- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
A Tour of the Cell презентация
Содержание
- 1. A Tour of the Cell
- 2. Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
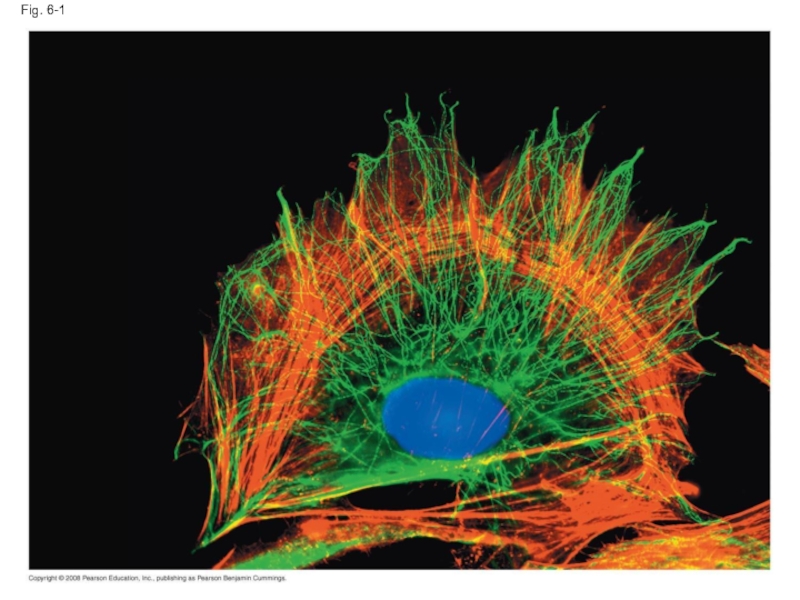
- 3. Fig. 6-1
- 4. Concept 6.1: To study cells, biologists use
- 5. Microscopy Scientists use microscopes to visualize cells
- 6. The quality of an image depends on
- 7. Fig. 6-2 10 m 1 m 0.1
- 8. LMs can magnify effectively to about 1,000
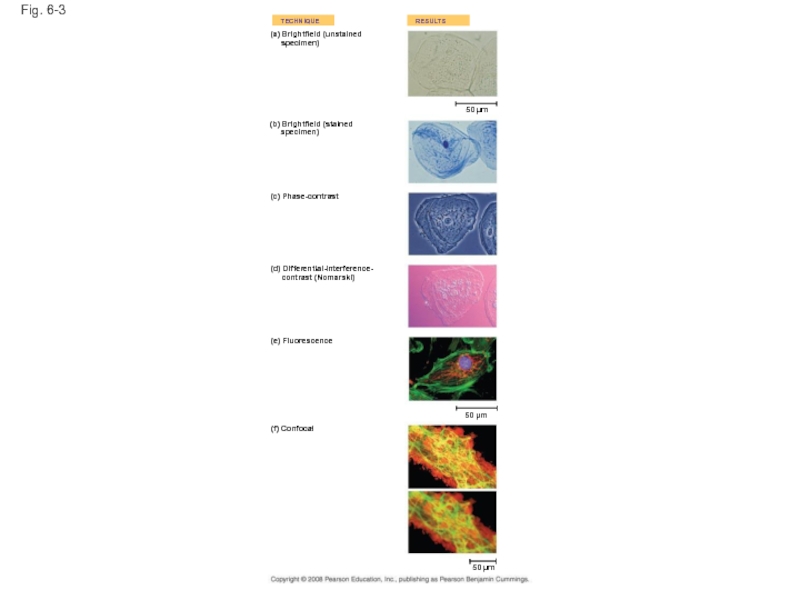
- 9. Fig. 6-3 TECHNIQUE RESULTS (a)
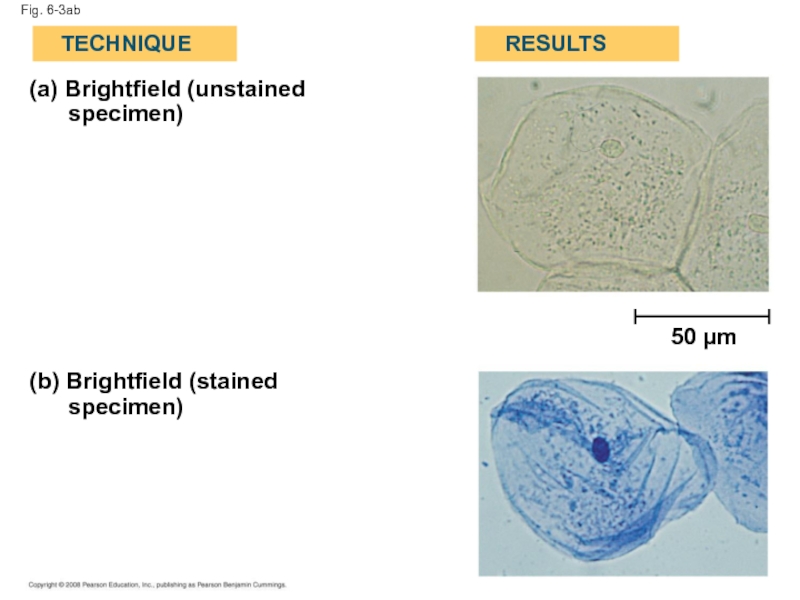
- 10. Fig. 6-3ab (a) Brightfield (unstained
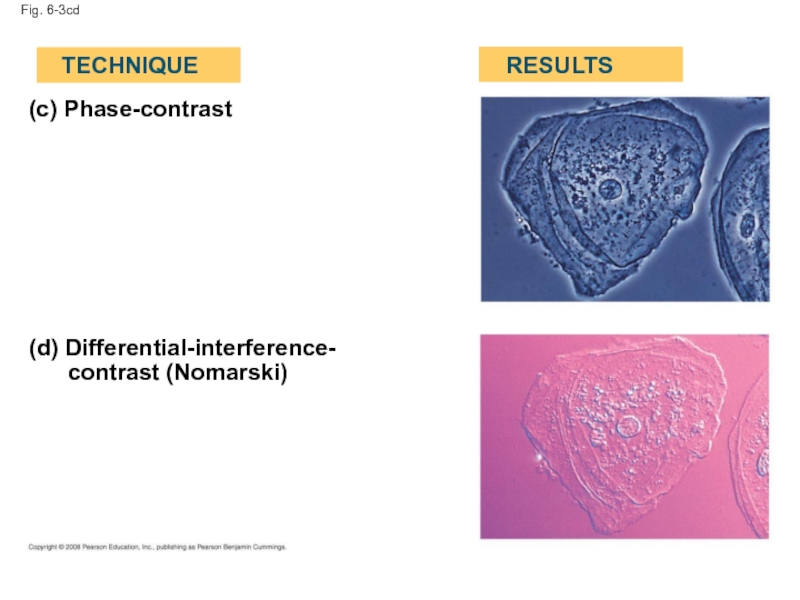
- 11. Fig. 6-3cd (c) Phase-contrast (d) Differential-interference- contrast (Nomarski) TECHNIQUE RESULTS
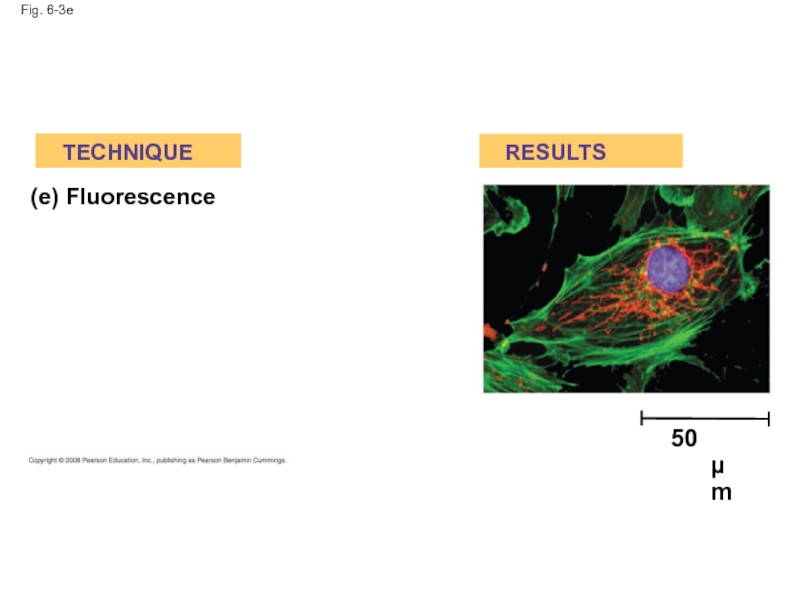
- 12. Fig. 6-3e (e) Fluorescence TECHNIQUE RESULTS 50 µm
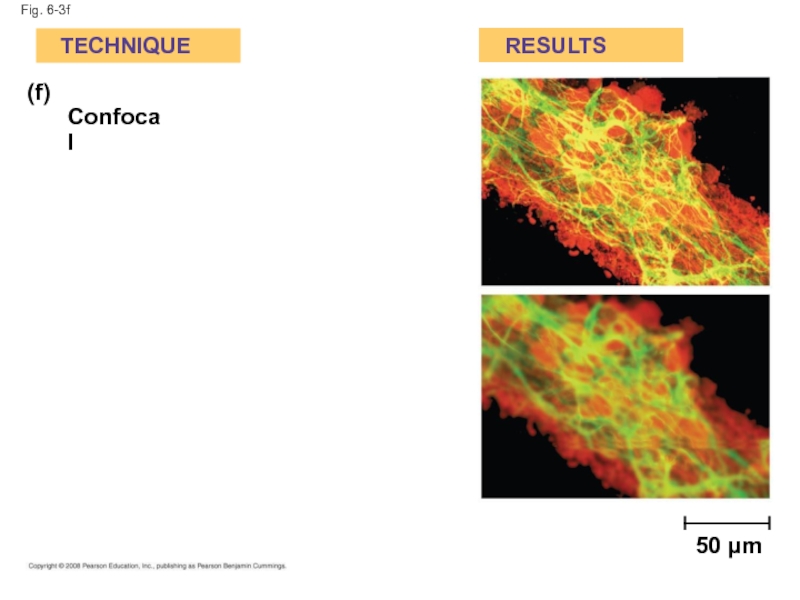
- 13. Fig. 6-3f (f) Confocal TECHNIQUE RESULTS 50 µm
- 14. Two basic types of electron microscopes (EMs)
- 15. Fig. 6-4 (a) Scanning electron
- 16. Cell Fractionation Cell fractionation takes cells apart
- 17. Fig. 6-5 Homogenization TECHNIQUE Homogenate Tissue
- 18. Fig. 6-5a Homogenization Homogenate Differential centrifugation Tissue cells TECHNIQUE
- 19. Fig. 6-5b 1,000 g (1,000 times
- 20. Concept 6.2: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes
- 21. Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Basic features
- 22. Prokaryotic cells are characterized by having No
- 23. Fig. 6-6 Fimbriae Nucleoid Ribosomes Plasma membrane
- 24. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by having DNA
- 25. The plasma membrane is a selective barrier
- 26. Fig. 6-7 TEM of a plasma membrane
- 27. The logistics of carrying out cellular metabolism
- 28. Fig. 6-8 Surface area increases while total
- 29. A Panoramic View of the Eukaryotic Cell
- 30. Fig. 6-9a ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Smooth ER
- 31. Fig. 6-9b NUCLEUS Nuclear envelope Nucleolus
- 32. Concept 6.3: The eukaryotic cell’s genetic instructions
- 33. The Nucleus: Information Central The nucleus contains
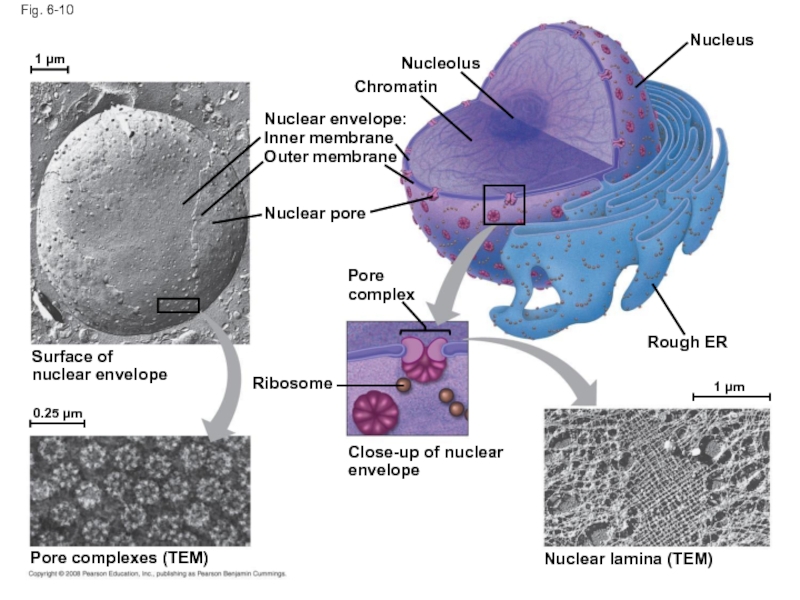
- 34. Fig. 6-10 Nucleolus Nucleus Rough ER Nuclear
- 35. Pores regulate the entry and exit of
- 36. In the nucleus, DNA and proteins form
- 37. Ribosomes: Protein Factories Ribosomes are particles made
- 38. Fig. 6-11 Cytosol Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Free
- 39. Concept 6.4: The endomembrane system regulates protein
- 40. The Endoplasmic Reticulum: Biosynthetic Factory The endoplasmic
- 41. Fig. 6-12 Smooth ER Rough ER Nuclear
- 42. Functions of Smooth ER The smooth ER
- 43. Functions of Rough ER The rough ER
- 44. The Golgi apparatus consists of flattened membranous
- 45. Fig. 6-13 cis face (“receiving” side of
- 46. Lysosomes: Digestive Compartments A lysosome is a
- 47. Some types of cell can engulf another
- 48. Fig. 6-14 Nucleus 1 µm Lysosome Digestive
- 49. Fig. 6-14a Nucleus 1 µm Lysosome Lysosome
- 50. Fig. 6-14b Vesicle containing two damaged organelles
- 51. Vacuoles: Diverse Maintenance Compartments A plant cell
- 52. Food vacuoles are formed by phagocytosis Contractile
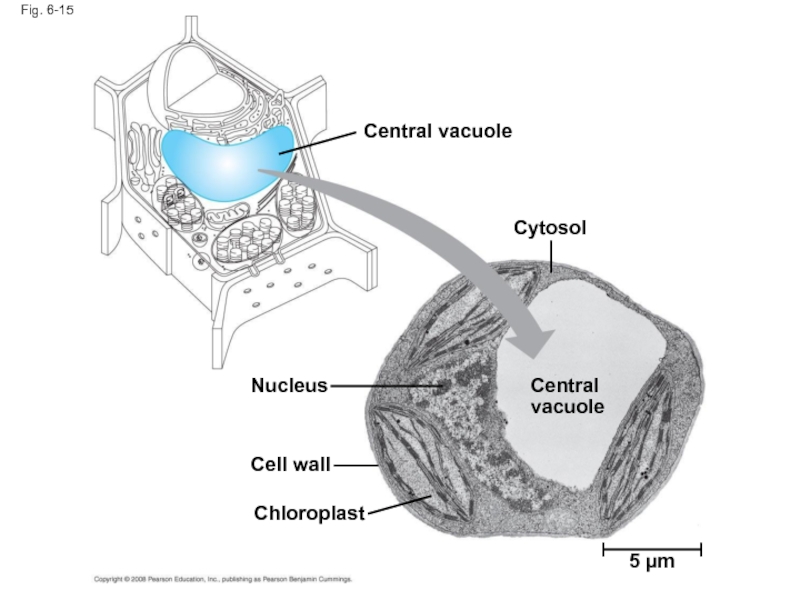
- 53. Fig. 6-15 Central vacuole Cytosol Central vacuole Nucleus Cell wall Chloroplast 5 µm
- 54. The Endomembrane System: A Review The endomembrane
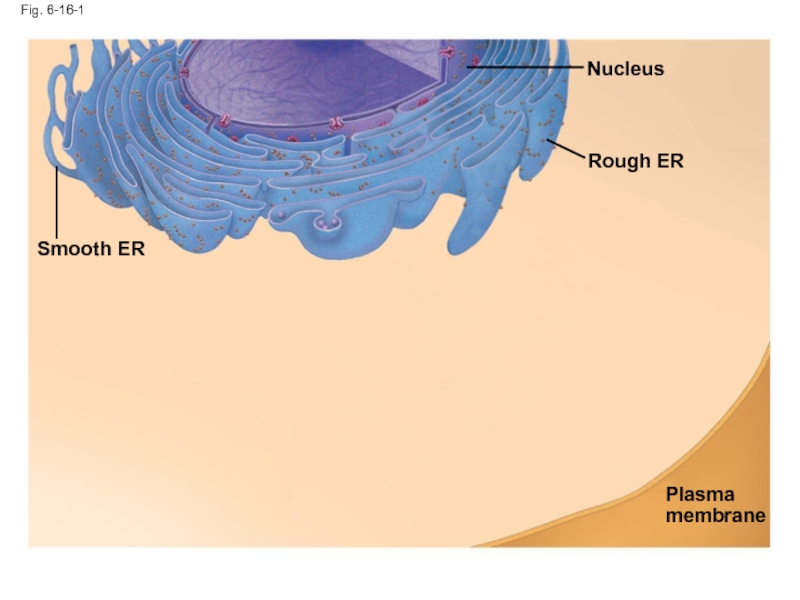
- 55. Fig. 6-16-1 Smooth ER Nucleus Rough ER Plasma membrane
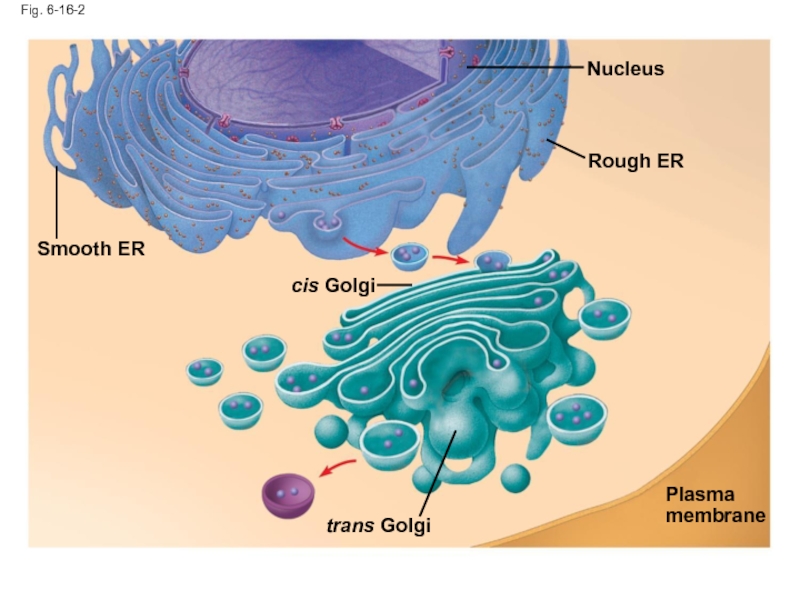
- 56. Fig. 6-16-2 Smooth ER Nucleus Rough ER Plasma membrane cis Golgi trans Golgi
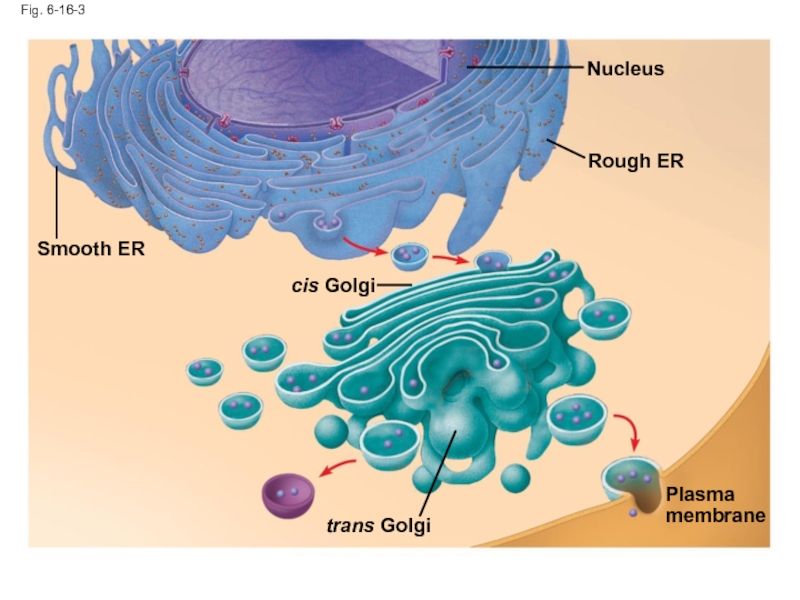
- 57. Fig. 6-16-3 Smooth ER Nucleus Rough ER Plasma membrane cis Golgi trans Golgi
- 58. Concept 6.5: Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy
- 59. Mitochondria and chloroplasts Are not part
- 60. Mitochondria: Chemical Energy Conversion Mitochondria are in
- 61. Fig. 6-17 Free ribosomes in the mitochondrial
- 62. Chloroplasts: Capture of Light Energy The chloroplast
- 63. Chloroplast structure includes: Thylakoids, membranous sacs, stacked
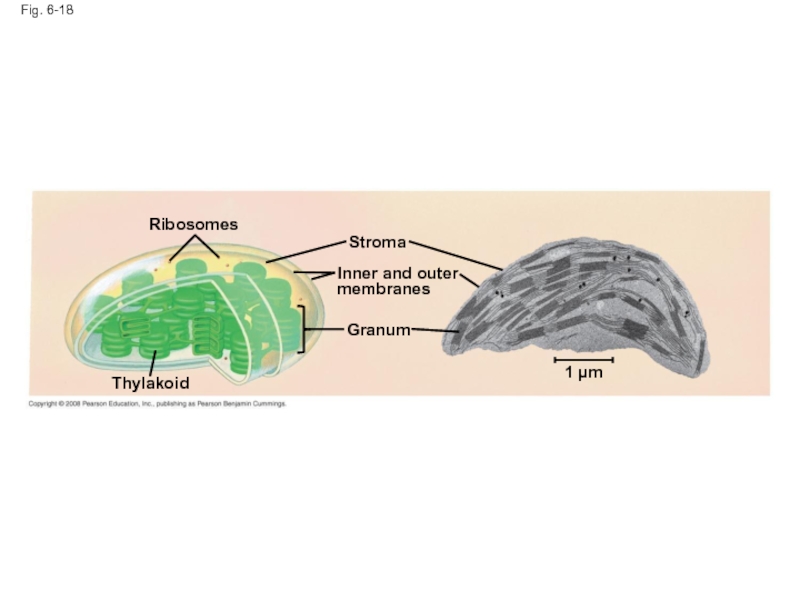
- 64. Fig. 6-18 Ribosomes Thylakoid Stroma Granum Inner and outer membranes 1 µm
- 65. Peroxisomes: Oxidation Peroxisomes are specialized metabolic compartments
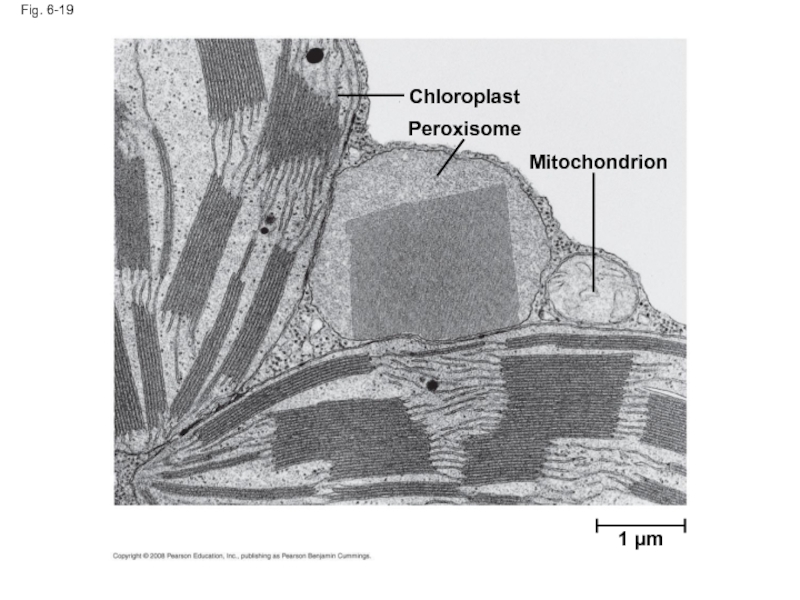
- 66. Fig. 6-19 1 µm Chloroplast Peroxisome Mitochondrion
- 67. Concept 6.6: The cytoskeleton is a network
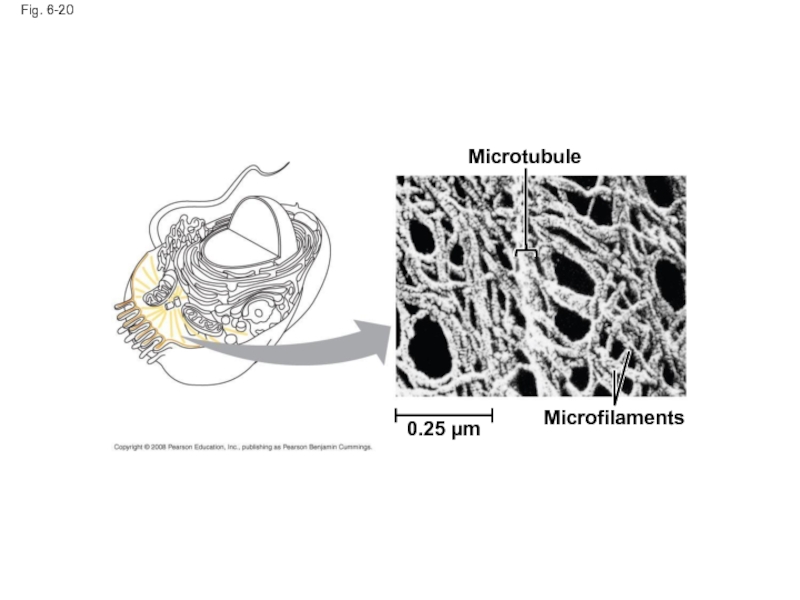
- 68. Fig. 6-20 Microtubule Microfilaments 0.25 µm
- 69. Roles of the Cytoskeleton: Support, Motility, and
- 70. Fig. 6-21 Vesicle ATP Receptor for motor
- 71. Components of the Cytoskeleton Three main types
- 72. Table 6-1 10 µm 10 µm 10
- 73. Table 6-1a 10 µm Column of tubulin
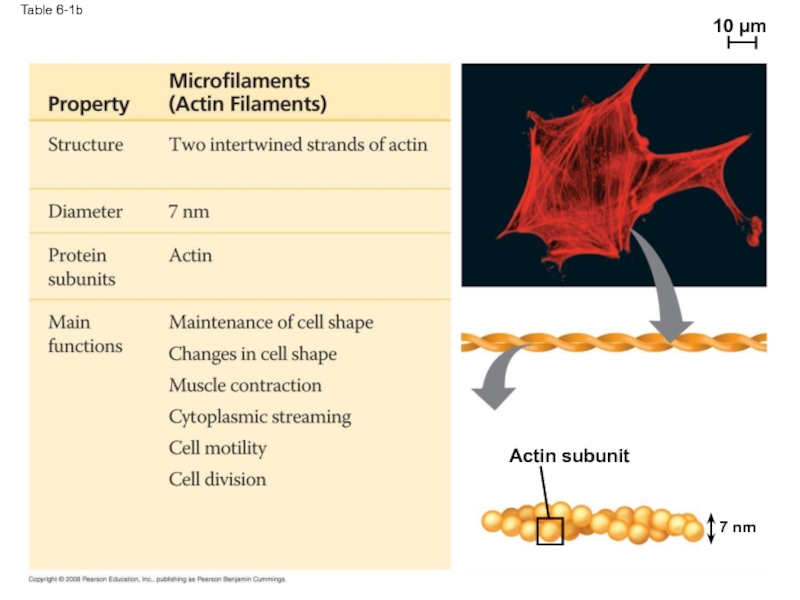
- 74. Table 6-1b Actin subunit 10 µm 7 nm
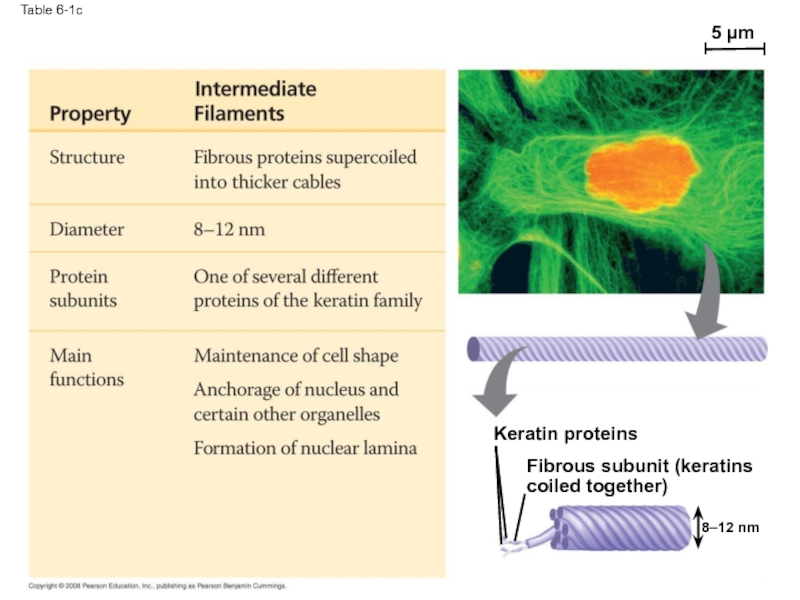
- 75. Table 6-1c 5 µm Keratin proteins Fibrous subunit (keratins coiled together) 8–12 nm
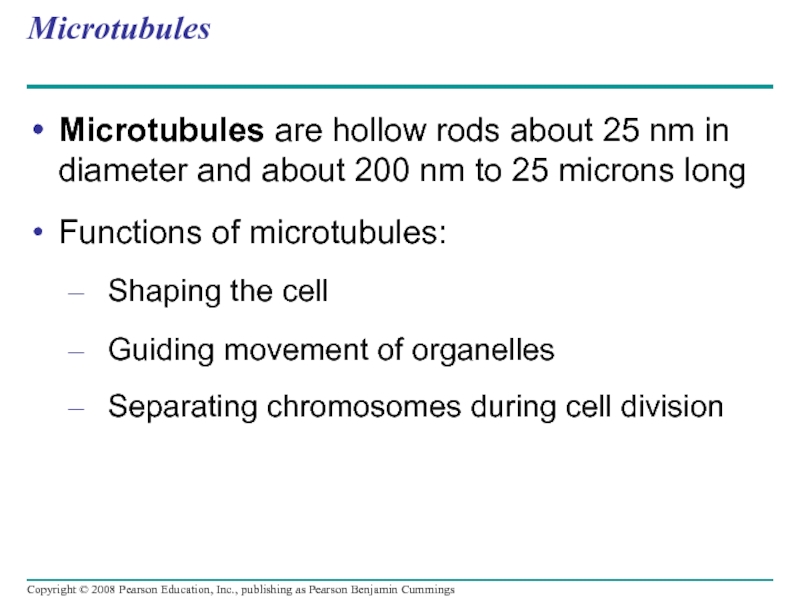
