- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Commercial Hydroponics Viability & Economic Preview презентация
Содержание
- 1. Commercial Hydroponics Viability & Economic Preview
- 2. “I am delighted that HGTIPL is being
- 3. Agenda Executive summary
- 4. Importance of water
- 5. What does a plant need to grow
- 6. Executive Summary
- 7. Executive Summary The Issue facing us Need
- 8. Presentation aims to Hydroponics Make you aware
- 9. What is Hydroponics
- 10. Basics of Hydroponics Vegetables grown from simple
- 11. Types of hydroponics – based on water
- 12. Types of hydroponics – disposal of nutrient
- 13. Types of hydroponics – based on medium
- 14. Types of hydroponic systems Nutrient Film Technique
- 15. Types of hydroponic systems Drip Method Deep
- 16. Primary benefits of Hydroponic cultivation Reduced labor
- 17. Secondary benefits Plants in hydroponics gain in
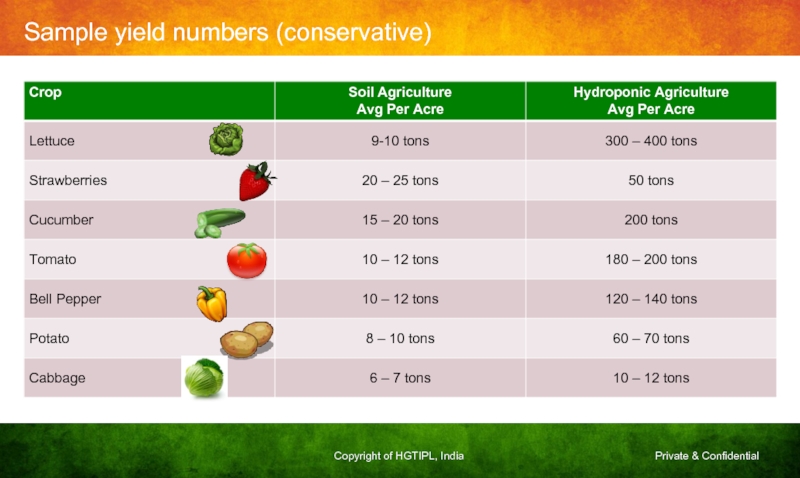
- 18. Sample yield numbers (conservative)
- 19. Market takers for hydroponic plants
- 20. Hydroponic agriculture – the global outlook Global
- 21. How is it implemented
- 22. Standards Laws Water Source Container System
- 23. Plants grown in hydroponic systems Tomato's Lettuce Bell Pepper Cucumber Strawberries Water Lemon Potato Onion
- 24. Nutrient Solutions / Fertilizer Introduction Plant nutrients
- 25. Implementation process The HGTIPL assisted implementation process
- 26. Implementation process details
- 27. Hydroponics in India
- 28. Opportunity in India Production and labor
- 29. Catalyst for hydroponic farming in India
- 30. SWOT analysis for hydroponic farming Makes any
- 31. Challenges in India to overcome Capital costs
- 32. Commercial Viability
- 33. Cost buckets Capital costs Operational costs Drip
- 34. Revenue flow (when land is owned) Revenue
- 35. Revenue flow (when land is bought) Revenue
- 36. Revenue flow (when land is leased) Revenue
- 37. Reasons for failure Venture not established in
- 38. Who we are
- 39. Who we are CV Prakash The Farmer
- 40. How can we help
- 41. How can we help Setting up of
- 42. Success Stories
- 43. Some successful commercial installations Hydroponic Strawberry System
- 44. Thank You
Слайд 2“I am delighted that HGTIPL is being given this opportunity to
I am a former Officer of the Indian Navy. Upon my retirement, I migrated to Australia in 2001. I learnt Hydroponics from the best of growers and consultants in the Hydroponics Industry in Australia and I am a passionate proponent and pioneer in the field of Hydroponics in India.
Our firm is distinguished by the extent of its global knowledge base, in the way we think, the way we work together and the way we are structured to provide the best practices Hydroponics.
I am confident that our well qualified team will consistently exceed your expectations and we honestly believe that we can bring you true value and prosperity on the table.
Farmer-In-Chief
Lt Cdr (retd) CV Prakash
Слайд 3
Agenda
Executive summary
What is Hydroponics
How is it implemented
Hydroponics in India
Commercial Viability
Who we
How can we help
Success stories
Слайд 4Importance of water
Water is Food is
No Water-No Food! Simple
Hydroponics Needs Clean Water
Слайд 5What does a plant need to grow ?
Soil is just a
Sun Light
Nutrients
Soil
Water
Слайд 7Executive Summary
The Issue facing us
Need for a solution
Introduction to Hydroponics
Advantages of
Today Indian farmers face the following challenges
Drought conditions and unpredictable weather
Rising temperatures
Polluted water systems
Lack of irrigation
Poor water management
Under-nourished or over nourished crops
India today needs food security which entails that all people at all times have physical and economic access to safe and nutritious food to meet dietary needs.
Lack of water for agriculture leads to production of lesser food which means more hunger and malnutrition
We are going to highlight the need for technology in agriculture that can contribute towards water savings and have a positive impact on food production and availability.
Hydroponics is one methodology of soil-less cultivation.
It is a method of growing plants using mineral nutrient solutions, in water, without soil.
The earliest published work on growing terrestrial plants without soil was the 1627 book Sylva Sylvarum by Francis Bacon.
