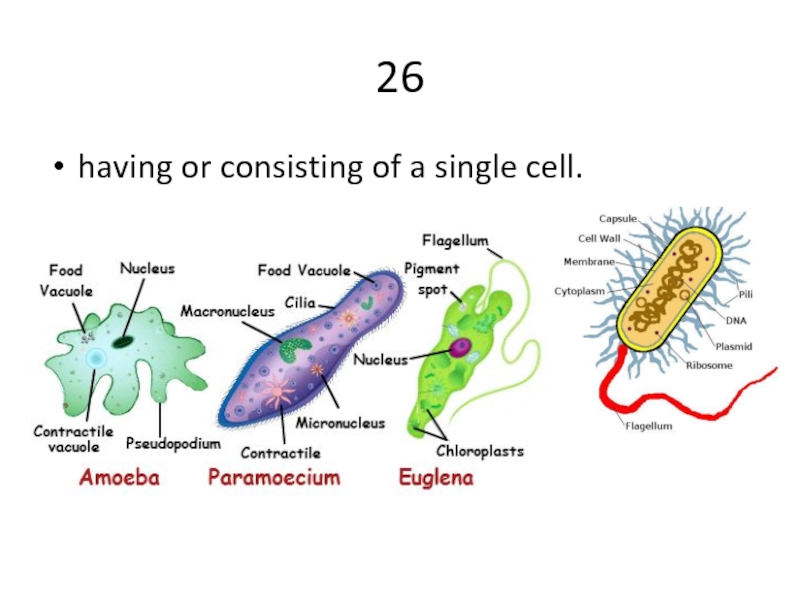
Слайд 4027
A round body located inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
Слайд 41Answers
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Active Transport
Cell Membrane
Multicellular
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi
Ribosome
Selective Permeability
Chloroplast
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Mitochondria
Cytoskeleton
Lysosome
Centrioles
Phospholipids
Eukaryote
Vacuole
Animal Cell
Cell Wall
DNA
Fluid Mosaic Model
Passive Transport
Prokaryote
Plant Cell
Unicellular
Nucleolus
Слайд 45Lesson objective/ Learning outcomes
1 - Describe the common behavior of protista
2 –From the picture SEM find the organisms
and divide them into the kingdoms
3- Name the protista from the picture and
explain why is a protista?
4 – Find commonalities and differences
5 – Create ppt on type of protista
Слайд 46KEY CONCEPTS
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms, most of
Слайд 47Protista
Not a really valid “Kingdom”
Few real evolutionary relationships
Contains
Algae: “plant-like” protists
Protozoa:
Slime & Water molds: fungal-like protists
Слайд 48What Are Protists?
“Dumping ground” kingdom
Eukaryotic
Heterotrophic and/or autotrophic
Single or multicellular
Ancestors to animals,
Слайд 49Investigation of four different unicells. Prepare a PowerPoint Presentation for the
1 - One free living protist, which does not participate in photosynthesis (for example, ameba or infusorium- paramecium)
2 - One free living protist, which participates in photosynthesis (for example, spirogyra or evglena)
3 - One parasitizing protist (for example, malarian parasite, plasmode or intestinal parasite, Lamblia)
4 - One protist, which forms colony or large mass (for example, Volvox or any other sea weeds)
Слайд 50Presentation criteria may include:
Clear diagrams
A video clip of moving organism,
Details of inner structure
List of inner structure functions
The role of organism in food web, for example, type of feeding
Special adaptation, allowing to survive in a definite habitat