- 76. Microtubules Microtubules are hollow rods about 25
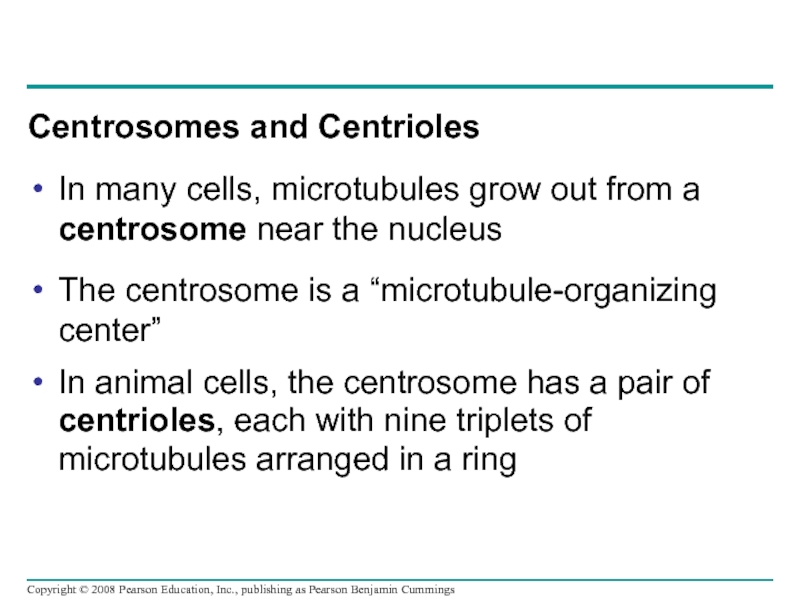
- 77. Centrosomes and Centrioles In many
- 78. Fig. 6-22 Centrosome Microtubule Centrioles 0.25 µm
- 79. Cilia and Flagella Microtubules control
- 80. Fig. 6-23 5 µm Direction of swimming
- 81. Cilia and flagella share a common ultrastructure:
- 82. Fig. 6-24 0.1 µm Triplet
- 83. How dynein “walking” moves flagella and cilia:
- 84. Fig. 6-25 Microtubule doublets
- 85. Fig. 6-25a Microtubule doublets Dynein protein (a) Effect of unrestrained dynein movement ATP
- 86. Fig. 6-25b Cross-linking proteins inside outer doublets
- 87. Microfilaments (Actin Filaments) Microfilaments are solid rods
- 88. Fig. 6-26 Microvillus Plasma membrane Microfilaments (actin filaments) Intermediate filaments 0.25 µm
- 89. Microfilaments that function in cellular motility contain
- 90. Fig. 6-27 Muscle cell Actin filament Myosin
- 91. Fig, 6-27a Muscle cell Actin filament Myosin
- 92. Fig. 6-27bc Cortex (outer cytoplasm): gel with
- 93. Localized contraction brought about by actin and
- 94. Cytoplasmic streaming is a circular flow of
- 95. Intermediate Filaments Intermediate filaments range in diameter
- 96. Concept 6.7: Extracellular components and connections between
- 97. Cell Walls of Plants The cell wall
- 98. Plant cell walls may have multiple layers:
- 99. Fig. 6-28 Secondary cell wall Primary cell
- 100. Fig. 6-29 10 µm Distribution of
- 101. The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) of Animal Cells
- 102. Fig. 6-30 EXTRACELLULAR FLUID Collagen Fibronectin Plasma
- 103. Fig. 6-30a Collagen Fibronectin Plasma membrane Proteoglycan complex Integrins CYTOPLASM Micro-filaments EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
- 104. Fig. 6-30b Polysaccharide molecule Carbo-hydrates Core protein Proteoglycan molecule Proteoglycan complex
- 105. Functions of the ECM: Support Adhesion Movement
- 106. Intercellular Junctions Neighboring cells in tissues, organs,
- 107. Plasmodesmata in Plant Cells Plasmodesmata are channels
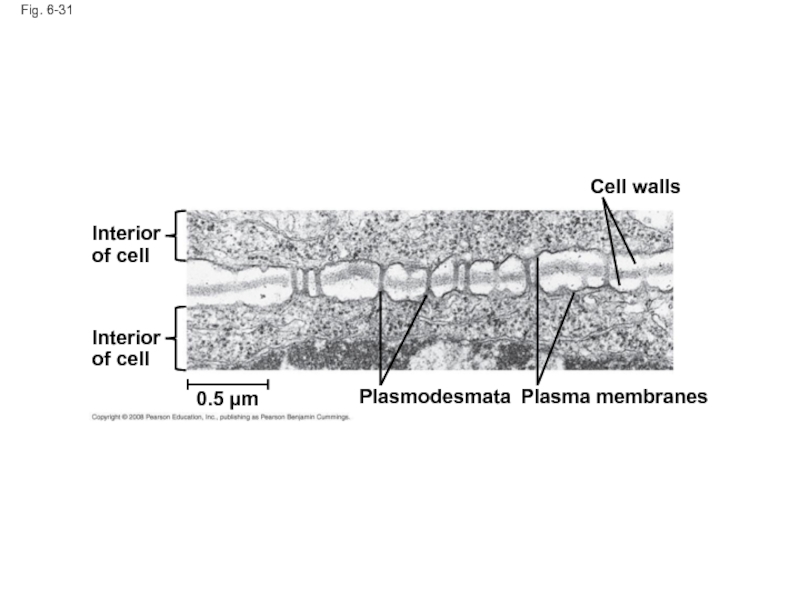
- 108. Fig. 6-31 Interior of cell Interior
- 109. Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, and Gap Junctions in
- 110. Fig. 6-32 Tight junction 0.5 µm 1
- 111. Fig. 6-32a Tight junctions prevent fluid from
- 112. Fig. 6-32b Tight junction 0.5 µm
- 113. Fig. 6-32c Desmosome 1 µm
- 114. Fig. 6-32d Gap junction 0.1 µm
- 115. The Cell: A Living Unit Greater Than
- 116. Fig. 6-33 5 µm
- 117. Fig. 6-UN1 Cell Component Structure
- 118. Fig. 6-UN1a Cell Component Structure
- 119. Fig. 6-UN1b Cell Component Structure
- 120. Fig. 6-UN1c Cell Component Concept 6.5
- 121. Fig. 6-UN2
- 122. Fig. 6-UN3
- 123. You should now be able to: Distinguish
- 124. Compare the structure and functions of microtubules,
Слайд 2Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life
All organisms are made of cells
The
Cell structure is correlated to cellular function
All cells are related by their descent from earlier cells
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 4Concept 6.1: To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools
Though usually too small to be seen by the unaided eye, cells can be complex
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 5Microscopy
Scientists use microscopes to visualize cells too small to see with
In a light microscope (LM), visible light passes through a specimen and then through glass lenses, which magnify the image
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 6The quality of an image depends on
Magnification, the ratio of an
Resolution, the measure of the clarity of the image, or the minimum distance of two distinguishable points
Contrast, visible differences in parts of the sample
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
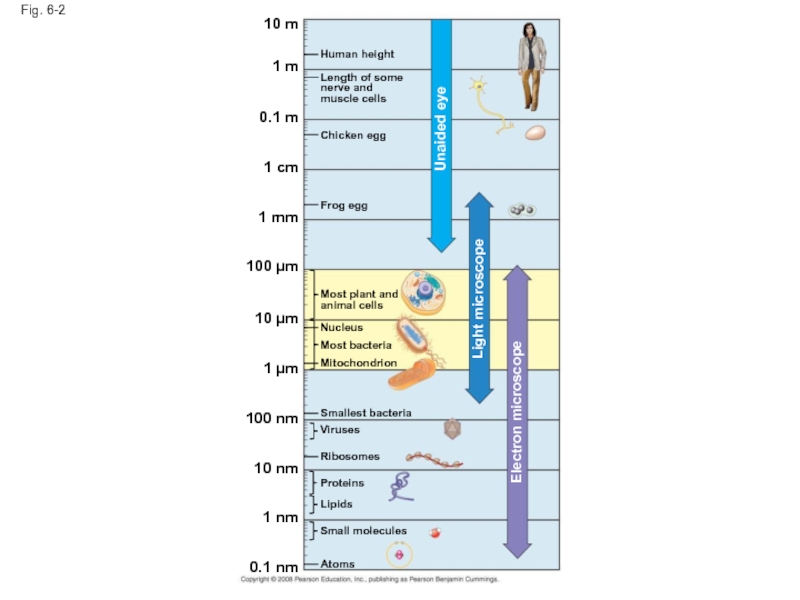
Слайд 7Fig. 6-2
10 m
1 m
0.1 m
1 cm
1 mm
100 µm
10 µm
1 µm
100 nm
10
1 nm
0.1 nm
Atoms
Small molecules
Lipids
Proteins
Ribosomes
Viruses
Smallest bacteria
Mitochondrion
Nucleus
Most bacteria
Most plant and animal cells
Frog egg
Chicken egg
Length of some nerve and muscle cells
Human height
Unaided eye
Light microscope
Electron microscope
Слайд 8LMs can magnify effectively to about 1,000 times the size of
Various techniques enhance contrast and enable cell components to be stained or labeled
Most subcellular structures, including organelles (membrane-enclosed compartments), are too small to be resolved by an LM
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 9
Fig. 6-3
TECHNIQUE
RESULTS
(a) Brightfield (unstained
specimen)
(b) Brightfield (stained
50 µm
(c) Phase-contrast
(d) Differential-interference-
contrast (Nomarski)
(e) Fluorescence
(f) Confocal
50 µm
50 µm
Слайд 10
Fig. 6-3ab
(a) Brightfield (unstained
specimen)
(b) Brightfield (stained
TECHNIQUE
RESULTS
50 µm
Слайд 11Fig. 6-3cd
(c) Phase-contrast
(d) Differential-interference-
contrast (Nomarski)
TECHNIQUE
RESULTS
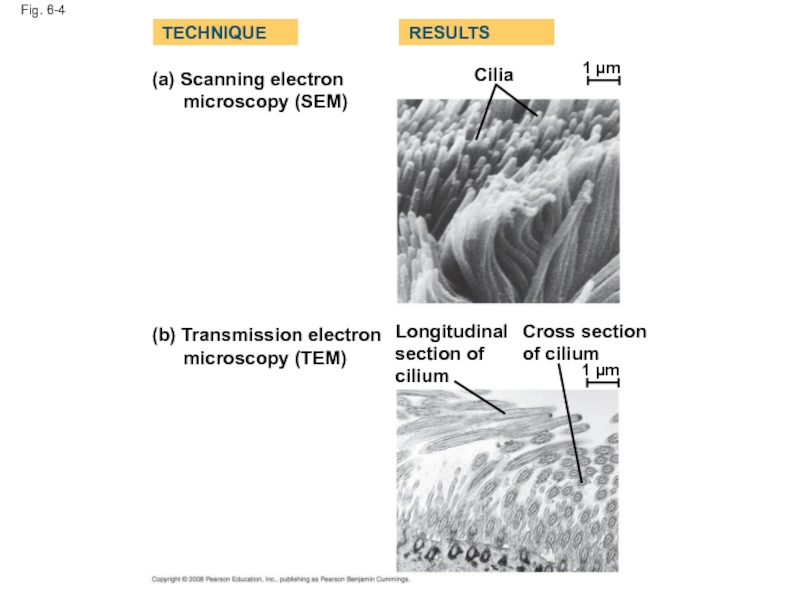
Слайд 14Two basic types of electron microscopes (EMs) are used to study
Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) focus a beam of electrons onto the surface of a specimen, providing images that look 3-D
Transmission electron microscopes (TEMs) focus a beam of electrons through a specimen
TEMs are used mainly to study the internal structure of cells
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 15Fig. 6-4
(a) Scanning electron
microscopy (SEM)
TECHNIQUE
RESULTS
(b) Transmission electron
Cilia
Longitudinal
section of
cilium
Cross section
of cilium
1 µm
1 µm
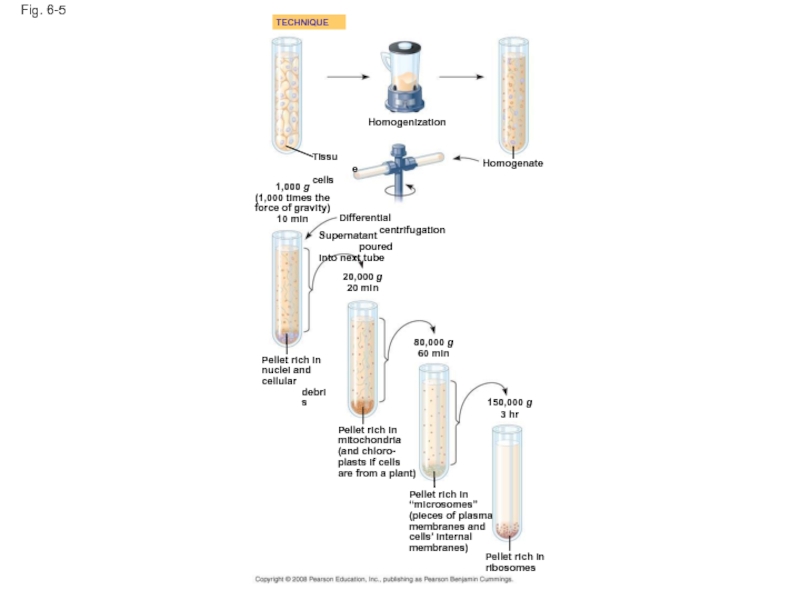
Слайд 16Cell Fractionation
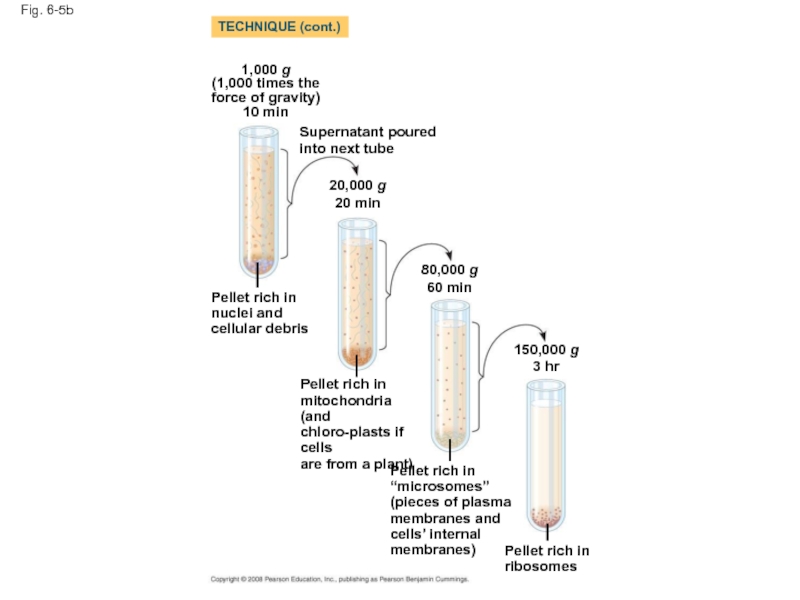
Cell fractionation takes cells apart and separates the major organelles
Ultracentrifuges fractionate cells into their component parts
Cell fractionation enables scientists to determine the functions of organelles
Biochemistry and cytology help correlate cell function with structure
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
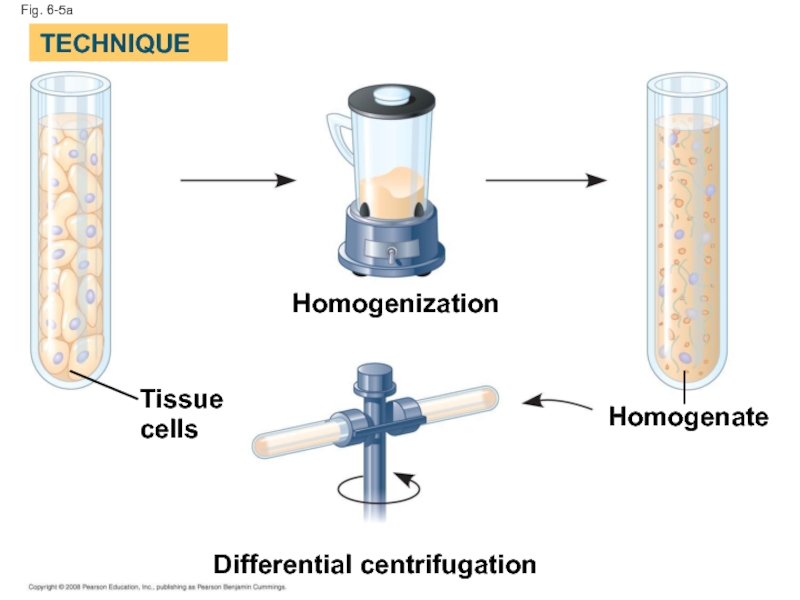
Слайд 17
Fig. 6-5
Homogenization
TECHNIQUE
Homogenate
Tissue
cells
1,000 g
(1,000 times the
force of gravity)
10 min
Differential centrifugation
Supernatant poured
into next
20,000 g
20 min
80,000 g
60 min
Pellet rich in
nuclei and
cellular debris
Pellet rich in
mitochondria
(and chloro-
plasts if cells
are from a plant)
Pellet rich in
“microsomes”
(pieces of plasma
membranes and
cells’ internal
membranes)
150,000 g
3 hr
Pellet rich in
ribosomes
Слайд 19
Fig. 6-5b
1,000 g
(1,000 times the force of gravity)
10 min
Supernatant poured into
20,000 g
20 min
80,000 g
60 min
150,000 g
3 hr
Pellet rich in nuclei and cellular debris
Pellet rich in mitochondria (and chloro-plasts if cells
are from a plant)
Pellet rich in “microsomes” (pieces of plasma
membranes and cells’ internal membranes)
Pellet rich in ribosomes
TECHNIQUE (cont.)
Слайд 20Concept 6.2: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions
The
Only organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea consist of prokaryotic cells
Protists, fungi, animals, and plants all consist of eukaryotic cells
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 21Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Basic features of all cells:
Plasma membrane
Semifluid
Chromosomes (carry genes)
Ribosomes (make proteins)
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 22Prokaryotic cells are characterized by having
No nucleus
DNA in an unbound region
No membrane-bound organelles
Cytoplasm bound by the plasma membrane
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
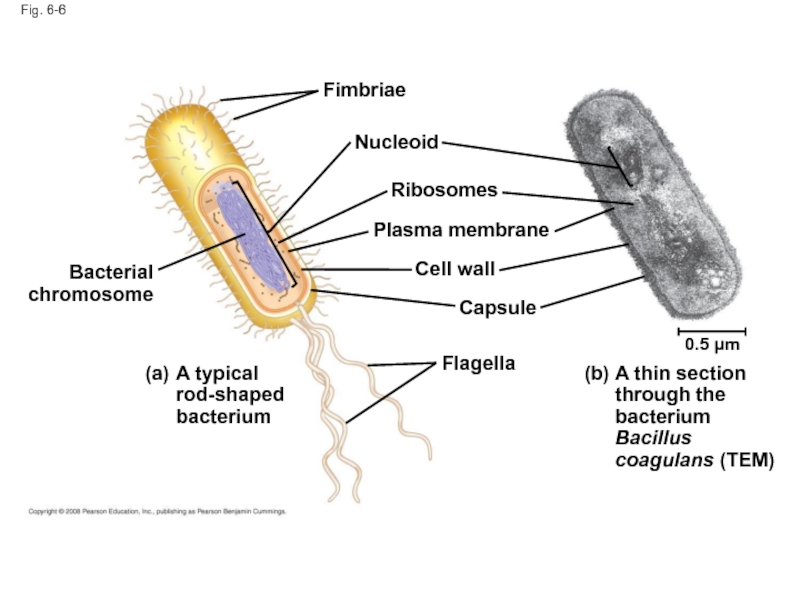
Слайд 23Fig. 6-6
Fimbriae
Nucleoid
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Capsule
Flagella
Bacterial
chromosome
(a)
A typical rod-shaped bacterium
(b)
A thin section through the
0.5 µm
Слайд 24Eukaryotic cells are characterized by having
DNA in a nucleus that is
Membrane-bound organelles
Cytoplasm in the region between the plasma membrane and nucleus
Eukaryotic cells are generally much larger than prokaryotic cells
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 25The plasma membrane is a selective barrier that allows sufficient passage
The general structure of a biological membrane is a double layer of phospholipids
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
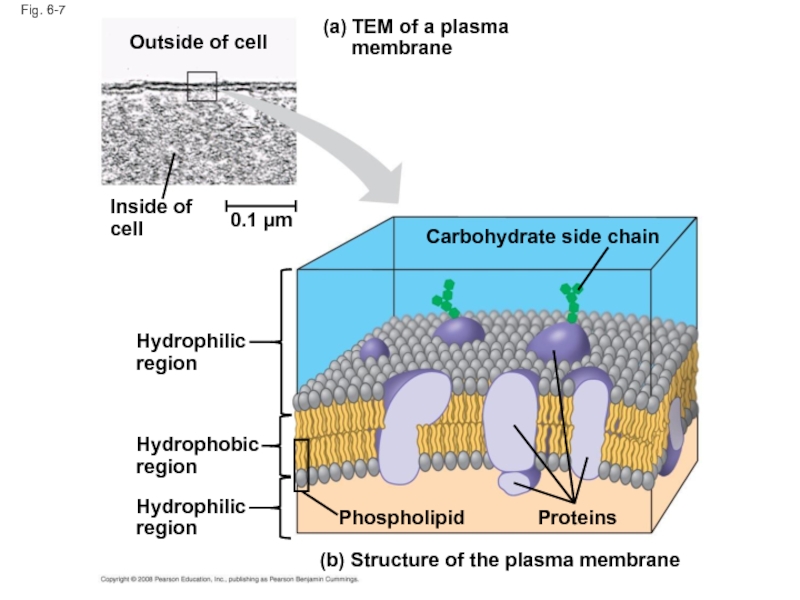
Слайд 26Fig. 6-7
TEM of a plasma
membrane
(a)
(b) Structure of the plasma membrane
Outside of
Inside of
cell
0.1 µm
Hydrophilic
region
Hydrophobic
region
Hydrophilic
region
Phospholipid
Proteins
Carbohydrate side chain
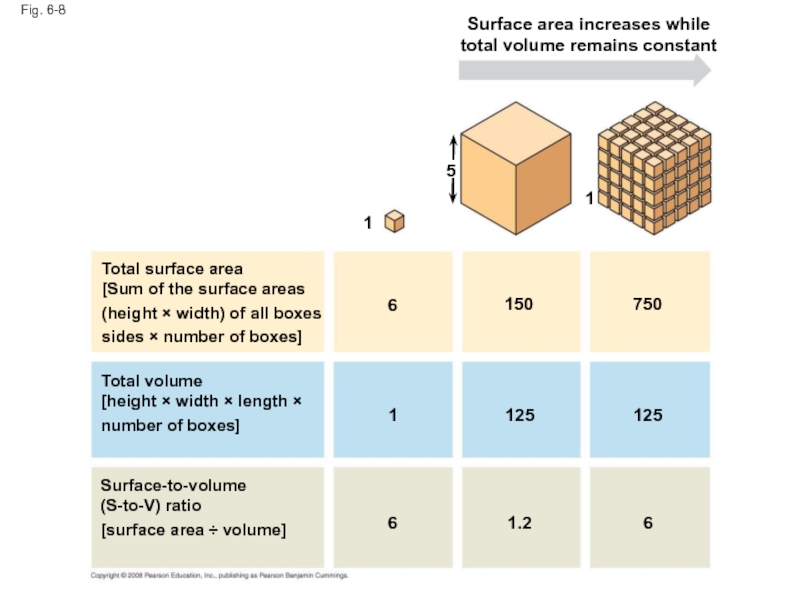
Слайд 27The logistics of carrying out cellular metabolism sets limits on the
The surface area to volume ratio of a cell is critical
As the surface area increases by a factor of n2, the volume increases by a factor of n3
Small cells have a greater surface area relative to volume
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
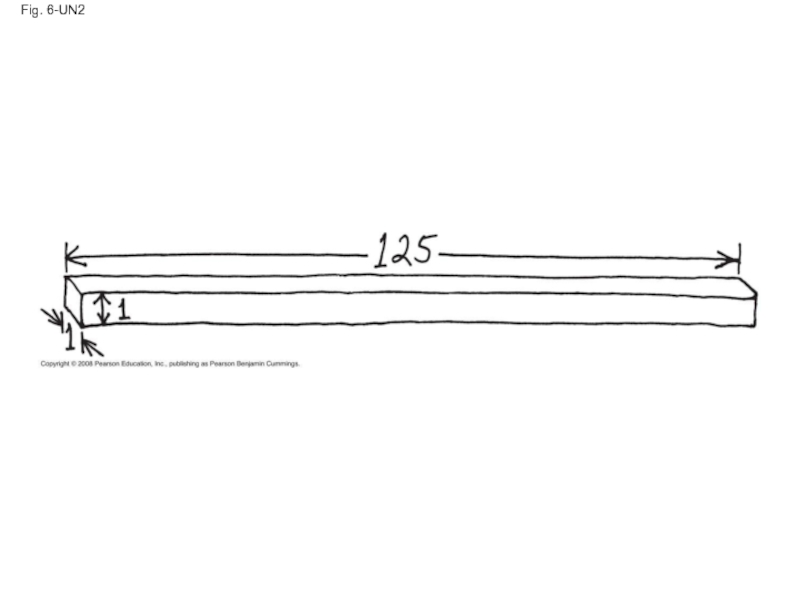
Слайд 28Fig. 6-8
Surface area increases while
total volume remains constant
5
1
1
6
150
750
125
125
1
6
6
1.2
Total surface area
[Sum of
(height × width) of all boxes
sides × number of boxes]
Total volume
[height × width × length ×
number of boxes]
Surface-to-volume
(S-to-V) ratio
[surface area ÷ volume]
Слайд 29A Panoramic View of the Eukaryotic Cell
A eukaryotic cell has internal
Plant and animal cells have most of the same organelles
BioFlix: Tour Of An Animal Cell
BioFlix: Tour Of A Plant Cell
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
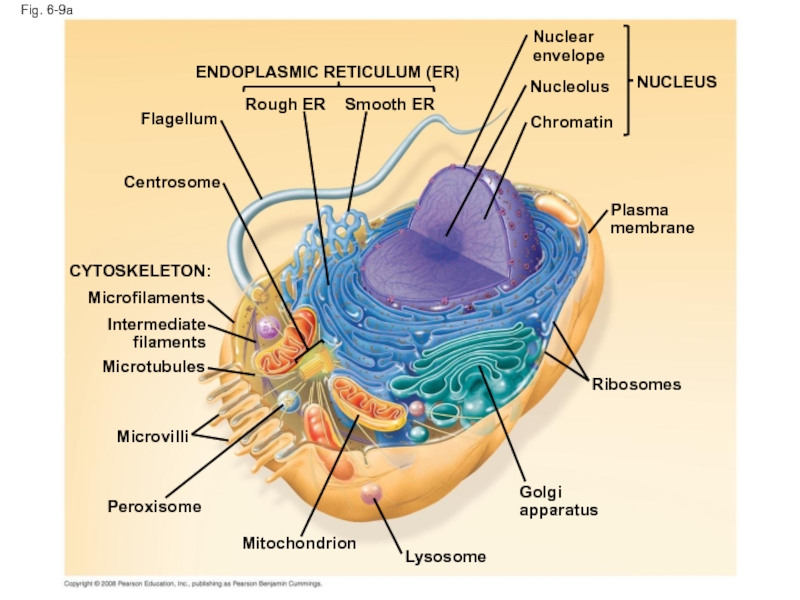
Слайд 30Fig. 6-9a
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)
Smooth ER
Rough ER
Flagellum
Centrosome
CYTOSKELETON:
Microfilaments
Intermediate
filaments
Microtubules
Microvilli
Peroxisome
Mitochondrion
Lysosome
Golgi
apparatus
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Nuclear
envelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
NUCLEUS
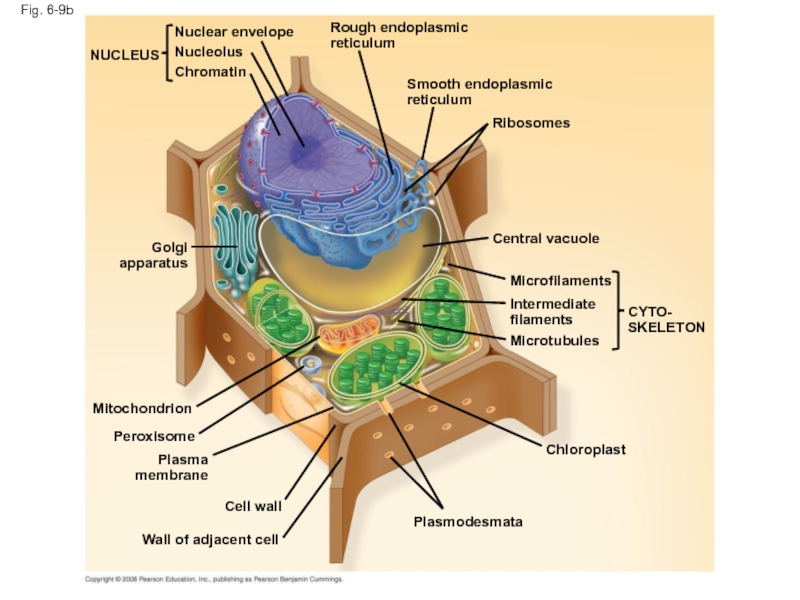
Слайд 31Fig. 6-9b
NUCLEUS
Nuclear envelope