Some of the reasons why hydroponics is being adopted around the world for food production are the following:
No soil is needed for hydroponics
The water stays in the system and can be reused
It is possible to control the nutrition levels accurately
It is stable and provides high yields hence economically viable
Pests and diseases are easier to get rid of
Ease of harvesting
It is better for consumption
Слайд 8Presentation aims to
Hydroponics
Make you aware of
Describe advantages of
Implementation strategy
Commercial viability of
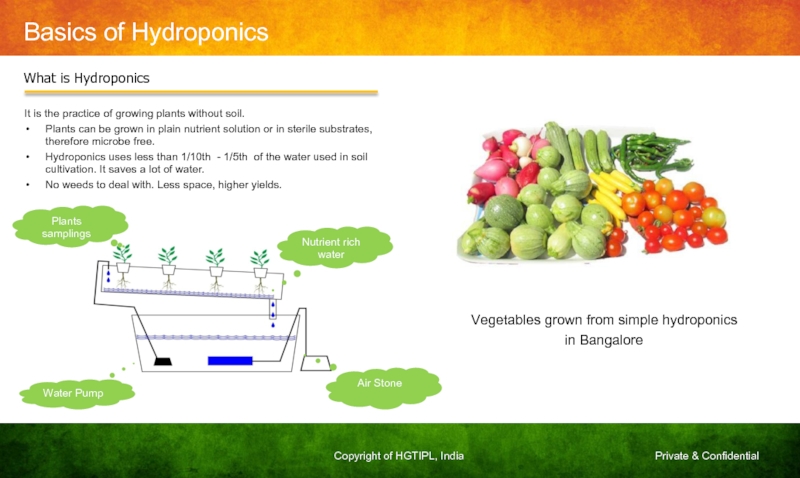
Слайд 10Basics of Hydroponics
Vegetables grown from simple hydroponics
in Bangalore
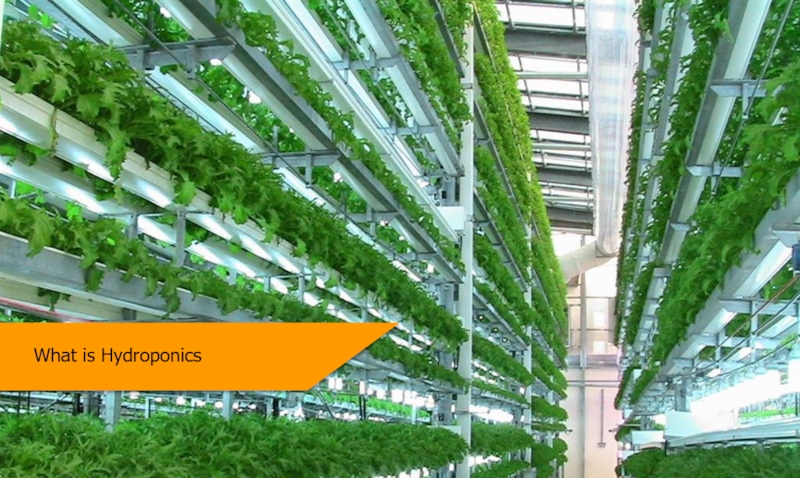
What is Hydroponics
It
Plants can be grown in plain nutrient solution or in sterile substrates, therefore microbe free.
Hydroponics uses less than 1/10th - 1/5th of the water used in soil cultivation. It saves a lot of water.
No weeds to deal with. Less space, higher yields.
Nutrient rich water
Air Stone
Water Pump
Plants samplings
Слайд 11Types of hydroponics – based on water flow
Static solution culture
Continuous
In static solution culture, plants are grown in containers of nutrient solution, such as glass jars, plastic buckets, tubs, or tanks. The solution is usually gently aerated but may be un-aerated. A hole is cut in the lid of the reservoir for each plant. There can be one to many plants per reservoir. A home made system can be constructed from plastic food containers or glass canning jars with aeration provided by an aquarium pump, aquarium airline tubing and aquarium valves.
In continuous-flow solution culture, the nutrient solution constantly flows past the roots. It is much easier to automate than the static solution culture because sampling and adjustments to the temperature and nutrient concentrations can be made in a large storage tank together. A popular variation is the nutrient film technique or NFT, whereby a very shallow stream of water containing all the dissolved nutrients is recirculated past the bare roots of plants in a watertight thick root mat, which develops in the bottom of the channel. Subsequent to this, an abundant supply of oxygen is provided to the roots of the plants.
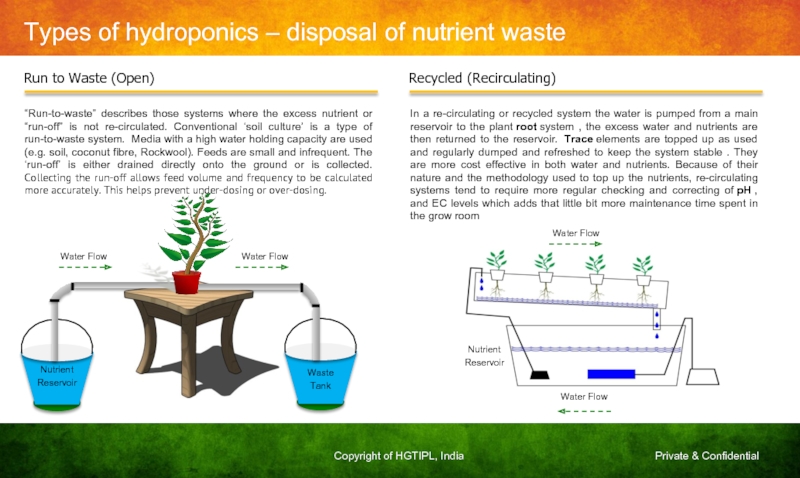
Слайд 12Types of hydroponics – disposal of nutrient waste
Run to Waste
Recycled (Recirculating)
Nutrient
Reservoir
Waste
Tank
“Run-to-waste” describes those systems where the excess nutrient or “run-off” is not re-circulated. Conventional ‘soil culture’ is a type of run-to-waste system. Media with a high water holding capacity are used (e.g. soil, coconut fibre, Rockwool). Feeds are small and infrequent. The ‘run-off’ is either drained directly onto the ground or is collected. Collecting the run-off allows feed volume and frequency to be calculated more accurately. This helps prevent under-dosing or over-dosing.