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes
Central vacuole
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
CYTO-
SKELETON
Chloroplast
Plasmodesmata
Wall of adjacent
Cell wall
Plasma membrane
Peroxisome
Mitochondrion
Golgi
apparatus
Слайд 32Concept 6.3: The eukaryotic cell’s genetic instructions are housed in the
The nucleus contains most of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell
Ribosomes use the information from the DNA to make proteins
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 33The Nucleus: Information Central
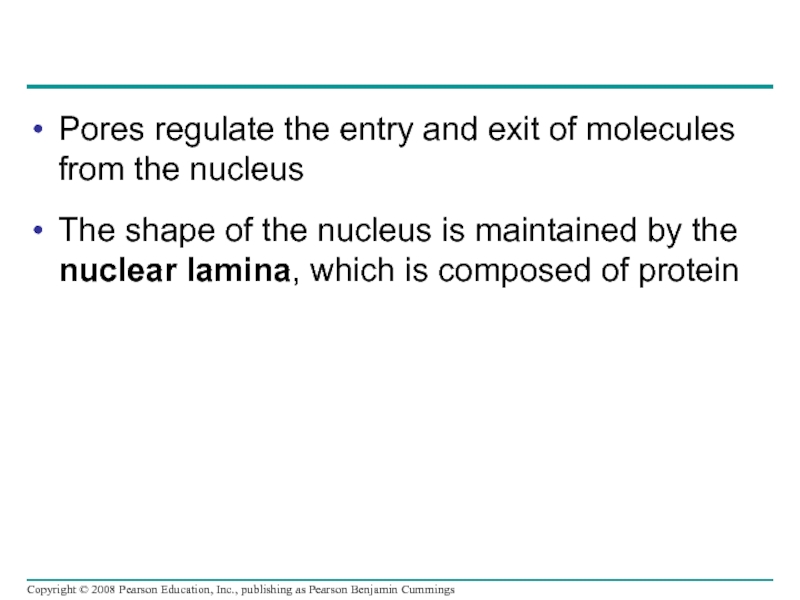
The nucleus contains most of the cell’s genes
The nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus, separating it from the cytoplasm
The nuclear membrane is a double membrane; each membrane consists of a lipid bilayer
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 34Fig. 6-10
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Rough ER
Nuclear lamina (TEM)
Close-up of nuclear envelope
1 µm
1 µm
0.25 µm
Ribosome
Pore
Nuclear pore
Outer membrane
Inner membrane
Nuclear envelope:
Chromatin
Surface of
nuclear envelope
Pore complexes (TEM)
Слайд 35Pores regulate the entry and exit of molecules from the nucleus
The
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
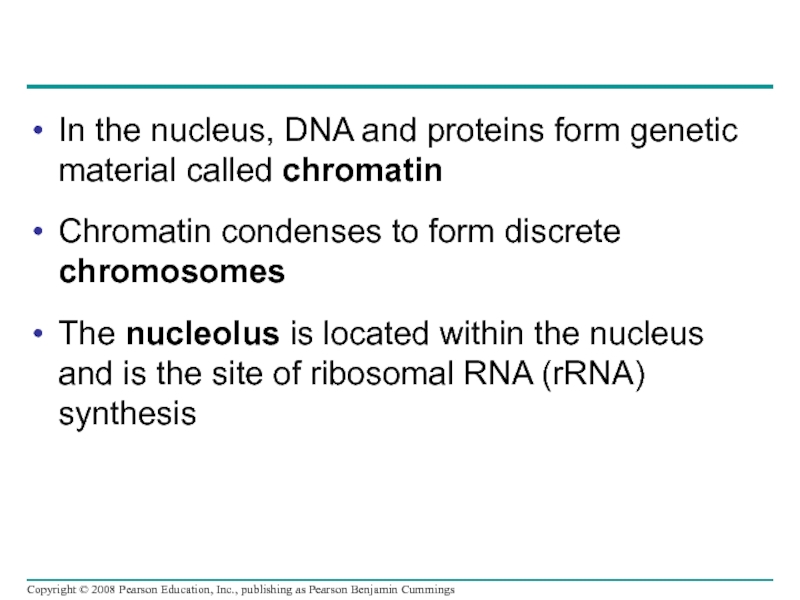
Слайд 36In the nucleus, DNA and proteins form genetic material called chromatin
Chromatin condenses to form discrete chromosomes
The nucleolus is located within the nucleus and is the site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
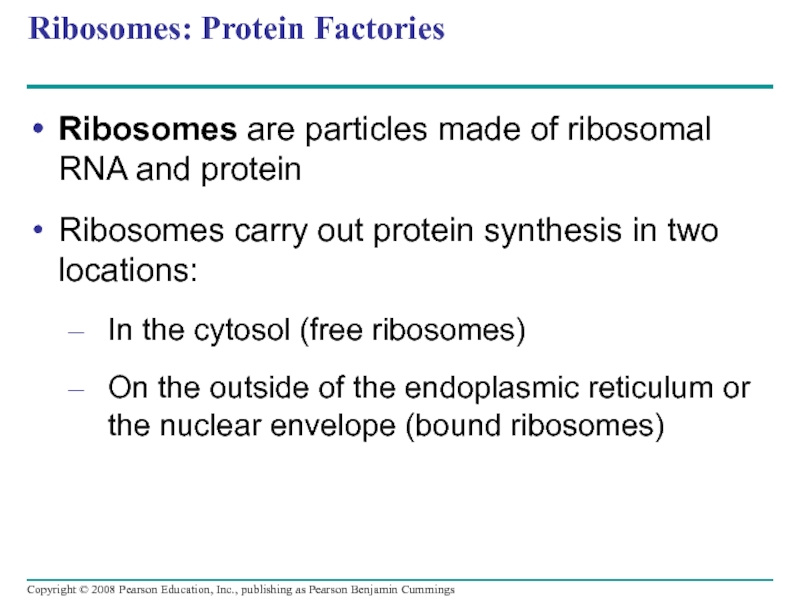
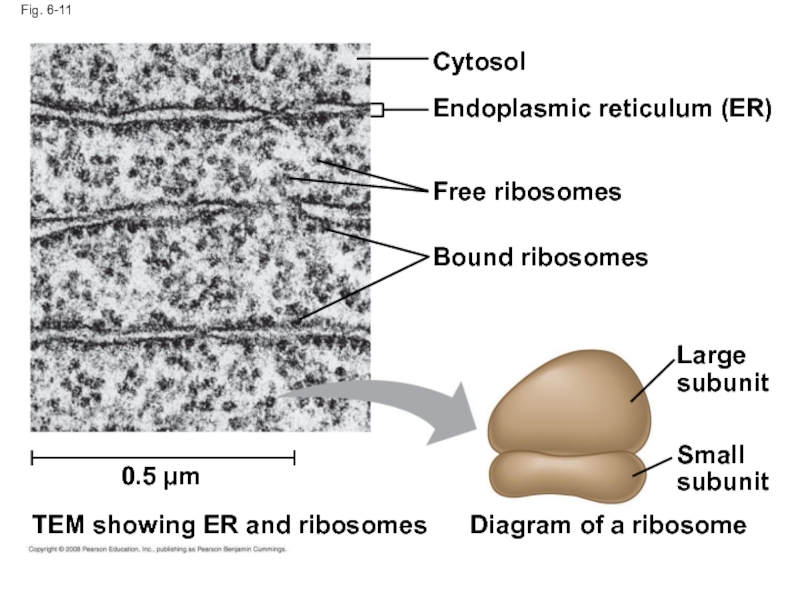
Слайд 37Ribosomes: Protein Factories
Ribosomes are particles made of ribosomal RNA and protein
Ribosomes
In the cytosol (free ribosomes)
On the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum or the nuclear envelope (bound ribosomes)
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 38Fig. 6-11
Cytosol
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Free ribosomes
Bound ribosomes
Large subunit
Small subunit
Diagram of a ribosome
TEM
0.5 µm
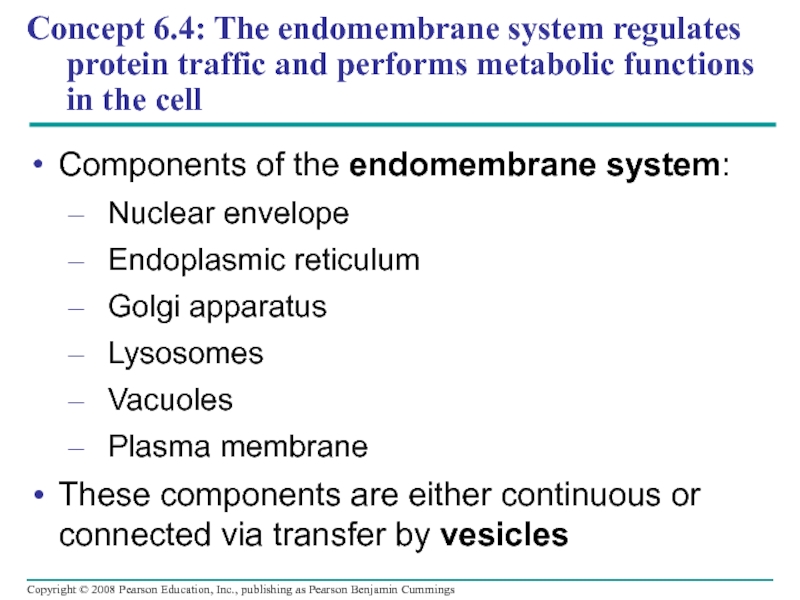
Слайд 39Concept 6.4: The endomembrane system regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic
Components of the endomembrane system:
Nuclear envelope
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Plasma membrane
These components are either continuous or connected via transfer by vesicles
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
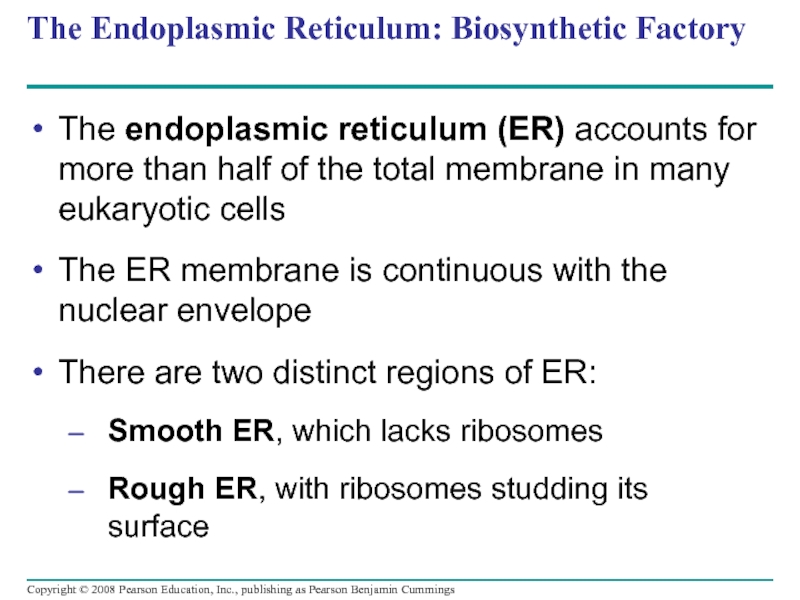
Слайд 40The Endoplasmic Reticulum: Biosynthetic Factory
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) accounts for more
The ER membrane is continuous with the nuclear envelope
There are two distinct regions of ER:
Smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes
Rough ER, with ribosomes studding its surface
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
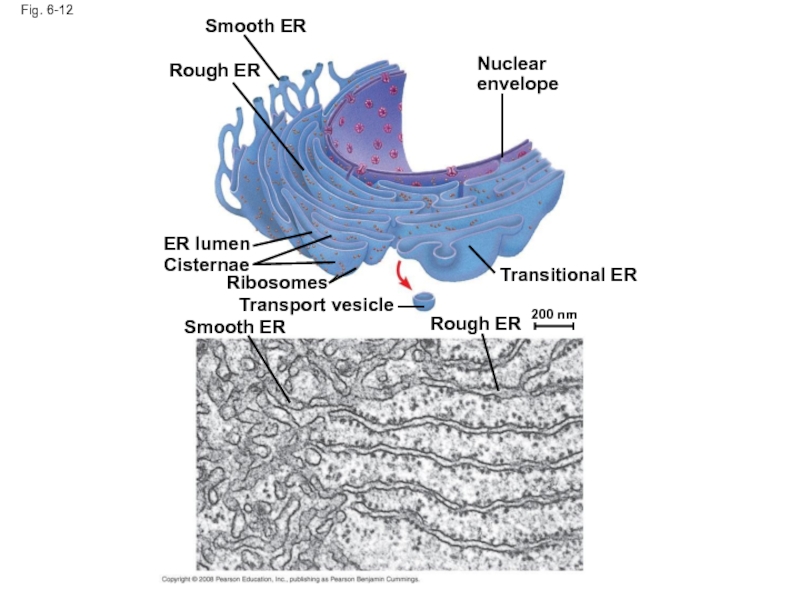
Слайд 41Fig. 6-12
Smooth ER
Rough ER
Nuclear envelope
Transitional ER
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Transport vesicle
Ribosomes
Cisternae
ER lumen
200 nm
Слайд 42Functions of Smooth ER
The smooth ER
Synthesizes lipids
Metabolizes carbohydrates
Detoxifies poison
Stores calcium
Copyright ©
Слайд 43Functions of Rough ER
The rough ER
Has bound ribosomes, which secrete glycoproteins
Distributes transport vesicles, proteins surrounded by membranes
Is a membrane factory for the cell
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 44The Golgi apparatus consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
Functions of
Modifies products of the ER
Manufactures certain macromolecules
Sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles
The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and
Receiving Center
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
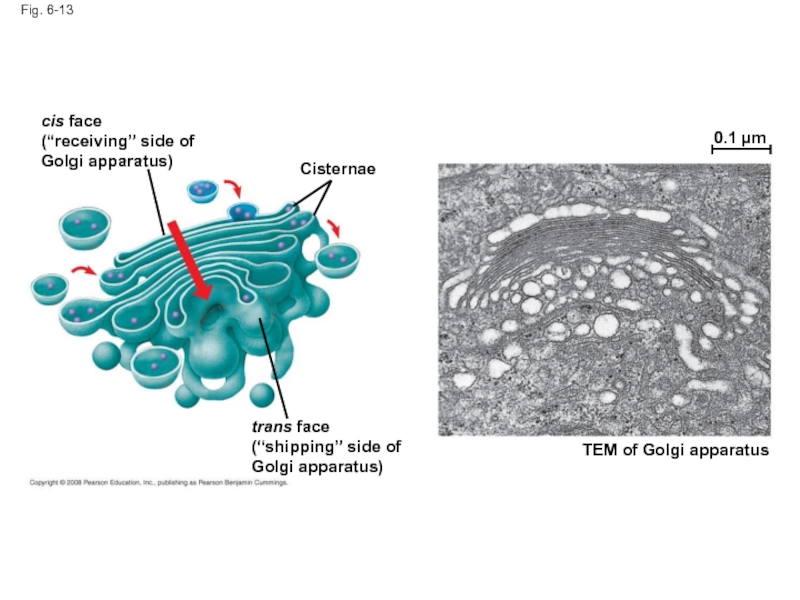
Слайд 45Fig. 6-13
cis face
(“receiving” side of Golgi apparatus)
Cisternae
trans face
(“shipping” side of Golgi
TEM of Golgi apparatus
0.1 µm
Слайд 46Lysosomes: Digestive Compartments
A lysosome is a membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes
Lysosomal enzymes can hydrolyze proteins, fats, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids
Animation: Lysosome Formation
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
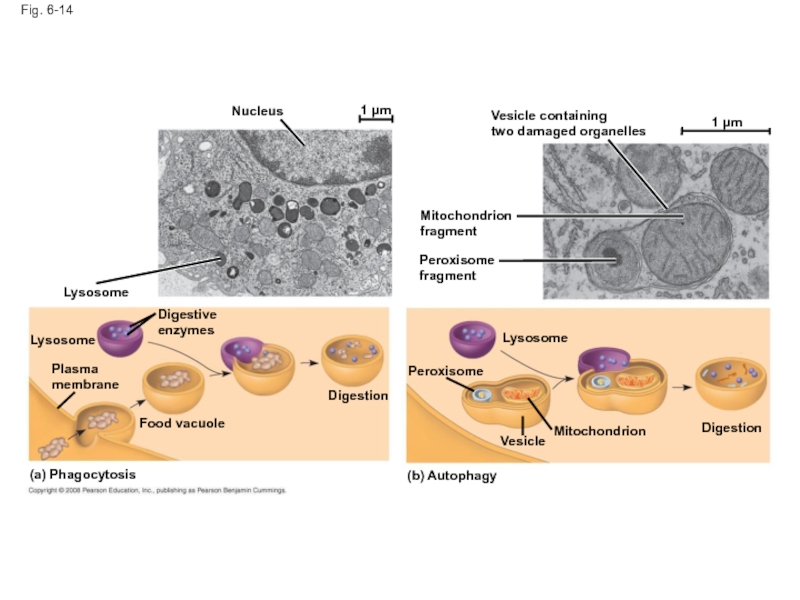
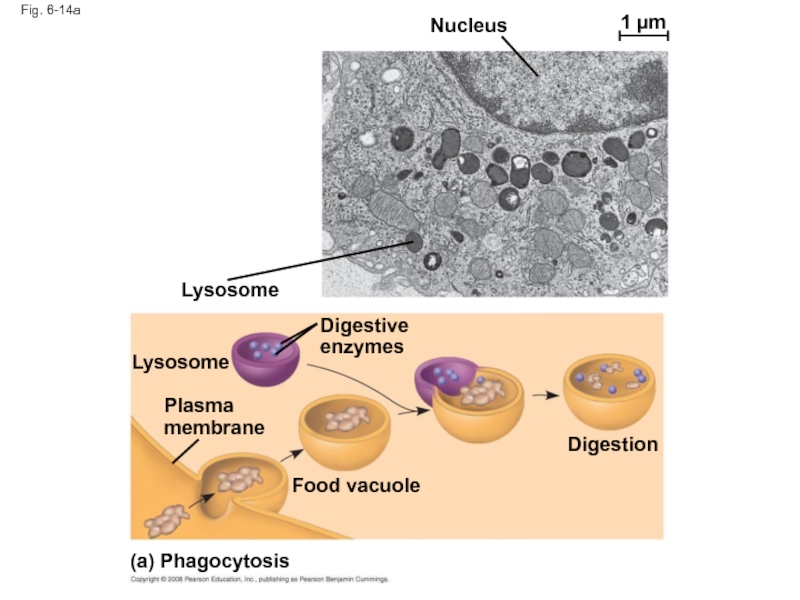
Слайд 47Some types of cell can engulf another cell by phagocytosis; this
A lysosome fuses with the food vacuole and digests the molecules
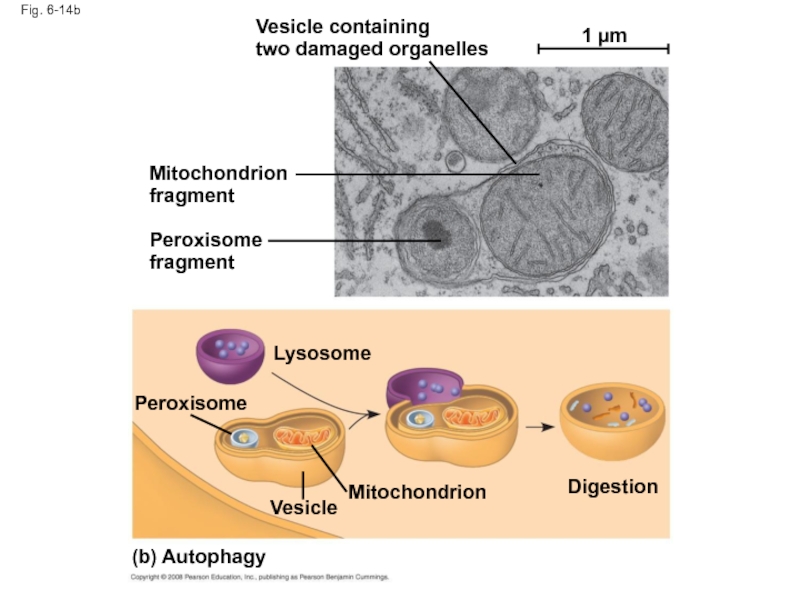
Lysosomes also use enzymes to recycle the cell’s own organelles and macromolecules, a process called autophagy
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 48Fig. 6-14
Nucleus
1 µm
Lysosome
Digestive
enzymes
Lysosome
Plasma
membrane
Food vacuole
(a) Phagocytosis
Digestion
(b) Autophagy
Peroxisome
Vesicle
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Peroxisome
fragment
Mitochondrion
fragment
Vesicle containing
two damaged organelles
1 µm
Digestion
Слайд 49Fig. 6-14a
Nucleus
1 µm
Lysosome
Lysosome
Digestive enzymes
Plasma membrane
Food vacuole
Digestion
(a) Phagocytosis
Слайд 50Fig. 6-14b
Vesicle containing
two damaged organelles
Mitochondrion fragment
Peroxisome fragment
Peroxisome
Lysosome
Digestion
Mitochondrion
Vesicle
(b) Autophagy
1 µm
Слайд 51Vacuoles: Diverse Maintenance Compartments
A plant cell or fungal cell may have
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 52Food vacuoles are formed by phagocytosis
Contractile vacuoles, found in many freshwater
Central vacuoles, found in many mature plant cells, hold organic compounds and water
Video: Paramecium Vacuole
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 54The Endomembrane System: A Review
The endomembrane system is a complex and
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 58Concept 6.5: Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to
Mitochondria are the sites of cellular respiration, a metabolic process that generates ATP
Chloroplasts, found in plants and algae, are the sites of photosynthesis
Peroxisomes are oxidative organelles
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 59Mitochondria and chloroplasts
Are not part of the endomembrane system
Have a
Have proteins made by free ribosomes
Contain their own DNA
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
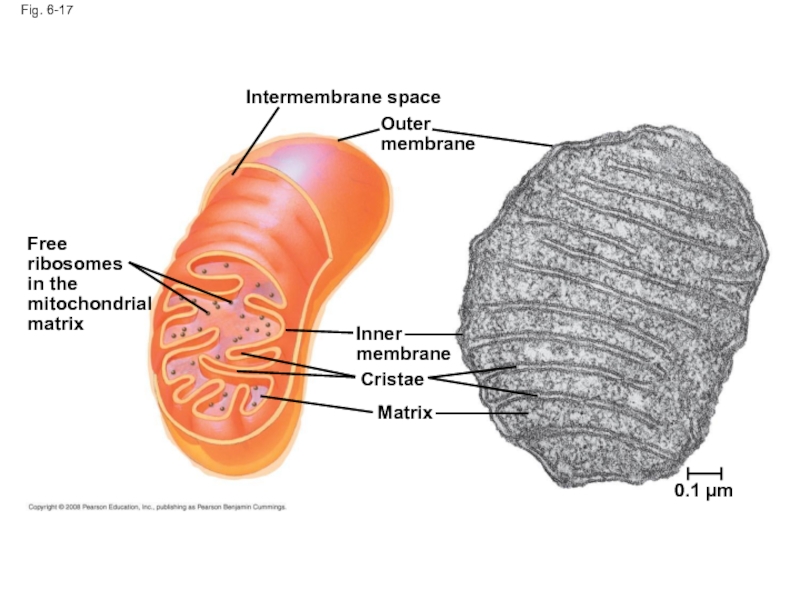
Слайд 60Mitochondria: Chemical Energy Conversion
Mitochondria are in nearly all eukaryotic cells
They have
The inner membrane creates two compartments: intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix
Some metabolic steps of cellular respiration are catalyzed in the mitochondrial matrix
Cristae present a large surface area for enzymes that synthesize ATP
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 61Fig. 6-17
Free ribosomes
in the mitochondrial matrix
Intermembrane space
Outer membrane
Inner membrane
Cristae
Matrix
0.1 µm
Слайд 62Chloroplasts: Capture of Light Energy
The chloroplast is a member of a
Chloroplasts contain the green pigment chlorophyll, as well as enzymes and other molecules that function in photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are found in leaves and other green organs of plants and in algae
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 63Chloroplast structure includes:
Thylakoids, membranous sacs, stacked to form a granum
Stroma, the
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 65Peroxisomes: Oxidation
Peroxisomes are specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single membrane
Peroxisomes
Oxygen is used to break down different types of molecules
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
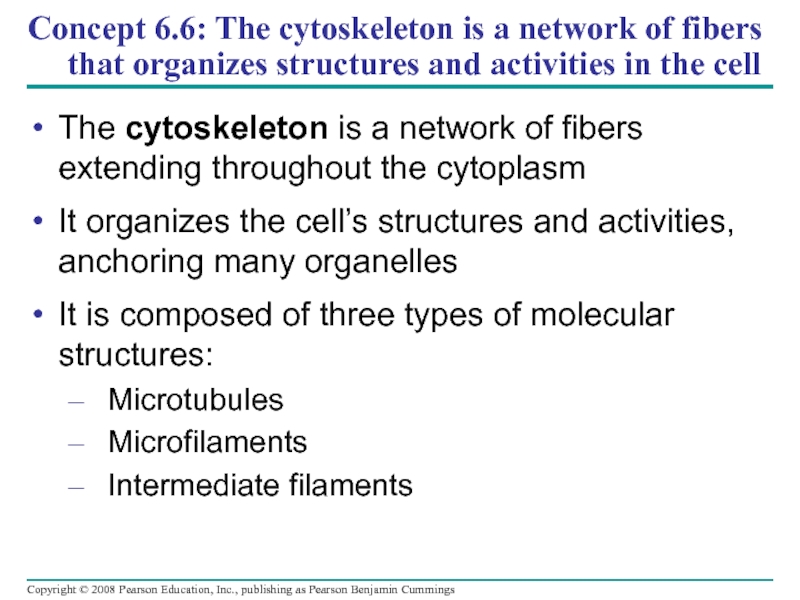
Слайд 67Concept 6.6: The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes
The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm
It organizes the cell’s structures and activities, anchoring many organelles
It is composed of three types of molecular structures:
Microtubules
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
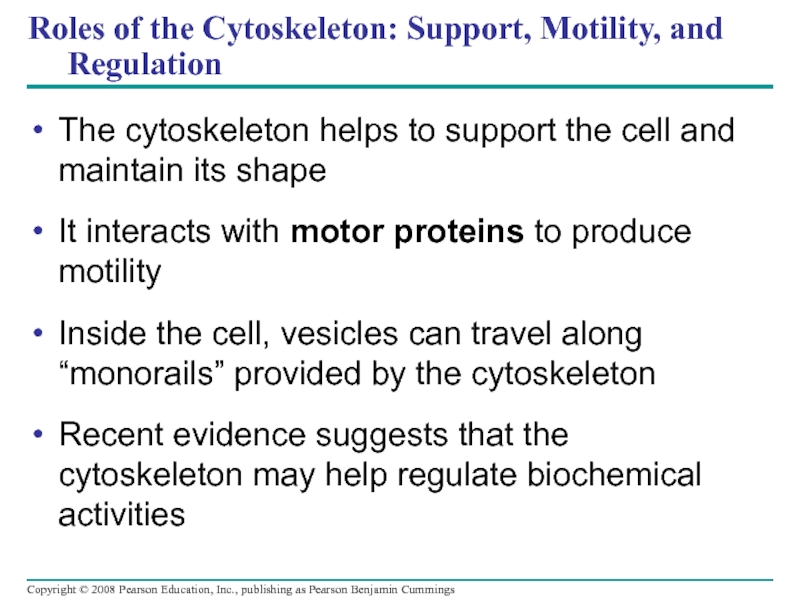
Слайд 69Roles of the Cytoskeleton: Support, Motility, and Regulation
The cytoskeleton helps to
It interacts with motor proteins to produce motility
Inside the cell, vesicles can travel along “monorails” provided by the cytoskeleton
Recent evidence suggests that the cytoskeleton may help regulate biochemical activities
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
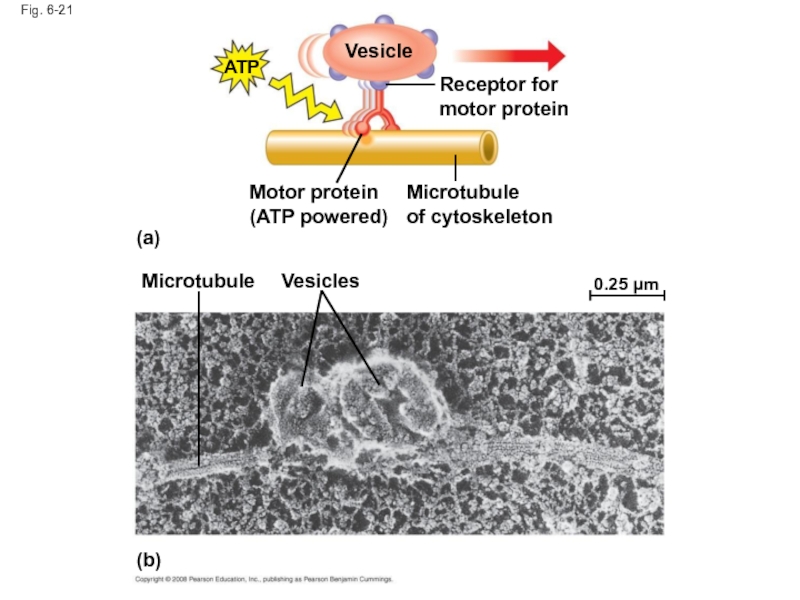
Слайд 70Fig. 6-21
Vesicle
ATP
Receptor for motor protein
Microtubule
of cytoskeleton
Motor protein (ATP powered)
(a)
Microtubule
Vesicles
(b)
0.25 µm
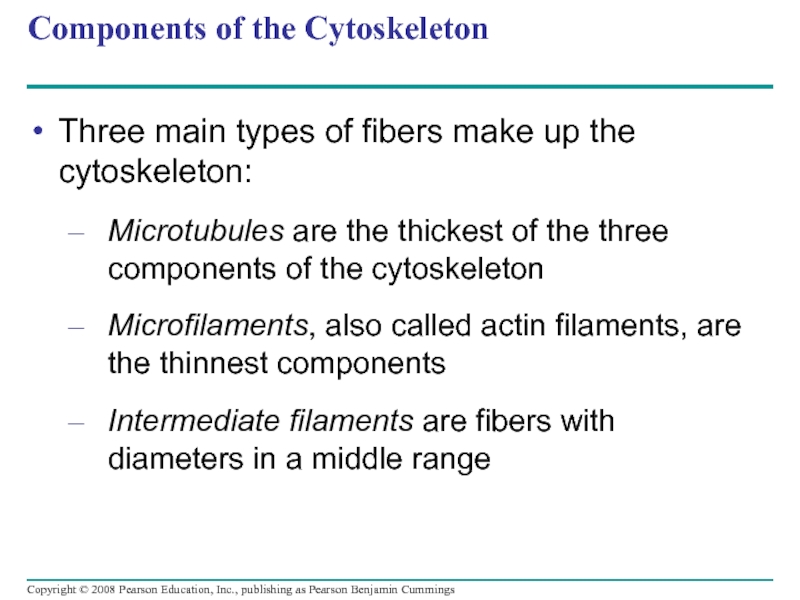
Слайд 71Components of the Cytoskeleton
Three main types of fibers make up the
Microtubules are the thickest of the three components of the cytoskeleton
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are the thinnest components
Intermediate filaments are fibers with diameters in a middle range
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
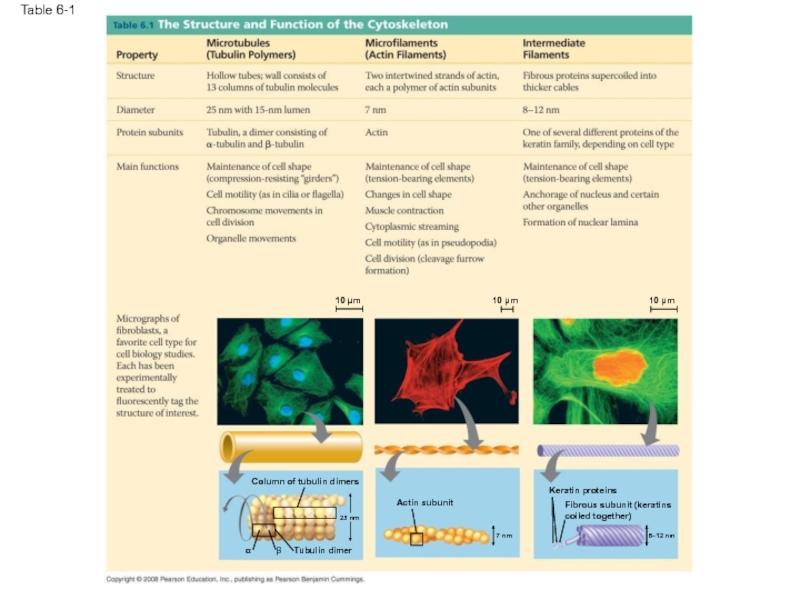
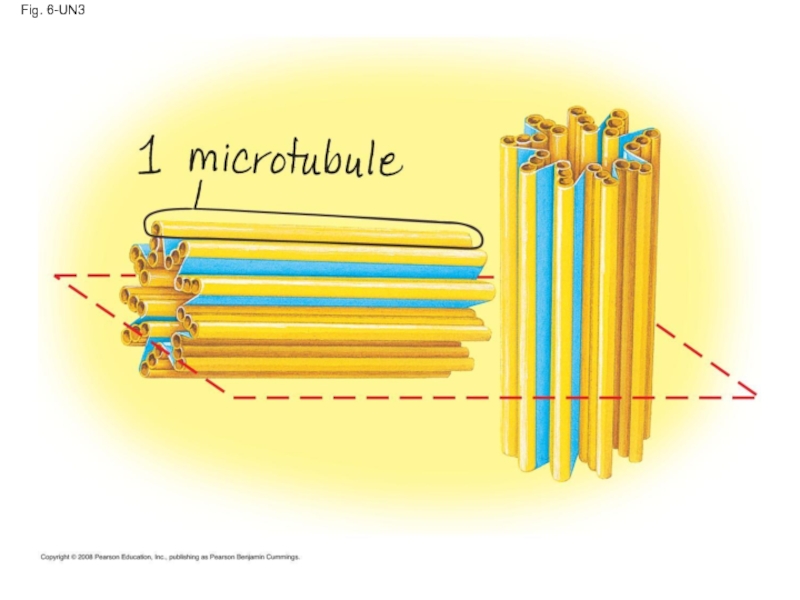
Слайд 72Table 6-1
10 µm
10 µm
10 µm
Column of tubulin dimers
Tubulin dimer
Actin subunit
α
β
25 nm
7 nm
Keratin proteins
Fibrous subunit (keratins coiled together)
8–12 nm
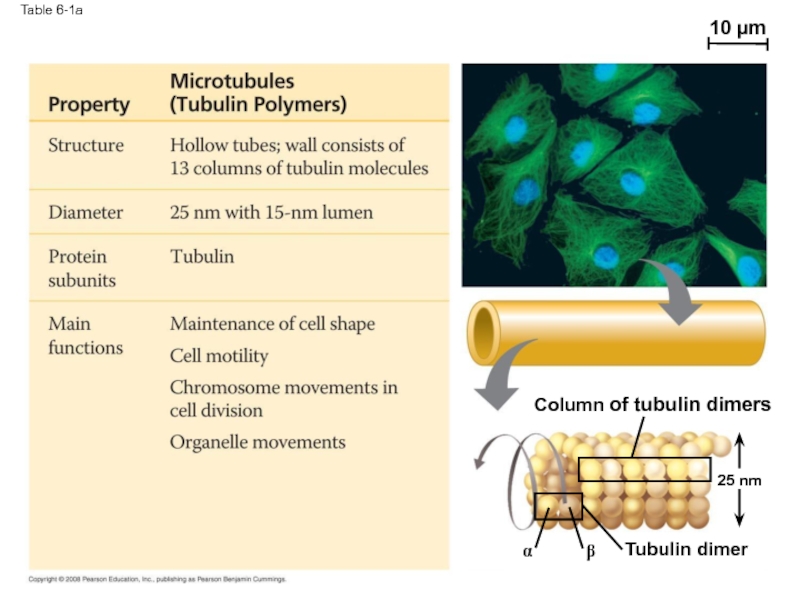
Слайд 76Microtubules
Microtubules are hollow rods about 25 nm in diameter and about
Functions of microtubules:
Shaping the cell
Guiding movement of organelles
Separating chromosomes during cell division
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 77
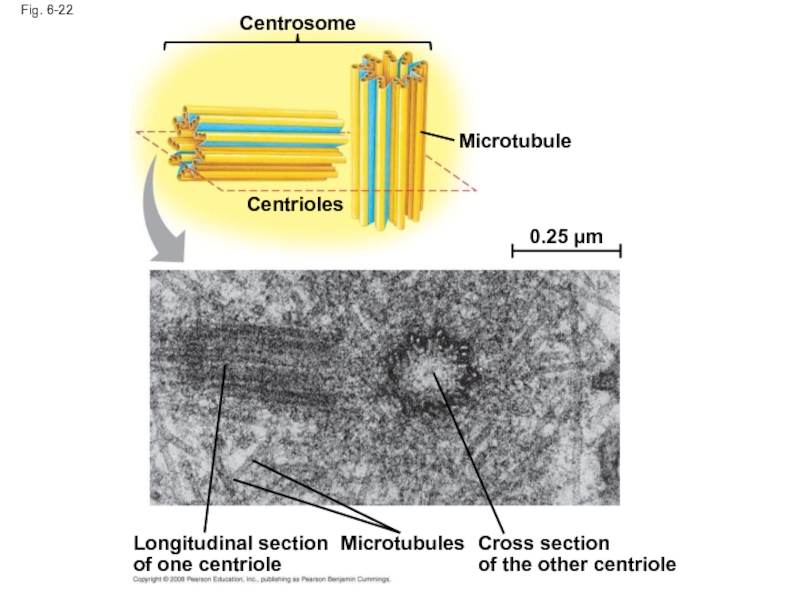
Centrosomes and Centrioles
In many cells, microtubules grow out from a
The centrosome is a “microtubule-organizing center”
In animal cells, the centrosome has a pair of centrioles, each with nine triplets of microtubules arranged in a ring
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 78Fig. 6-22