Water Flow
In a re-circulating or recycled system the water is pumped from a main reservoir to the plant root system , the excess water and nutrients are then returned to the reservoir. Trace elements are topped up as used and regularly dumped and refreshed to keep the system stable . They are more cost effective in both water and nutrients. Because of their nature and the methodology used to top up the nutrients, re-circulating systems tend to require more regular checking and correcting of pH , and EC levels which adds that little bit more maintenance time spent in the grow room
Nutrient
Reservoir
Water Flow
Water Flow
Water Flow
Слайд 13Types of hydroponics – based on medium / substrates
Expanded clay aggregate
Growstones
Baked
Growstones, made from glass waste, have both more air and water retention space than perlite and peat. This aggregate holds more water than parboiled rice hulls.
Coir
Perlite
Coco Peat, also known as coir or coco, is the leftover material after the fibres have been removed from the outermost shell (bolster) of the coconut. Coir is a 100% natural grow and flowering medium. Coconut Coir is colonized with Trichoderma Fungi, which protects roots and stimulates root growth.
Perlite is a volcanic rock that has been superheated into very lightweight expanded glass pebbles. It is used loose or in plastic sleeves immersed in the water. It is also used in potting soil mixes to decrease soil density.
Sand
Gravel
Sand is cheap and easily available. However, it is heavy, does not hold water very well, and it must be sterilized between use.
The same type that is used in aquariums, though any small gravel can be used, provided it is washed first. Indeed, plants growing in a typical traditional gravel filter bed, with water circulated using electric powerhead pumps, are in effect being grown using gravel hydroponics. Gravel is inexpensive, easy to keep clean, drains well and will not become waterlogged.
Слайд 14Types of hydroponic systems
Nutrient Film Technique
Ebb and flow
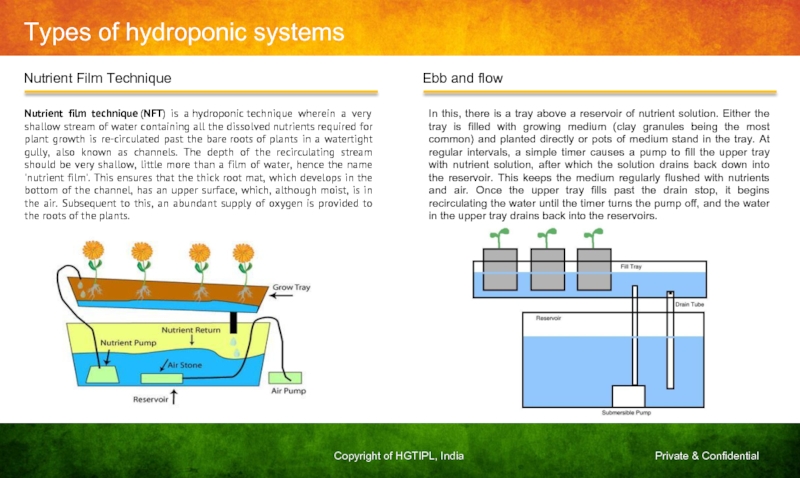
Nutrient film technique (NFT) is
In this, there is a tray above a reservoir of nutrient solution. Either the tray is filled with growing medium (clay granules being the most common) and planted directly or pots of medium stand in the tray. At regular intervals, a simple timer causes a pump to fill the upper tray with nutrient solution, after which the solution drains back down into the reservoir. This keeps the medium regularly flushed with nutrients and air. Once the upper tray fills past the drain stop, it begins recirculating the water until the timer turns the pump off, and the water in the upper tray drains back into the reservoirs.
Слайд 15Types of hydroponic systems
Drip Method
Deep water
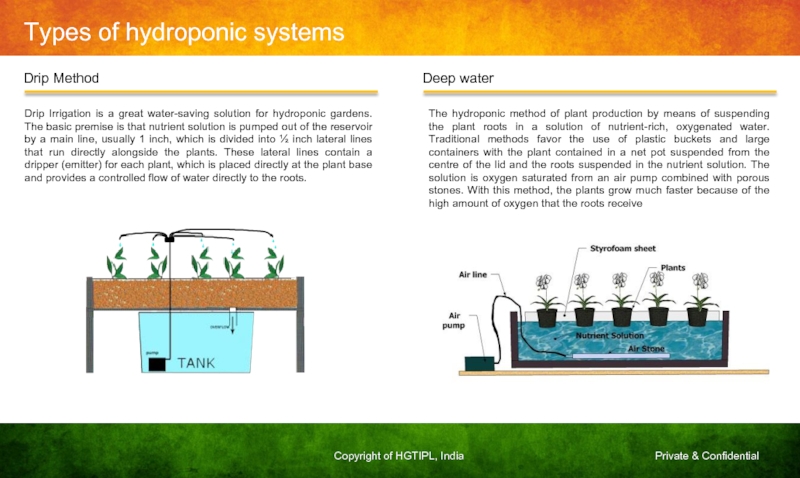
Drip Irrigation is a great water-saving
The hydroponic method of plant production by means of suspending the plant roots in a solution of nutrient-rich, oxygenated water. Traditional methods favor the use of plastic buckets and large containers with the plant contained in a net pot suspended from the centre of the lid and the roots suspended in the nutrient solution. The solution is oxygen saturated from an air pump combined with porous stones. With this method, the plants grow much faster because of the high amount of oxygen that the roots receive