Centrosome
Microtubule
Centrioles
0.25 µm
Longitudinal section of one centriole
Microtubules
Cross section
of the other centriole
Слайд 79
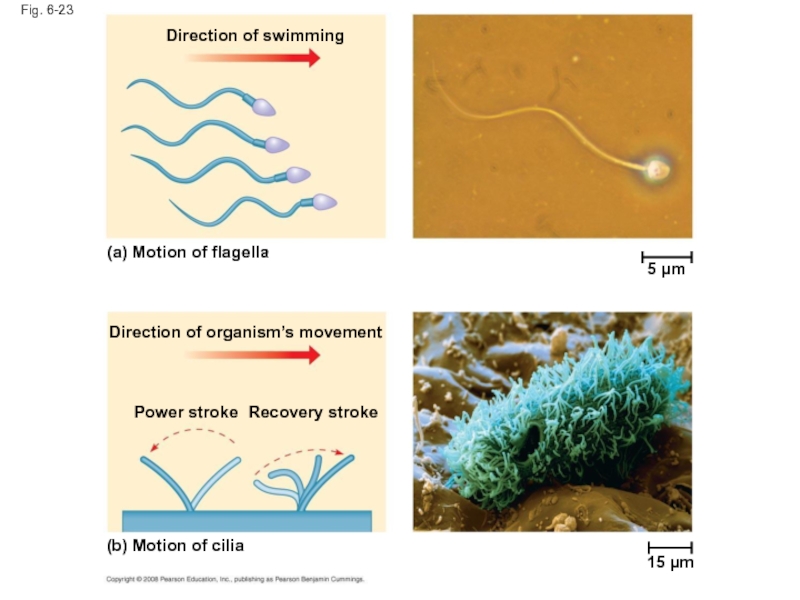
Cilia and Flagella
Microtubules control the beating of cilia and flagella,
Cilia and flagella differ in their beating patterns
Video: Chlamydomonas
Video: Paramecium Cilia
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 80Fig. 6-23
5 µm
Direction of swimming
(a) Motion of flagella
Direction of organism’s movement
Power
Recovery stroke
(b) Motion of cilia
15 µm
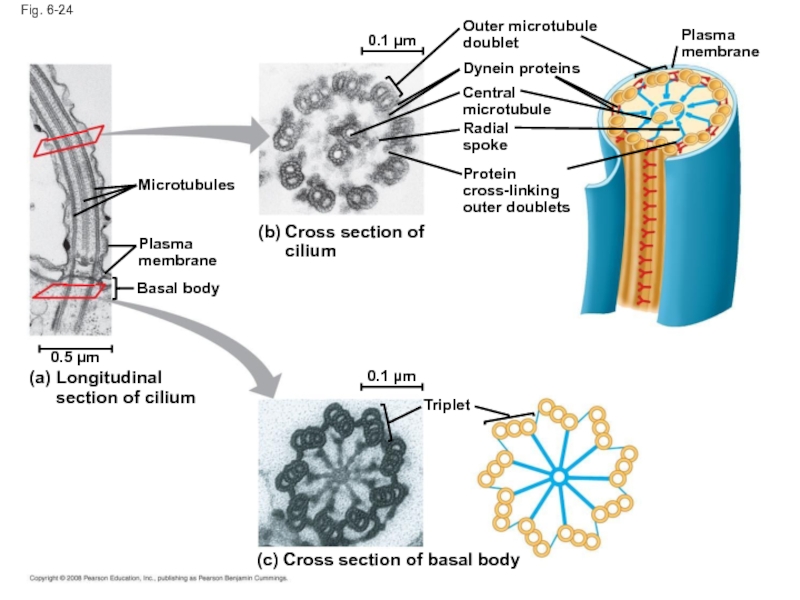
Слайд 81Cilia and flagella share a common ultrastructure:
A core of microtubules sheathed
A basal body that anchors the cilium or flagellum
A motor protein called dynein, which drives the bending movements of a cilium or flagellum
Animation: Cilia and Flagella
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 82Fig. 6-24
0.1 µm
Triplet
(c) Cross section of basal body
(a)
Longitudinal section of cilium
0.5
Plasma membrane
Basal body
Microtubules
(b)
Cross section of cilium
Plasma membrane
Outer microtubule doublet
Dynein proteins
Central microtubule
Radial spoke
Protein cross-linking outer doublets
0.1 µm
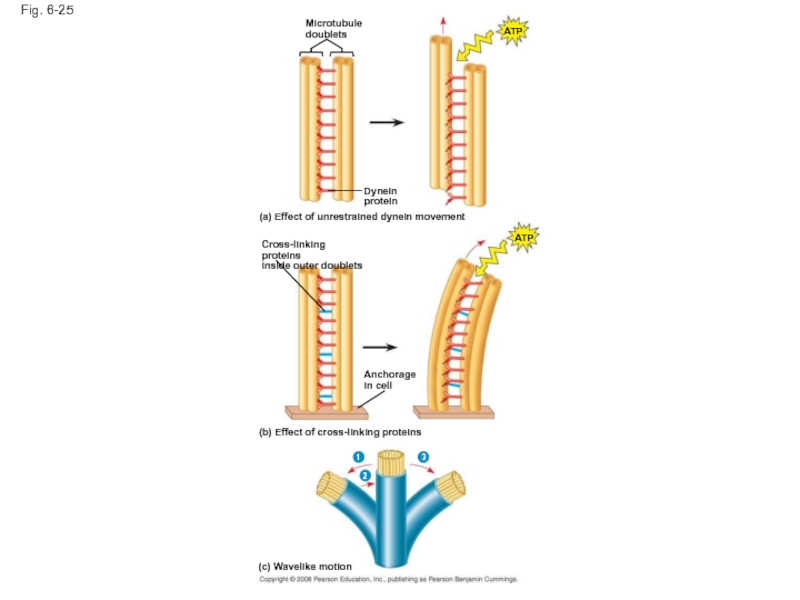
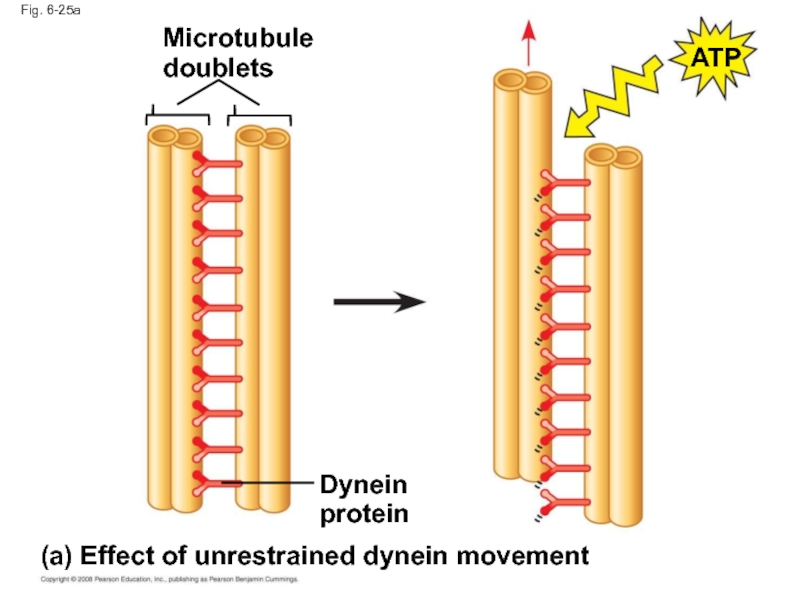
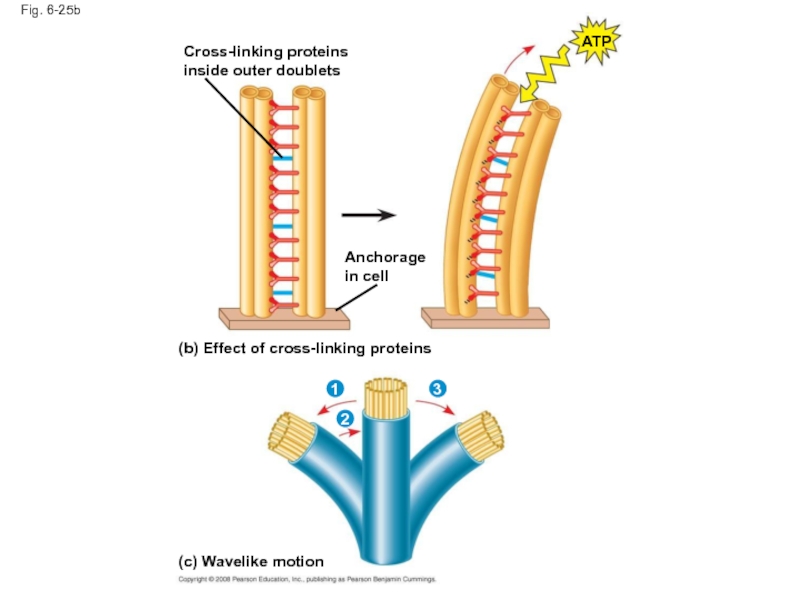
Слайд 83How dynein “walking” moves flagella and cilia:
Dynein arms alternately grab, move,
Protein cross-links limit sliding
Forces exerted by dynein arms cause doublets to curve, bending the cilium or flagellum
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 84
Fig. 6-25
Microtubule
doublets
Dynein
protein
ATP
ATP
(a) Effect of unrestrained dynein movement
Cross-linking proteins
inside outer doublets
Anchorage
in cell
(b)
1
3
2
(c) Wavelike motion
Слайд 86Fig. 6-25b
Cross-linking proteins inside outer doublets
Anchorage in cell
ATP
(b) Effect of cross-linking
(c) Wavelike motion
1
3
2
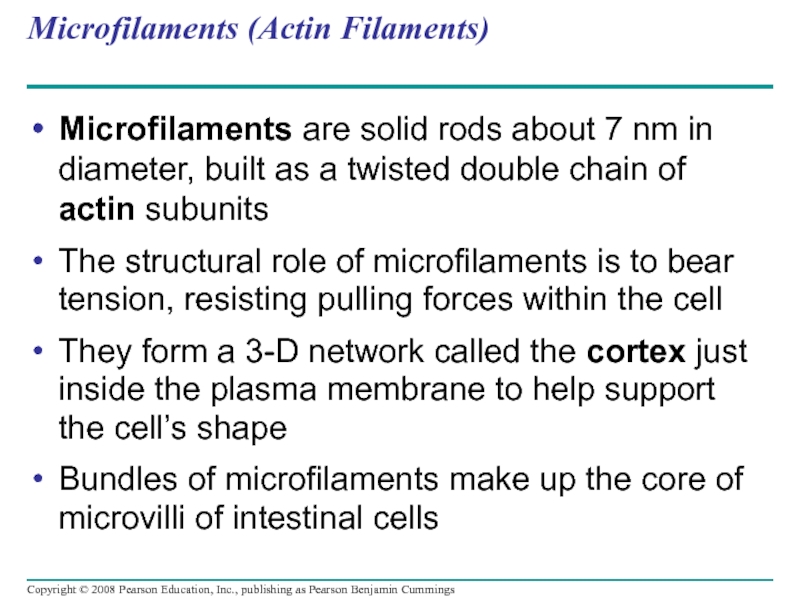
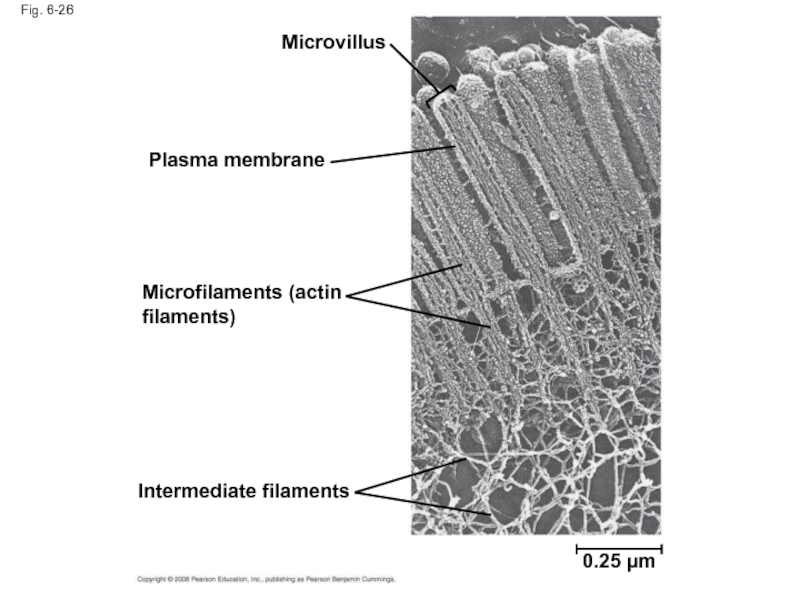
Слайд 87Microfilaments (Actin Filaments)
Microfilaments are solid rods about 7 nm in diameter,
The structural role of microfilaments is to bear tension, resisting pulling forces within the cell
They form a 3-D network called the cortex just inside the plasma membrane to help support the cell’s shape
Bundles of microfilaments make up the core of microvilli of intestinal cells
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 88Fig. 6-26
Microvillus
Plasma membrane
Microfilaments (actin filaments)
Intermediate filaments
0.25 µm
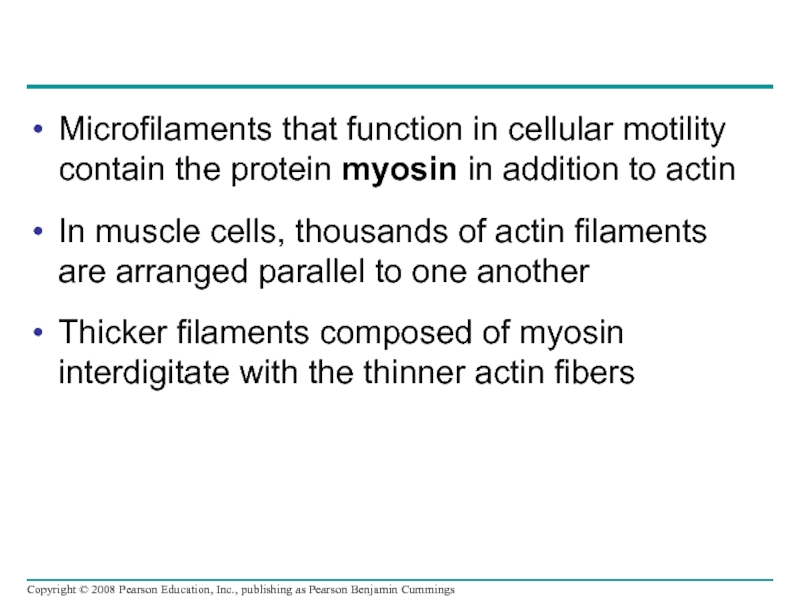
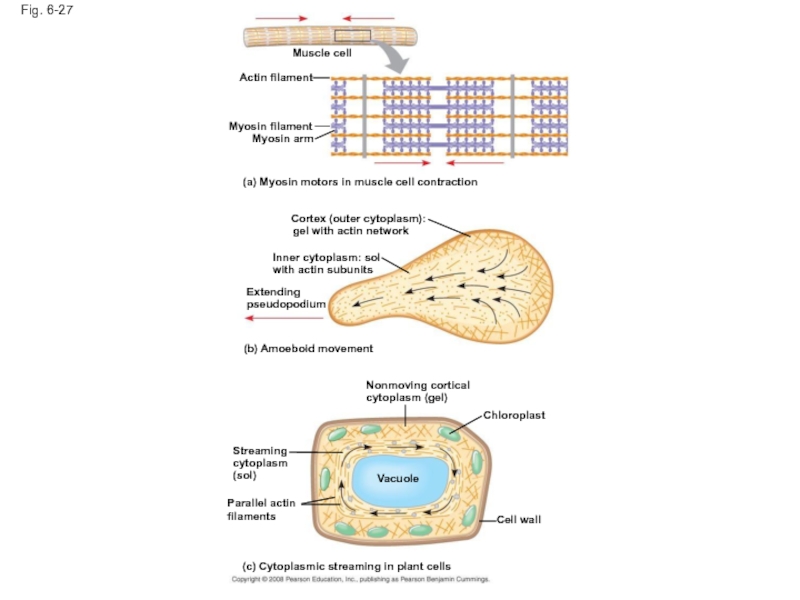
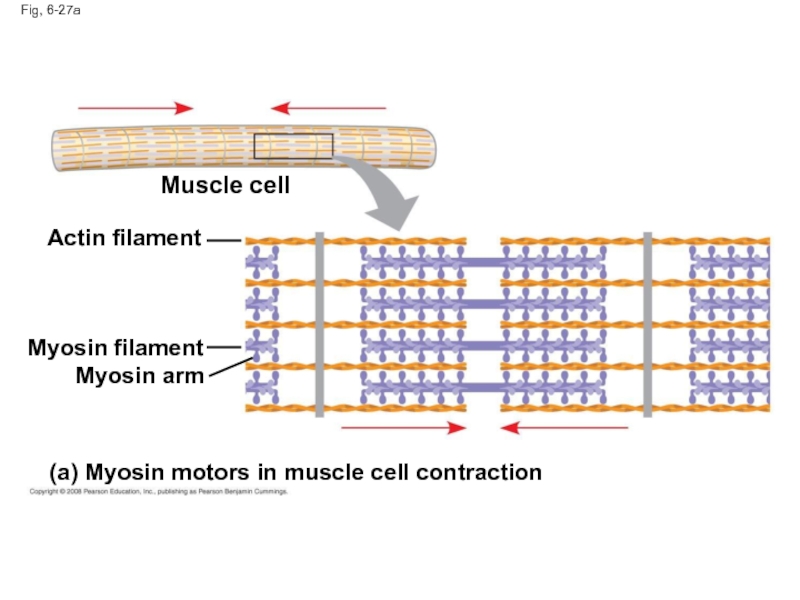
Слайд 89Microfilaments that function in cellular motility contain the protein myosin in
In muscle cells, thousands of actin filaments are arranged parallel to one another
Thicker filaments composed of myosin interdigitate with the thinner actin fibers
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 90Fig. 6-27
Muscle cell
Actin filament
Myosin filament
Myosin arm
(a) Myosin motors in muscle cell
Cortex (outer cytoplasm):
gel with actin network
Inner cytoplasm: sol
with actin subunits
Extending
pseudopodium
(b) Amoeboid movement
Nonmoving cortical
cytoplasm (gel)
Chloroplast
Streaming
cytoplasm
(sol)
Vacuole
Cell wall
Parallel actin
filaments
(c) Cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells
Слайд 91Fig, 6-27a
Muscle cell
Actin filament
Myosin filament
Myosin arm
(a) Myosin motors in muscle cell
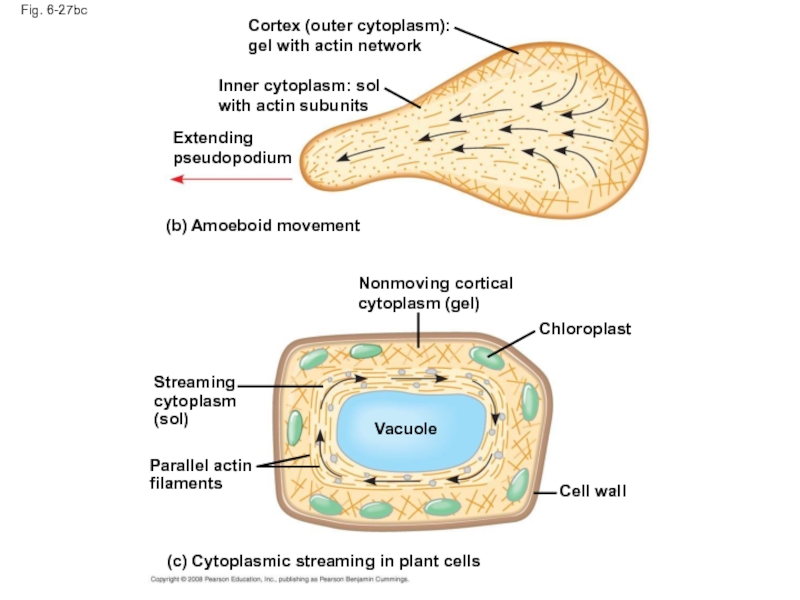
Слайд 92Fig. 6-27bc
Cortex (outer cytoplasm): gel with actin network
Inner cytoplasm: sol with
Extending pseudopodium
(b) Amoeboid movement
Nonmoving cortical cytoplasm (gel)
Chloroplast
Cell wall
Streaming cytoplasm (sol)
Parallel actin filaments
(c) Cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells
Vacuole
Слайд 93Localized contraction brought about by actin and myosin also drives amoeboid
Pseudopodia (cellular extensions) extend and contract through the reversible assembly and contraction of actin subunits into microfilaments
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 94Cytoplasmic streaming is a circular flow of cytoplasm within cells
This streaming
In plant cells, actin-myosin interactions and sol-gel transformations drive cytoplasmic streaming
Video: Cytoplasmic Streaming
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 95Intermediate Filaments
Intermediate filaments range in diameter from 8–12 nanometers, larger than
They support cell shape and fix organelles in place
Intermediate filaments are more permanent cytoskeleton fixtures than the other two classes
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 96Concept 6.7: Extracellular components and connections between cells help coordinate cellular
Most cells synthesize and secrete materials that are external to the plasma membrane
These extracellular structures include:
Cell walls of plants
The extracellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells
Intercellular junctions
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 97Cell Walls of Plants
The cell wall is an extracellular structure that
Prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists also have cell walls
The cell wall protects the plant cell, maintains its shape, and prevents excessive uptake of water
Plant cell walls are made of cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and protein
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
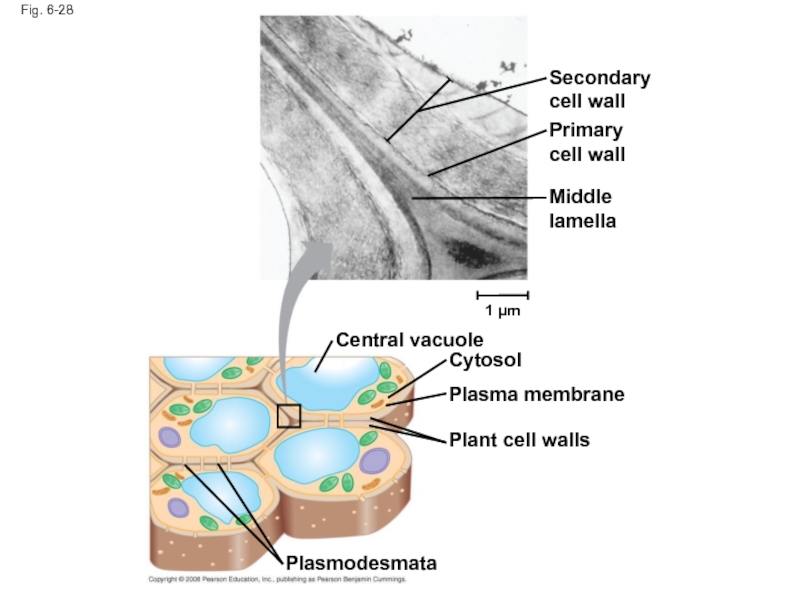
Слайд 98Plant cell walls may have multiple layers:
Primary cell wall: relatively thin
Middle lamella: thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells
Secondary cell wall (in some cells): added between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall
Plasmodesmata are channels between adjacent plant cells
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 99Fig. 6-28
Secondary cell wall
Primary cell wall
Middle lamella
Central vacuole
Cytosol
Plasma membrane
Plant cell walls
Plasmodesmata
1
Слайд 100
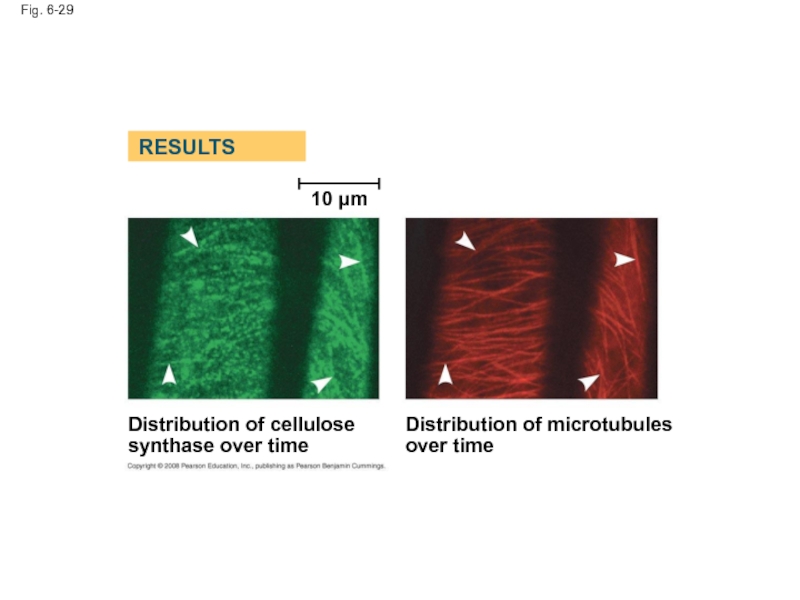
Fig. 6-29
10 µm
Distribution of cellulose synthase over time
Distribution of microtubules over
RESULTS
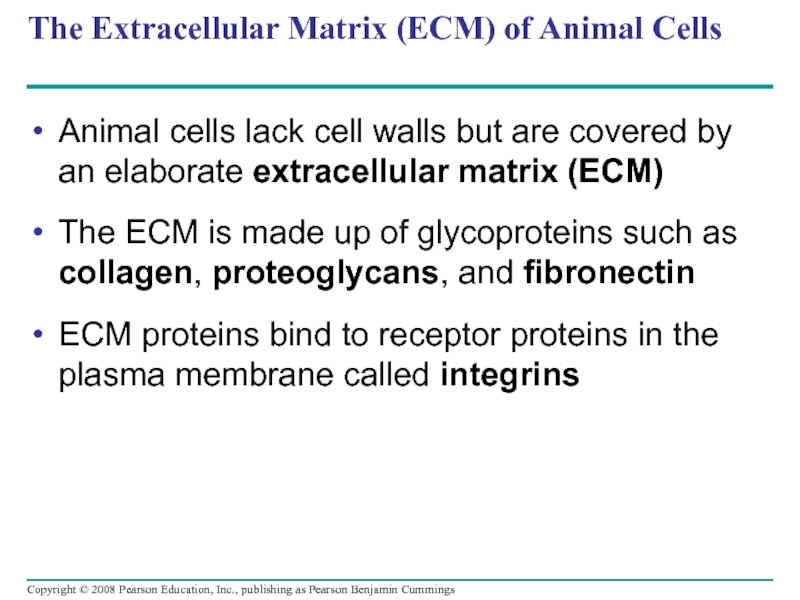
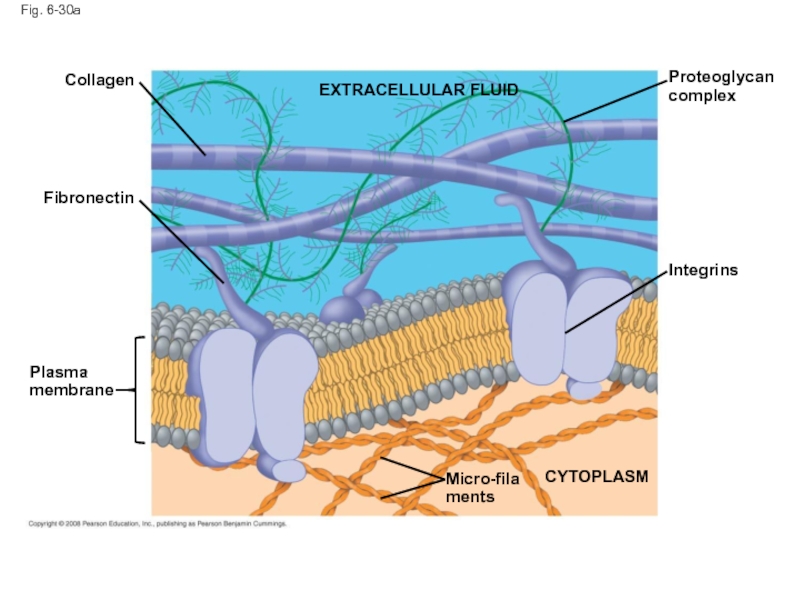
Слайд 101The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) of Animal Cells
Animal cells lack cell walls
The ECM is made up of glycoproteins such as collagen, proteoglycans, and fibronectin
ECM proteins bind to receptor proteins in the plasma membrane called integrins
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
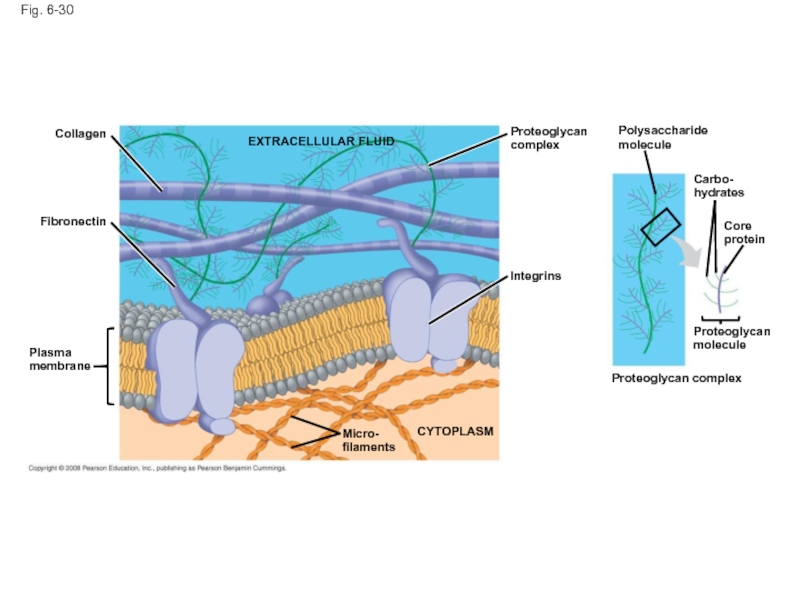
Слайд 102Fig. 6-30
EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
Collagen
Fibronectin
Plasma
membrane
Micro-
filaments
CYTOPLASM
Integrins
Proteoglycan
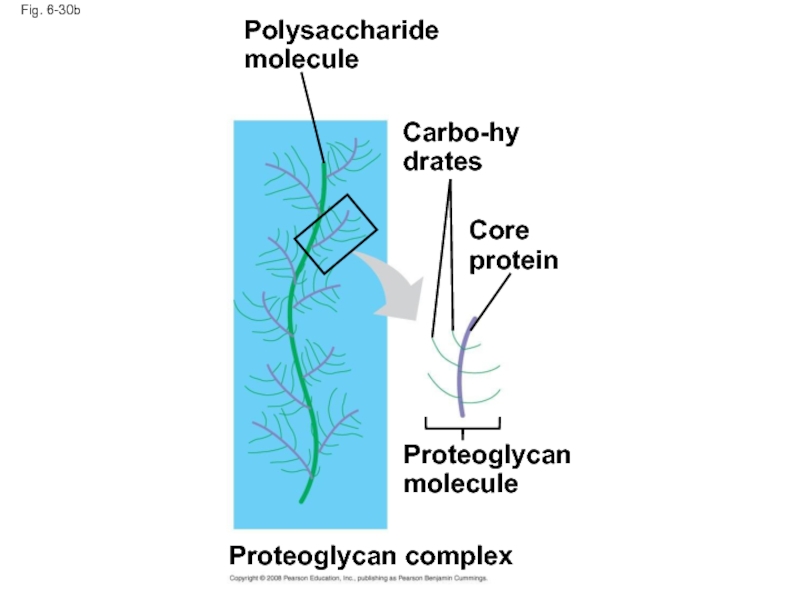
complex
Polysaccharide
molecule
Carbo-
hydrates
Core
protein
Proteoglycan
molecule
Proteoglycan complex
Слайд 103Fig. 6-30a
Collagen
Fibronectin
Plasma membrane
Proteoglycan complex
Integrins
CYTOPLASM
Micro-filaments
EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
Слайд 104Fig. 6-30b
Polysaccharide molecule
Carbo-hydrates
Core protein
Proteoglycan molecule
Proteoglycan complex
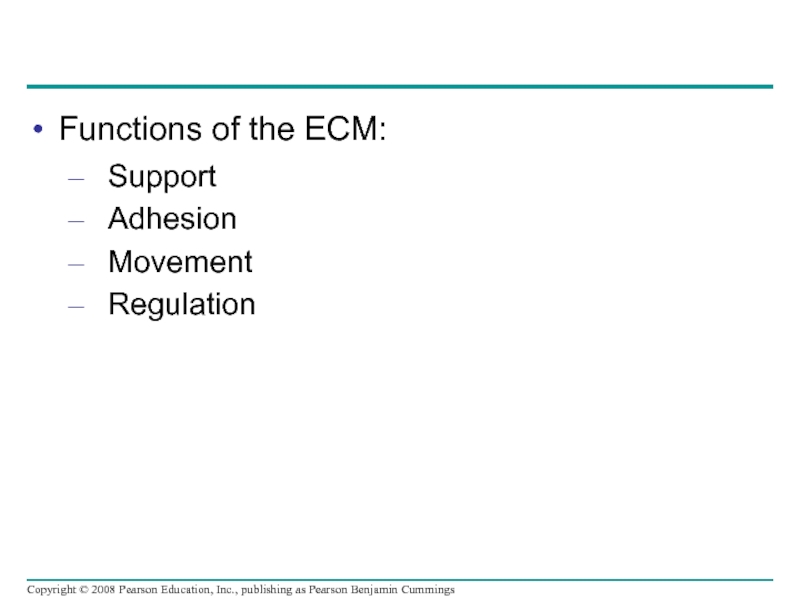
Слайд 105Functions of the ECM:
Support
Adhesion
Movement
Regulation
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as
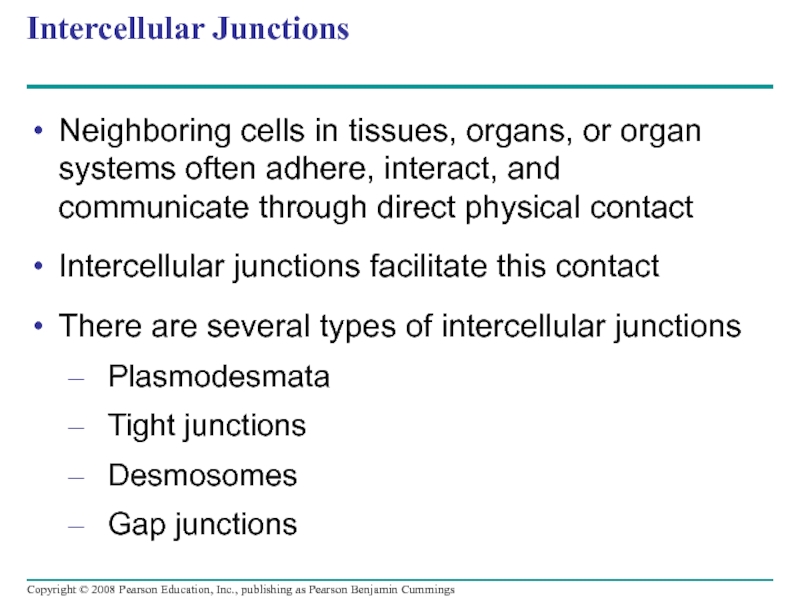
Слайд 106Intercellular Junctions
Neighboring cells in tissues, organs, or organ systems often adhere,
Intercellular junctions facilitate this contact
There are several types of intercellular junctions
Plasmodesmata
Tight junctions
Desmosomes
Gap junctions
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
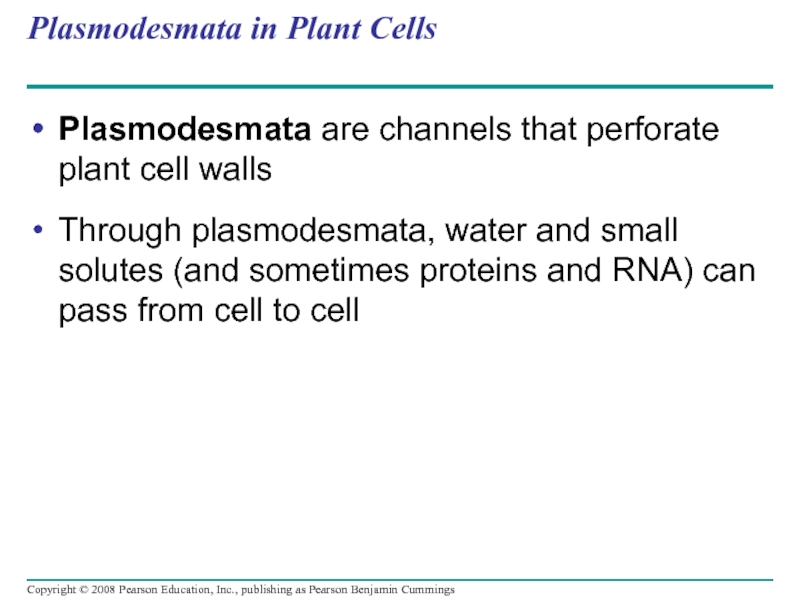
Слайд 107Plasmodesmata in Plant Cells
Plasmodesmata are channels that perforate plant cell walls
Through
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
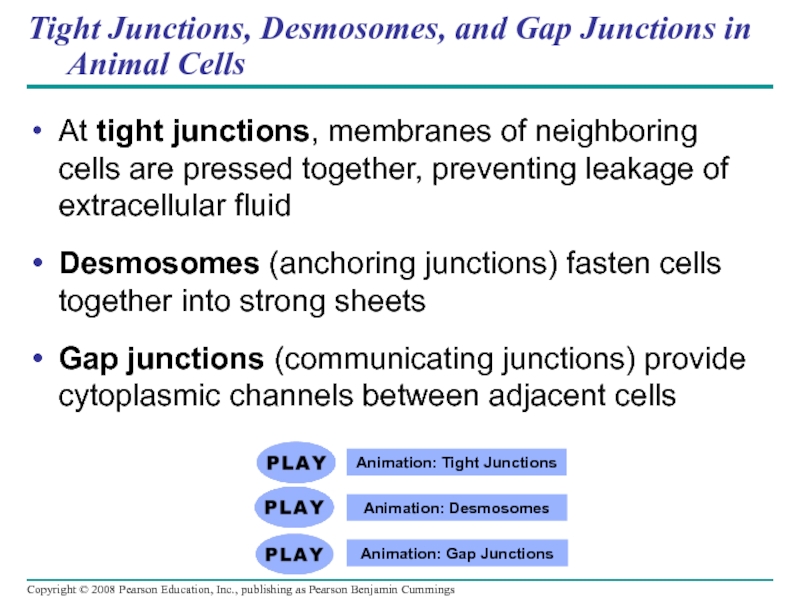
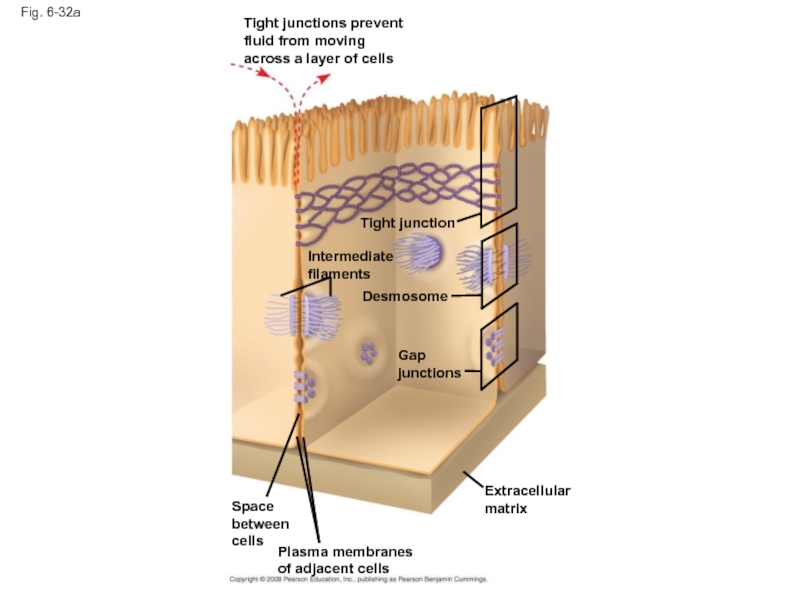
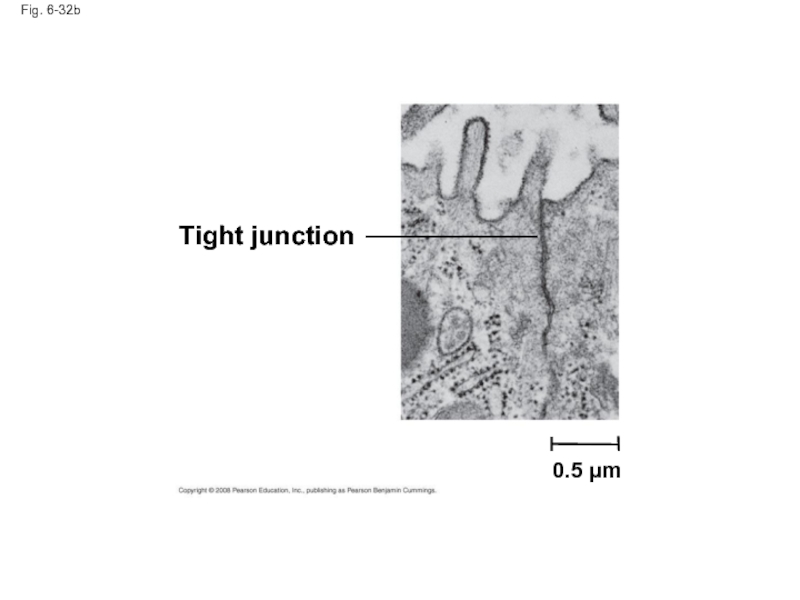
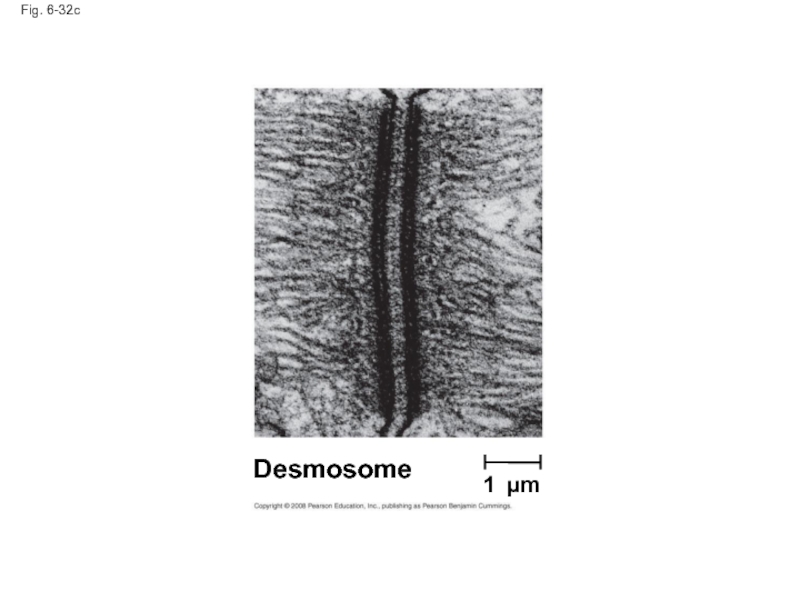
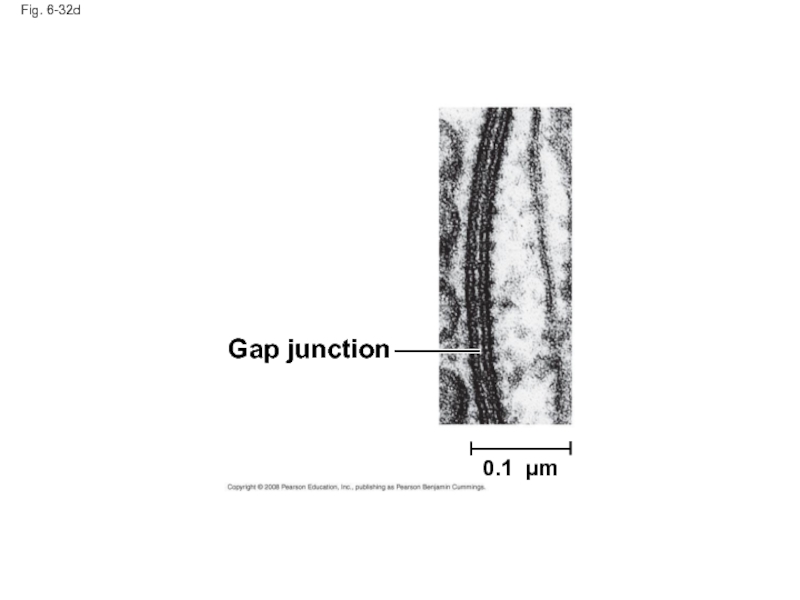
Слайд 109Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, and Gap Junctions in Animal Cells
At tight junctions,
Desmosomes (anchoring junctions) fasten cells together into strong sheets
Gap junctions (communicating junctions) provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells
Animation: Tight Junctions
Animation: Desmosomes
Animation: Gap Junctions
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
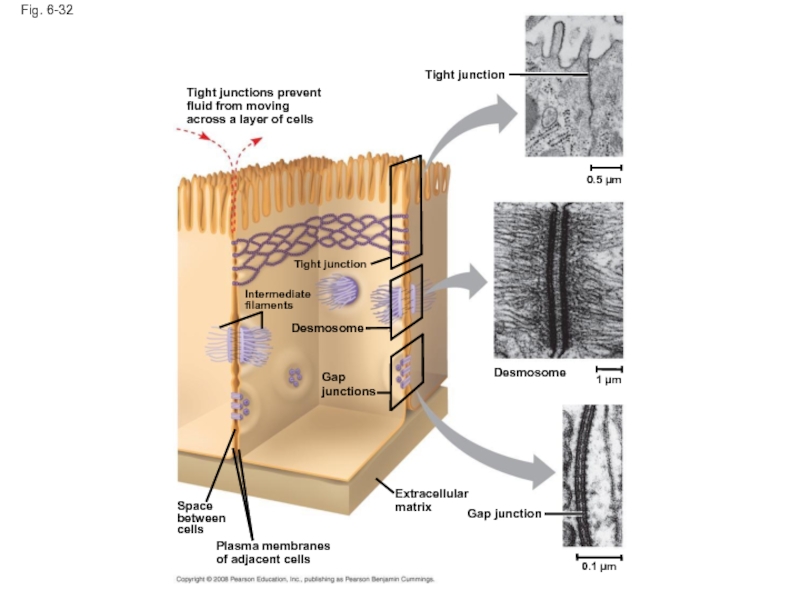
Слайд 110Fig. 6-32
Tight junction
0.5 µm
1 µm
Desmosome
Gap junction
Extracellular
matrix
0.1 µm
Plasma membranes
of adjacent cells
Space
between
cells
Gap
junctions
Desmosome
Intermediate
filaments
Tight junction
Tight
fluid from moving
across a layer of cells
Слайд 111Fig. 6-32a
Tight junctions prevent fluid from moving across a layer of
Tight junction
Intermediate filaments
Desmosome
Gap junctions
Extracellular matrix
Space between cells
Plasma membranes of adjacent cells
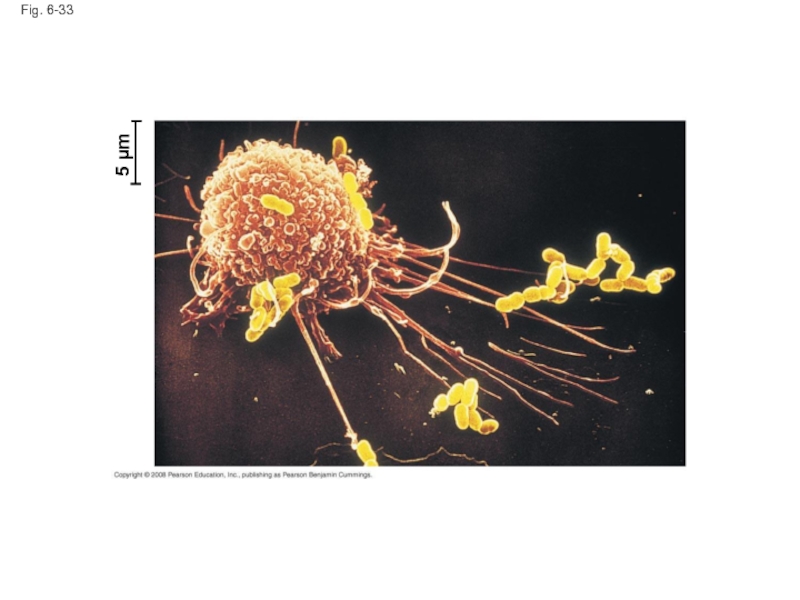
Слайд 115The Cell: A Living Unit Greater Than the Sum of Its
Cells rely on the integration of structures and organelles in order to function
For example, a macrophage’s ability to destroy bacteria involves the whole cell, coordinating components such as the cytoskeleton, lysosomes, and plasma membrane
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
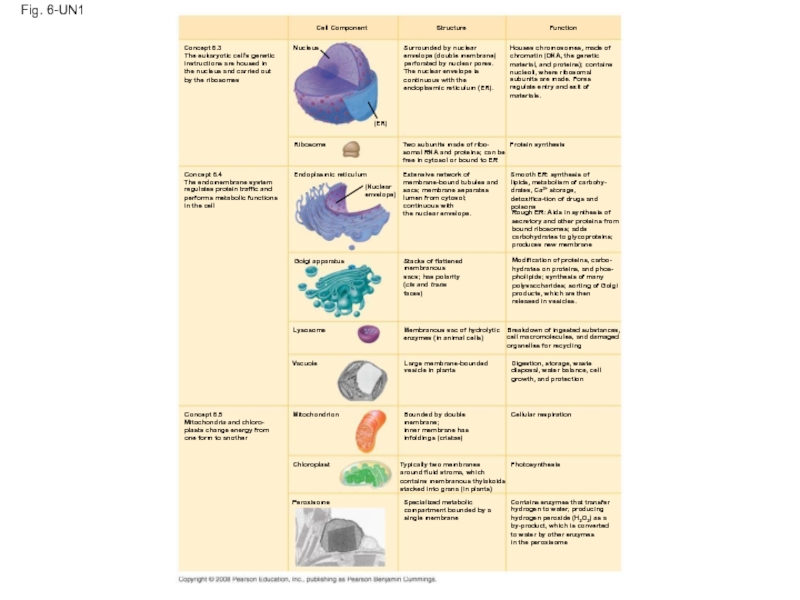
Слайд 117Fig. 6-UN1
Cell Component
Structure
Function
Houses chromosomes, made of
chromatin (DNA, the
material, and proteins); contains
nucleoli, where ribosomal
subunits are made. Pores
regulate entry and exit of
materials.
Nucleus
(ER)
Concept 6.3
The eukaryotic cell’s genetic
instructions are housed in
the nucleus and carried out
by the ribosomes
Ribosome
Concept 6.4
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endomembrane system
regulates protein traffic and
performs metabolic functions
in the cell