Слайд 16Primary benefits of Hydroponic cultivation
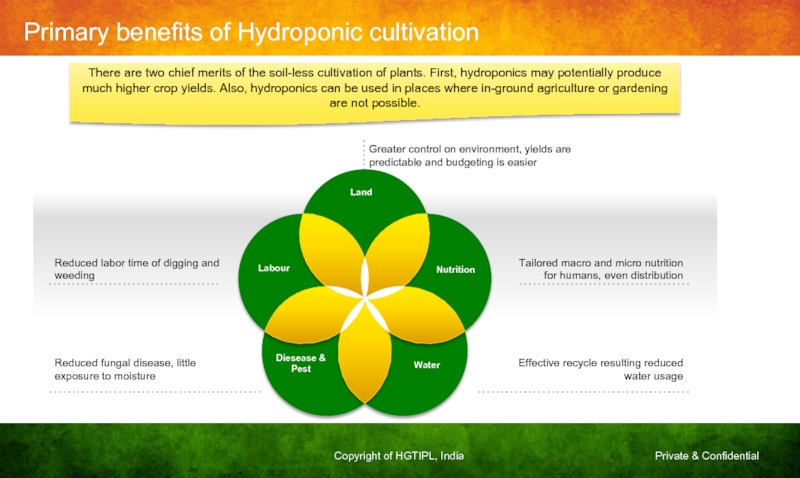
Reduced labor time of digging and weeding
Reduced
Greater control on environment, yields are predictable and budgeting is easier
Tailored macro and micro nutrition for humans, even distribution
Effective recycle resulting reduced water usage
Land
Labour
Nutrition
Diesease &
Pest
Water
There are two chief merits of the soil-less cultivation of plants. First, hydroponics may potentially produce much higher crop yields. Also, hydroponics can be used in places where in-ground agriculture or gardening are not possible.
Слайд 17Secondary benefits
Plants in hydroponics gain in
Plants are protected from UV
Offers safe biological control of insects and pests
Water is reused effectively
Allows nutrients to be reclaimed, re-balanced and re-used
Can be protected from unpredictable weather patterns
Have a good root system that is not at risk from contaminants and diseases
Make efficient use of labour, which is increasingly expensive
Produce outstanding crops by using optimum nutrient formulations
Production in Off season possible when market prices are highest.
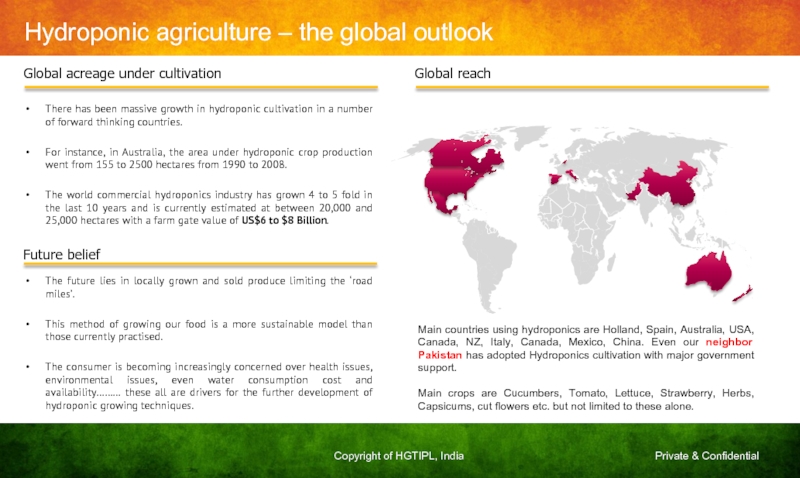
Слайд 20Hydroponic agriculture – the global outlook
Global acreage under cultivation
There has been
For instance, in Australia, the area under hydroponic crop production went from 155 to 2500 hectares from 1990 to 2008.
The world commercial hydroponics industry has grown 4 to 5 fold in the last 10 years and is currently estimated at between 20,000 and 25,000 hectares with a farm gate value of US$6 to $8 Billion.
Future belief
The future lies in locally grown and sold produce limiting the ‘road miles’.
This method of growing our food is a more sustainable model than those currently practised.
The consumer is becoming increasingly concerned over health issues, environmental issues, even water consumption cost and availability……… these all are drivers for the further development of hydroponic growing techniques.
Global reach
Main countries using hydroponics are Holland, Spain, Australia, USA, Canada, NZ, Italy, Canada, Mexico, China. Even our neighbor Pakistan has adopted Hydroponics cultivation with major government support.
Main crops are Cucumbers, Tomato, Lettuce, Strawberry, Herbs, Capsicums, cut flowers etc. but not limited to these alone.
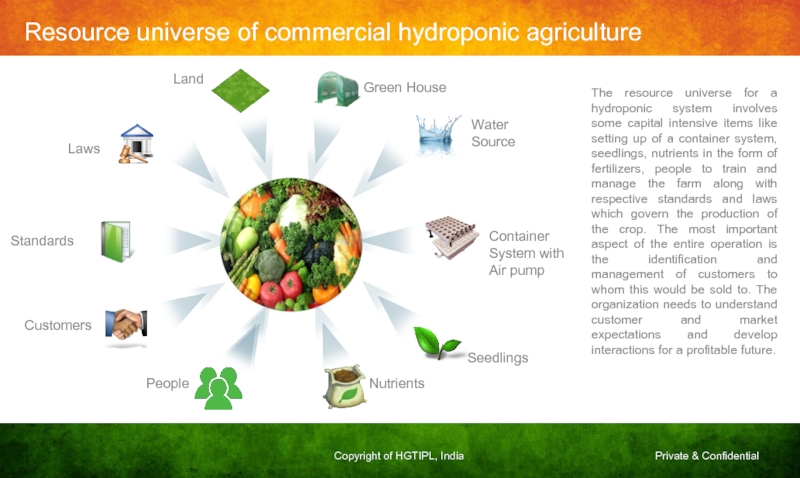
Слайд 22Standards
Laws
Water
Source
Container
System with
Air pump
Seedlings
Customers
People
Land
Nutrients
Green House
The resource universe for a hydroponic system
Resource universe of commercial hydroponic agriculture
Слайд 23Plants grown in hydroponic systems
Tomato's
Lettuce
Bell Pepper
Cucumber
Strawberries
Water Lemon
Potato
Onion
Слайд 24Nutrient Solutions / Fertilizer
Introduction
Plant nutrients used in hydroponics are dissolved in
Nutrient recipe
Numerous 'recipes' for hydroponic solutions are available. Many use different combinations of chemicals to reach similar total final compositions. Commonly used chemicals for the macronutrients include potassium nitrate, calcium nitrate, potassium phosphate, and magnesium sulfate. Various micronutrients are typically added to hydroponic solutions to supply essential elements; among them are Fe (iron), Mn (manganese), Cu (copper), Zn (zinc), B (boron), Cl (chlorine), and Ni (nickel).
Pre-mixed concentrated nutrient solutions are generally purchased from commercial nutrient manufacturers by hydroponic hobbyists and small commercial growers, several tools exists to help anyone prepare their own solutions without extensive knowledge about chemistry.
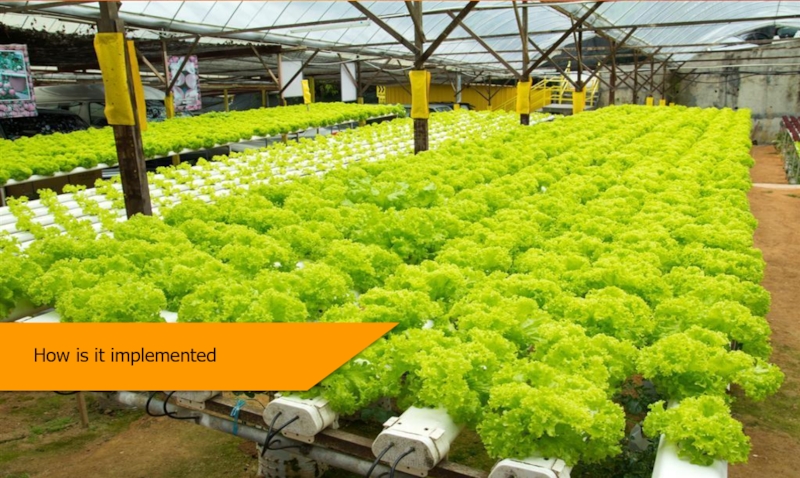
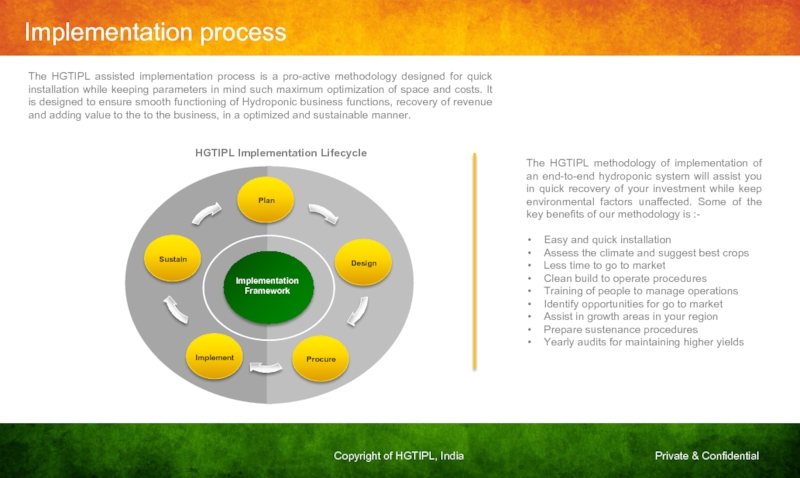
Слайд 25Implementation process
The HGTIPL assisted implementation process is a pro-active methodology designed
Sustain
Implement
Procure
Design
Plan
Implementation
Framework
HGTIPL Implementation Lifecycle
The HGTIPL methodology of implementation of an end-to-end hydroponic system will assist you in quick recovery of your investment while keep environmental factors unaffected. Some of the key benefits of our methodology is :-
Easy and quick installation
Assess the climate and suggest best crops
Less time to go to market
Clean build to operate procedures
Training of people to manage operations
Identify opportunities for go to market
Assist in growth areas in your region
Prepare sustenance procedures
Yearly audits for maintaining higher yields
Слайд 28Opportunity in India
Production and labor costs in developed countries are increasing
India has rich climatic conditions positioning us favorably to market such produce.
Labor costs in India as well as inputs makes India an ideal destination for food outsourcing.
Indian producers can address both domestic as well as International markets such as ME/EU/USA/Far East.
Has intelligent manpower. Can learn fast the operating protocols.
Usually gets a better price based on looks, texture, taste, consistency on daily basis, high nutrition value, reliable supply year round etc.
A country that can produce super-computers, satellites can definitely adopt Hydroponics easily in the author’s view.
Development in India
Marketing channels in India
Wholesale Channels
Retail Channels
Supermarket chains/Export markets.
Cooperatives to help sell their produce.
Producers specialize in one or two types of produce mainly and have full control over their produce.
Outside India
Sales opportunities abound from Indian producers due to better production costing achievable.
Markets are in USA, EU, Far and Middle East.
India has excellent connectivity to above by land, sea and air.
Freight costs from India are high at this time and with better governmental support can be alleviated.
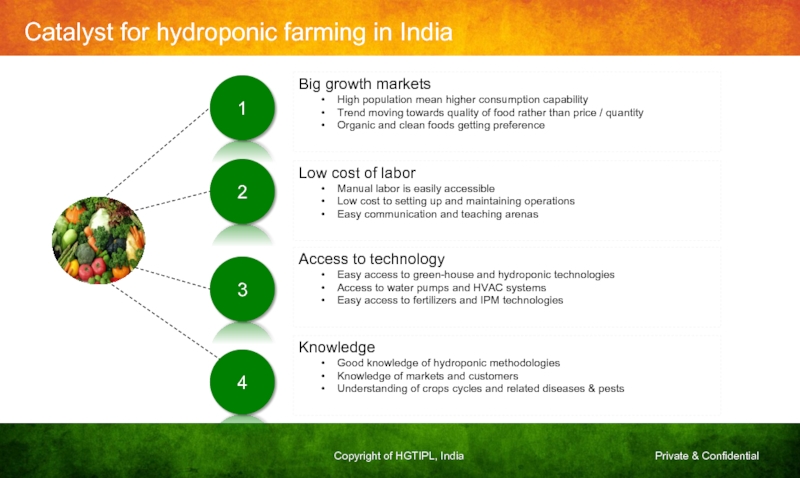
Слайд 29Catalyst for hydroponic farming in India
1
2
3
4
Big growth markets
High population mean higher
Trend moving towards quality of food rather than price / quantity
Organic and clean foods getting preference
Low cost of labor
Manual labor is easily accessible
Low cost to setting up and maintaining operations
Easy communication and teaching arenas
Access to technology
Easy access to green-house and hydroponic technologies
Access to water pumps and HVAC systems
Easy access to fertilizers and IPM technologies
Knowledge
Good knowledge of hydroponic methodologies
Knowledge of markets and customers
Understanding of crops cycles and related diseases & pests
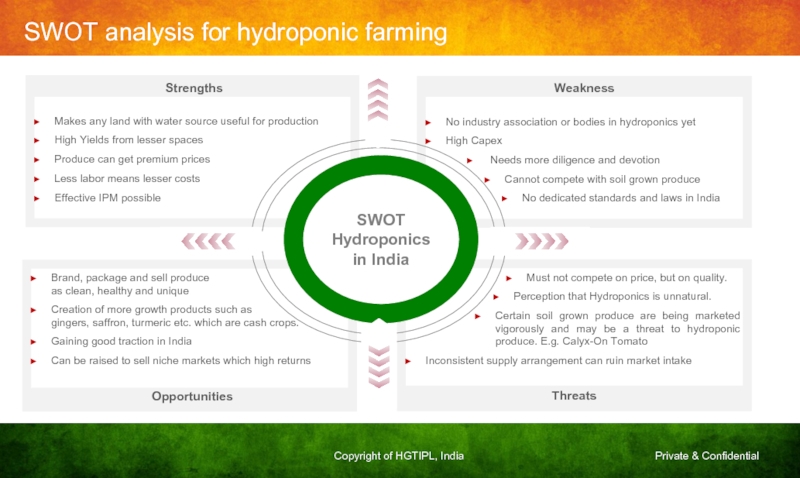
Слайд 30SWOT analysis for hydroponic farming
Makes any land with water source useful
High Yields from lesser spaces
Produce can get premium prices
Less labor means lesser costs
Effective IPM possible
Brand, package and sell produce
as clean, healthy and unique
Creation of more growth products such as
gingers, saffron, turmeric etc. which are cash crops.
Gaining good traction in India
Can be raised to sell niche markets which high returns
No industry association or bodies in hydroponics yet
High Capex
Needs more diligence and devotion
Cannot compete with soil grown produce
No dedicated standards and laws in India
Must not compete on price, but on quality.
Perception that Hydroponics is unnatural.
Certain soil grown produce are being marketed vigorously and may be a threat to hydroponic produce. E.g. Calyx-On Tomato
Inconsistent supply arrangement can ruin market intake
SWOT
Hydroponics in India
Weakness
Threats
Strengths
Opportunities
Слайд 31Challenges in India to overcome
Capital costs
Trained Manpower
Education required
Attention to shifting market
Attention to crop growing or cultural practices
Knowledge of IPM
Knowledge of Environment Controls in GH
Knowledge of Climate Controls
Knowledge of Bio-friendly insects
Indian hydroponic practitioners needs to overcome
Body of knowledge
We need to convene an association in India for Commercial Hydroponic Growers even before we start the first commercial system in our country.
We have a student of Simplified Hydroponics already having an association called Indian Hydroponics Pioneers Association.
Formulate industry standards
We need to use foreign Hydroponic experts to start with. This is an absolute must as there are no resource people in India at this time. Industry standards will be established as time goes by and more Indians adopt this kind of cultivation.
Marketing of hydroponic produce
It is marketed more on the quality and consistency, rather than the method of production.
More and more Indians are demanding high quality, pesticide free, fresh produce. Money not the criterion.
People are aware of dangers of pesticides, global warming and its ill effects. Media plays an important role.
Consistency, quality and yields possible only by modern techniques of cultivation.
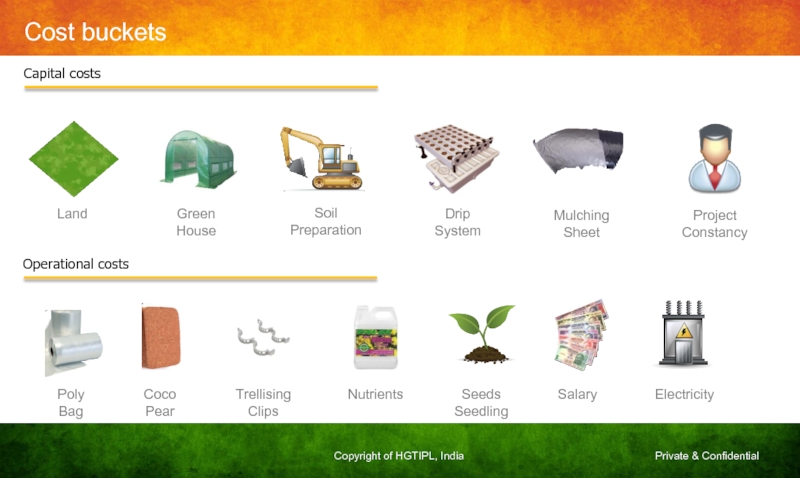
Слайд 33Cost buckets
Capital costs
Operational costs
Drip
System
Land
Green
House
Soil
Preparation
Mulching
Sheet
Project
Constancy
Poly
Bag
Coco
Pear
Trellising
Clips
Nutrients
Seeds
Seedling
Salary
Electricity
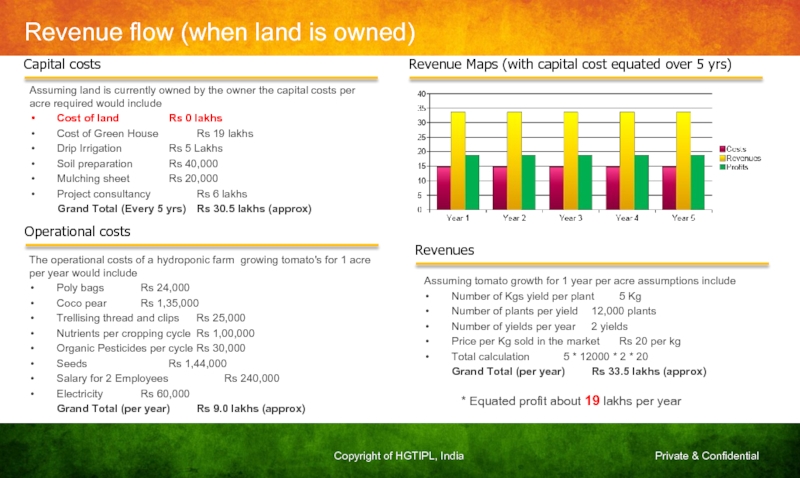
Слайд 34Revenue flow (when land is owned)
Revenue Maps (with capital cost equated
Capital costs
Assuming land is currently owned by the owner the capital costs per acre required would include
Cost of land Rs 0 lakhs
Cost of Green House Rs 19 lakhs
Drip Irrigation Rs 5 Lakhs
Soil preparation Rs 40,000
Mulching sheet Rs 20,000
Project consultancy Rs 6 lakhs
Grand Total (Every 5 yrs) Rs 30.5 lakhs (approx)
Operational costs
The operational costs of a hydroponic farm growing tomato's for 1 acre per year would include
Poly bags Rs 24,000
Coco pear Rs 1,35,000
Trellising thread and clips Rs 25,000
Nutrients per cropping cycle Rs 1,00,000
Organic Pesticides per cycle Rs 30,000
Seeds Rs 1,44,000
Salary for 2 Employees Rs 240,000
Electricity Rs 60,000
Grand Total (per year) Rs 9.0 lakhs (approx)
Revenues
Assuming tomato growth for 1 year per acre assumptions include
Number of Kgs yield per plant 5 Kg
Number of plants per yield 12,000 plants
Number of yields per year 2 yields
Price per Kg sold in the market Rs 20 per kg
Total calculation 5 * 12000 * 2 * 20
Grand Total (per year) Rs 33.5 lakhs (approx)
* Equated profit about 19 lakhs per year
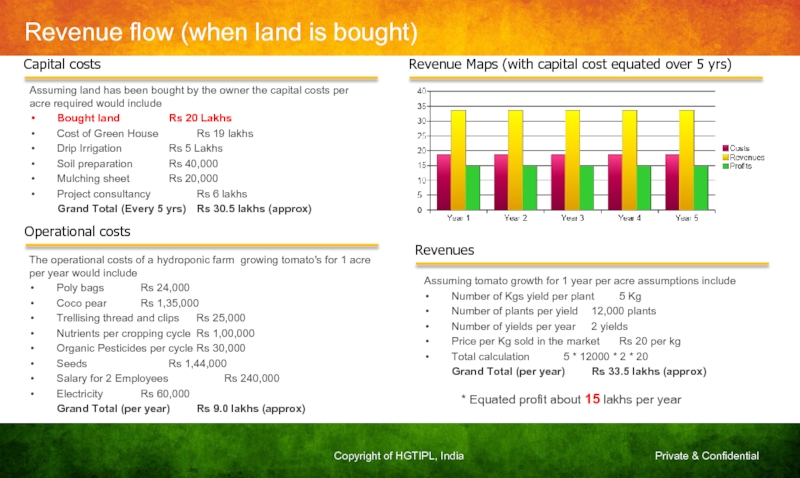
Слайд 35Revenue flow (when land is bought)
Revenue Maps (with capital cost equated
Capital costs
Assuming land has been bought by the owner the capital costs per acre required would include
Bought land Rs 20 Lakhs
Cost of Green House Rs 19 lakhs
Drip Irrigation Rs 5 Lakhs
Soil preparation Rs 40,000
Mulching sheet Rs 20,000
Project consultancy Rs 6 lakhs
Grand Total (Every 5 yrs) Rs 30.5 lakhs (approx)
Operational costs
The operational costs of a hydroponic farm growing tomato's for 1 acre per year would include
Poly bags Rs 24,000
Coco pear Rs 1,35,000
Trellising thread and clips Rs 25,000
Nutrients per cropping cycle Rs 1,00,000
Organic Pesticides per cycle Rs 30,000
Seeds Rs 1,44,000
Salary for 2 Employees Rs 240,000
Electricity Rs 60,000
Grand Total (per year) Rs 9.0 lakhs (approx)
Revenues
Assuming tomato growth for 1 year per acre assumptions include
Number of Kgs yield per plant 5 Kg
Number of plants per yield 12,000 plants
Number of yields per year 2 yields
Price per Kg sold in the market Rs 20 per kg
Total calculation 5 * 12000 * 2 * 20
Grand Total (per year) Rs 33.5 lakhs (approx)
* Equated profit about 15 lakhs per year
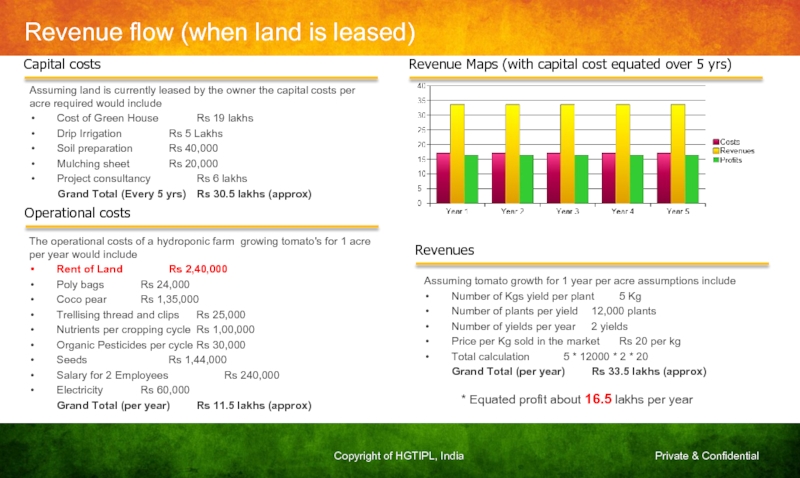
Слайд 36Revenue flow (when land is leased)
Revenue Maps (with capital cost equated
Capital costs
Assuming land is currently leased by the owner the capital costs per acre required would include
Cost of Green House Rs 19 lakhs
Drip Irrigation Rs 5 Lakhs
Soil preparation Rs 40,000
Mulching sheet Rs 20,000
Project consultancy Rs 6 lakhs
Grand Total (Every 5 yrs) Rs 30.5 lakhs (approx)
Operational costs
The operational costs of a hydroponic farm growing tomato's for 1 acre per year would include
Rent of Land Rs 2,40,000
Poly bags Rs 24,000
Coco pear Rs 1,35,000
Trellising thread and clips Rs 25,000
Nutrients per cropping cycle Rs 1,00,000
Organic Pesticides per cycle Rs 30,000
Seeds Rs 1,44,000
Salary for 2 Employees Rs 240,000
Electricity Rs 60,000
Grand Total (per year) Rs 11.5 lakhs (approx)
Revenues
Assuming tomato growth for 1 year per acre assumptions include
Number of Kgs yield per plant 5 Kg
Number of plants per yield 12,000 plants
Number of yields per year 2 yields
Price per Kg sold in the market Rs 20 per kg
Total calculation 5 * 12000 * 2 * 20
Grand Total (per year) Rs 33.5 lakhs (approx)
* Equated profit about 16.5 lakhs per year
Слайд 37Reasons for failure
Venture not established in a realistic economic framework like
Selection of system/crop/markets/correct management not done
Crop production management inadequate
Yield and quality did not meet budget projections
Lack of diligence on part of the crew
Non adherence to growing protocols
Insufficient attention to marketing
Lack of necessary labour
Incorrect pricing of produce
Product not tailored as per demand
Critical matters to be addressed
Profitability is linked to
Production scale, increasing returns to increasing size.
Ability to supply promised amount with quality and consistency
Capacity to Value add and/or
Find and exploit a unique and high return/value market niche
Слайд 39Who we are
CV Prakash
The Farmer In Chief
Mrs.Sangeeta Bojappa Moorthy
Chief of Operations
Hydroponic
Today, we, at HGT, are leaders in this field in India and our hard earned name has transcended international borders.
The “Pet Bharo” Project, meaning in Hindi, ‘Fill Your Tummy’ project and as we fondly christened it so, is a strong brand name, so much so that, when people call us they ask “Is this Pet Bharo? It’s a word synonymous with Indian Hydroponics.
This achievement has been no mean task. It has been nurtured by persistence, hard work, focus, integrity and above all, a strong sense of personality, character and ethos.
When you approach us you will see for yourself how we make it a point to serve you with humility and a very deep urge to help you.
Слайд 41How can we help
Setting up of Turnkey Commercial Hydroponics/Soil-less Greenhouse systems
Consultancy for Hydroponics/Soil-less Cultivation, Feasibility studies and Project Reports.
Training in Basics of Commercial Hydroponics
Setting up broad acre Hydroponics/Soil-less Food Parks with all facilities.
Supplies of Backyard Greenhouse systems Supply of Hydroponic nutrients and soil-less substrates like Coir Peat/Perlite etc.
Conducts seminars with foreign experts on Hydroponics/Soil-less cultivation from time to time.
Water testing facilities and reports rendered.
Supply of testing equipment's for pH/TDS/EC/Temperature probes etc.
Our key activities
Слайд 43Some successful commercial installations
Hydroponic Strawberry System
The Institute of Simplified Hydroponics
Hydroponics Lettuce/Herbs System
ISH bagged on 23rd March 2011, its second Commercial Hydroponics Lettuce/Herbs order" from a client in Coimbatore. This within three months of its first commercial hydroponics greenhouse order to set up a strawberry greenhouse at Bangalore. The state of the art Lettuce/Herbs Greenhouse will initially start with a one acre pilot expanding to 4 acres in next one year.