(Nuclear
envelope)
Concept 6.5
Mitochondria and chloro-
plasts change energy from
one form to another
Golgi apparatus
Lysosome
Vacuole
Mitochondrion
Chloroplast
Peroxisome
Two subunits made of ribo-
somal RNA and proteins; can be
free in cytosol or bound to ER
Extensive network of
membrane-bound tubules and
sacs; membrane separates
lumen from cytosol;
continuous with
the nuclear envelope.
Membranous sac of hydrolytic
enzymes (in animal cells)
Large membrane-bounded
vesicle in plants
Bounded by double
membrane;
inner membrane has
infoldings (cristae)
Typically two membranes
around fluid stroma, which
contains membranous thylakoids
stacked into grana (in plants)
Specialized metabolic
compartment bounded by a
single membrane
Protein synthesis
Smooth ER: synthesis of
lipids, metabolism of carbohy-
drates, Ca2+ storage, detoxifica-tion of drugs and poisons
Rough ER: Aids in synthesis of
secretory and other proteins from
bound ribosomes; adds
carbohydrates to glycoproteins;
produces new membrane
Modification of proteins, carbo-
hydrates on proteins, and phos-
pholipids; synthesis of many
polysaccharides; sorting of Golgi
products, which are then
released in vesicles.
Breakdown of ingested substances,
cell macromolecules, and damaged
organelles for recycling
Digestion, storage, waste
disposal, water balance, cell
growth, and protection
Cellular respiration
Photosynthesis
Contains enzymes that transfer
hydrogen to water, producing
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a
by-product, which is converted
to water by other enzymes
in the peroxisome
Stacks of flattened
membranous
sacs; has polarity
(cis and trans
faces)
Surrounded by nuclear
envelope (double membrane)
perforated by nuclear pores.
The nuclear envelope is
continuous with the
endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
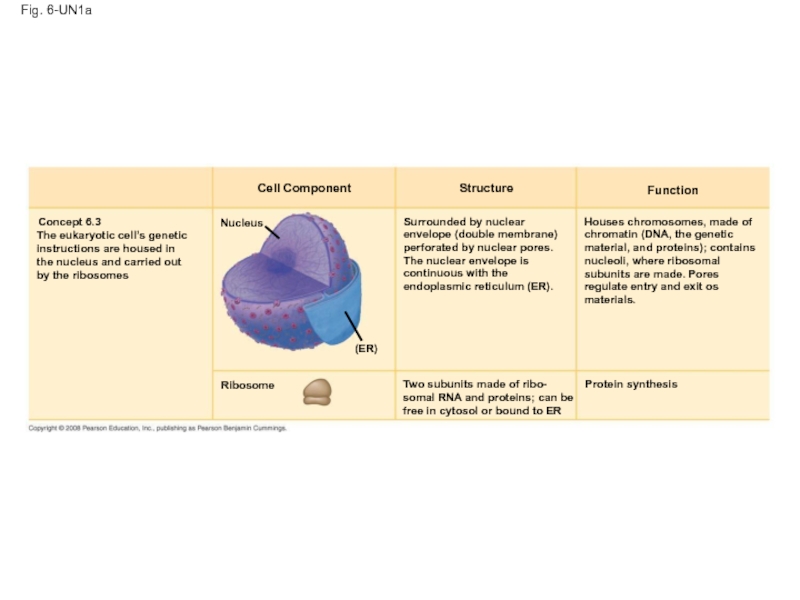
Слайд 118Fig. 6-UN1a
Cell Component
Structure
Function
Concept 6.3
The eukaryotic cell’s genetic
instructions
the nucleus and carried out
by the ribosomes
Nucleus
Surrounded by nuclear
envelope (double membrane)
perforated by nuclear pores.
The nuclear envelope is
continuous with the
endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
(ER)
Houses chromosomes, made of
chromatin (DNA, the genetic
material, and proteins); contains
nucleoli, where ribosomal
subunits are made. Pores
regulate entry and exit os
materials.
Ribosome
Two subunits made of ribo-
somal RNA and proteins; can be
free in cytosol or bound to ER
Protein synthesis
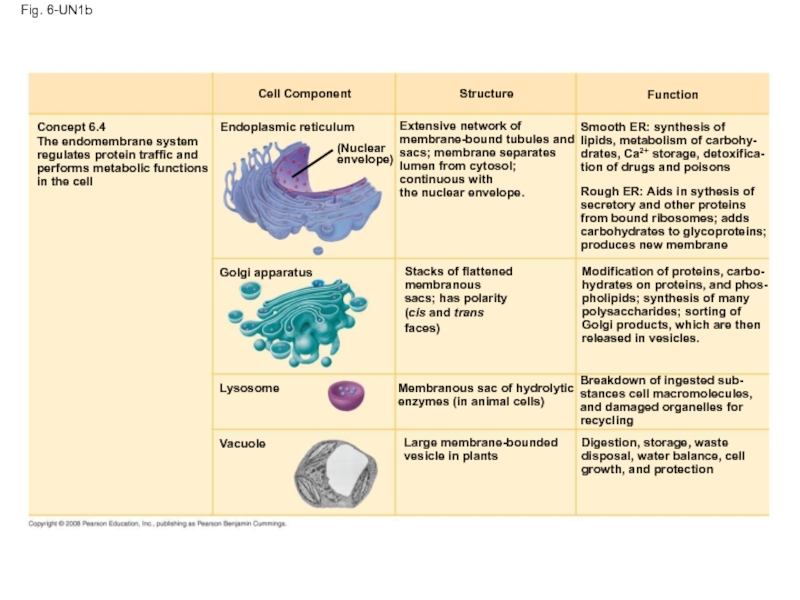
Слайд 119Fig. 6-UN1b
Cell Component
Structure
Function
Concept 6.4
The endomembrane system
regulates protein
performs metabolic functions
in the cell
Endoplasmic reticulum
(Nuclear
envelope)
Golgi apparatus
Lysosome
Vacuole
Large membrane-bounded
vesicle in plants
Membranous sac of hydrolytic
enzymes (in animal cells)
Stacks of flattened
membranous
sacs; has polarity
(cis and trans
faces)
Extensive network of
membrane-bound tubules and
sacs; membrane separates
lumen from cytosol;
continuous with
the nuclear envelope.
Smooth ER: synthesis of
lipids, metabolism of carbohy-
drates, Ca2+ storage, detoxifica-
tion of drugs and poisons
Rough ER: Aids in sythesis of
secretory and other proteins
from bound ribosomes; adds
carbohydrates to glycoproteins;
produces new membrane
Modification of proteins, carbo-
hydrates on proteins, and phos-
pholipids; synthesis of many
polysaccharides; sorting of
Golgi products, which are then
released in vesicles.
Breakdown of ingested sub-
stances cell macromolecules, and damaged organelles for recycling
Digestion, storage, waste
disposal, water balance, cell
growth, and protection
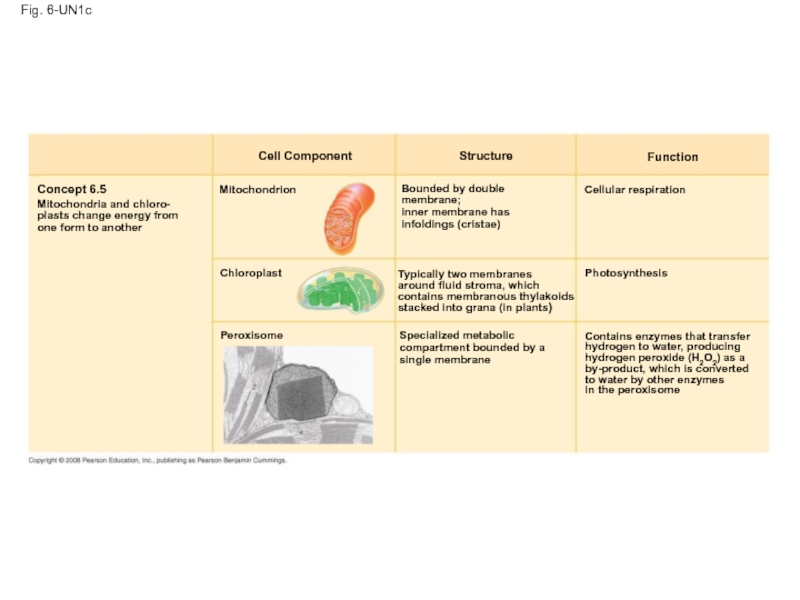
Слайд 120Fig. 6-UN1c
Cell Component
Concept 6.5
Mitochondria and chloro-
plasts change energy from
one form
Mitochondrion
Chloroplast
Peroxisome
Structure
Function
Bounded by double
membrane;
inner membrane has
infoldings (cristae)
Typically two membranes
around fluid stroma, which
contains membranous thylakoids
stacked into grana (in plants)
Specialized metabolic
compartment bounded by a
single membrane
Cellular respiration
Photosynthesis
Contains enzymes that transfer
hydrogen to water, producing
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a
by-product, which is converted
to water by other enzymes
in the peroxisome
Слайд 123You should now be able to:
Distinguish between the following pairs of
Describe the structure and function of the components of the endomembrane system
Briefly explain the role of mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes
Describe the functions of the cytoskeleton
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Слайд 124Compare the structure and functions of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments
Explain
Describe the structure of a plant cell wall
Describe the structure and roles of the extracellular matrix in animal cells
Describe four different intercellular junctions
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings