- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Tax law. (Lecture 1) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Tax law. (Lecture 1)
- 2. PIT (Personal Income Tax) – ИПН (Индивидуальный
- 3. Tax Burden under Employment Contract; Tax Burden
- 4. Tax Legislation is based on the: Constitution;
- 5. Tax Law regulate the government-directed relations associated
- 6. Sub-par.34 par.1 art.1 TC Taxes - obligatory
- 7. Subject of the tax law – taxpayer
- 8. Article 27. A Taxable Item and (or)
- 9. Principle of Personal Law – attraction of
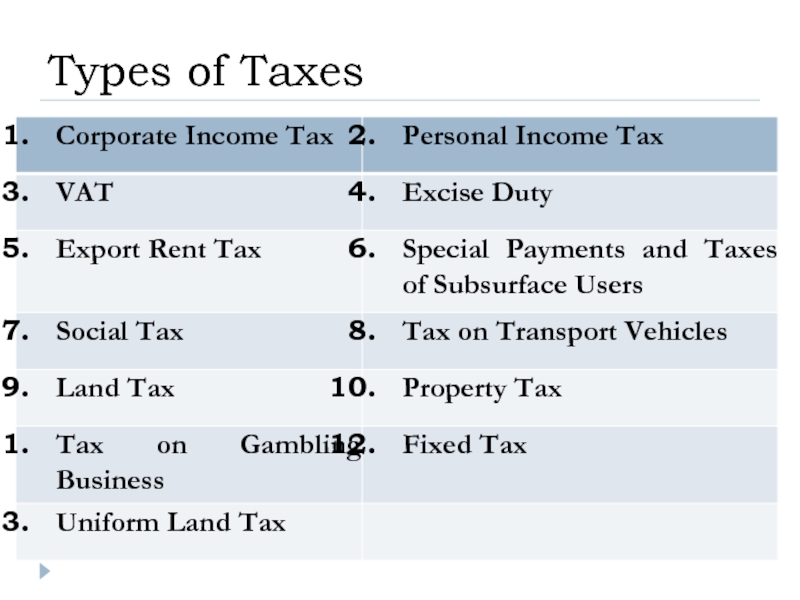
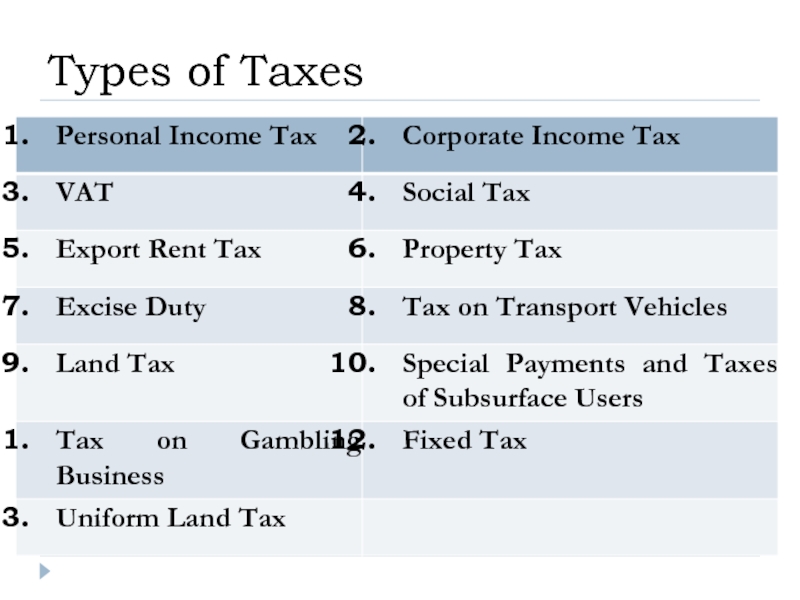
- 10. Types of Taxes
- 11. VAT, taxable items: taxable turnovers (selling goods,
- 12. Excisable Products: Alcohol; Tobacco; Gasoline; Diesel; Crude
- 13. Export Rent Tax: Crude Oil; Gas Condensate;
- 14. Hydrocarbon Resources; Solid Minerals; Common Minerals.
- 15. Paid by the owners of the Real-Estate; Subsurface Users Property Tax:
- 16. Article 26. Tax Liability The tax liability
- 17. Who has to pay PIT? Subjects
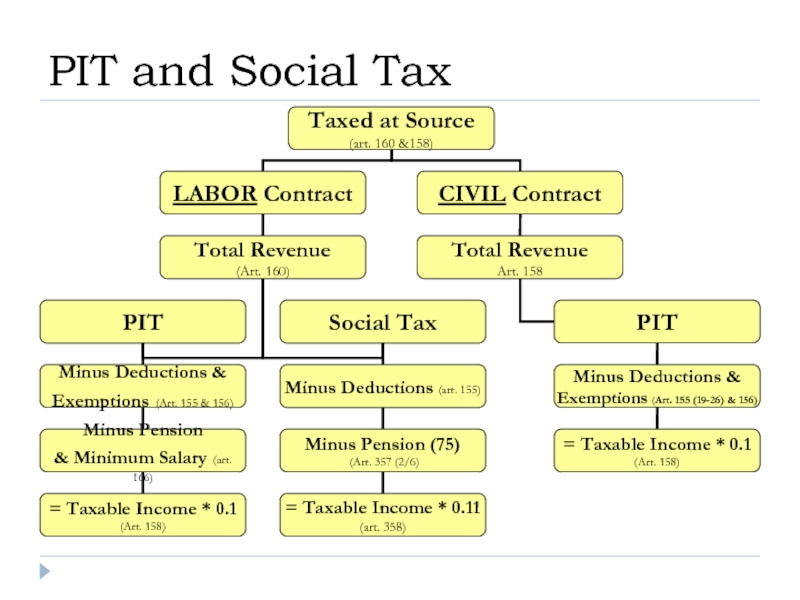
- 18. PIT and Social Tax
- 19. Object of the PIT: Revenues taxed at
- 20. Rates of the PIT: Revenues taxed at
- 21. Labor Contract: Your Official Salary is KZT
- 22. PIT – 10%; Social Tax = 11%
- 23. Calculation: Monthly pension payments are 10%; Minimum
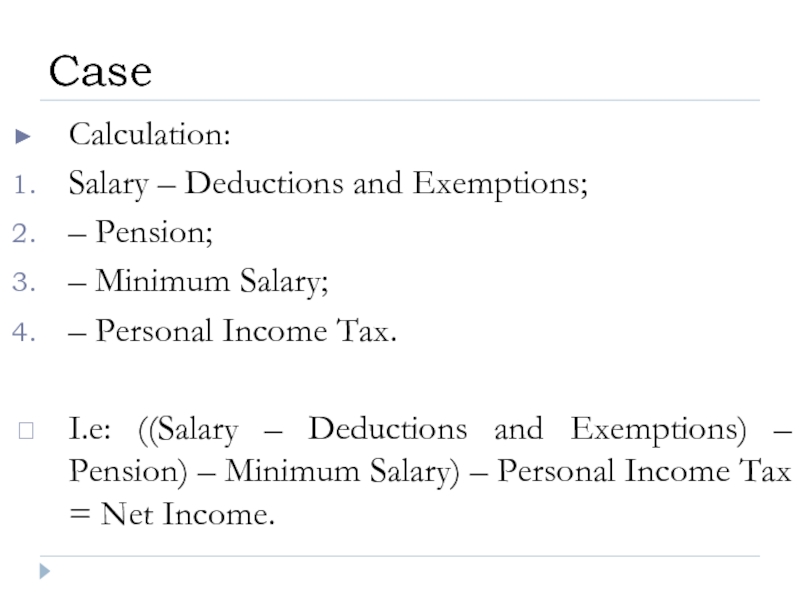
- 24. Calculation: Salary – Deductions and Exemptions; –
- 25. Calculation: Salary – Pension = (500,000 *
- 26. Calculation: Salary – Pension = (500,000 *
- 27. When COMPANY (Tax Agent) has to pay Personal Income Tax?
- 28. Who pays PIT?
- 29. “LLP GARANT” wants to sign a contract
- 30. PIT and Social Tax
- 31. Calculation: Salary – Deductions and Exemptions; –
- 32. LABOR CONTRACT KZT 300,000. PIT = Taxable
- 33. Calculation: Salary – Deductions and Exemptions; –
- 34. Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000.
- 35. Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000.
- 36. Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000.
- 37. “LLP GARANT” wants to sign a contract
- 38. Tax Regimes of the IP: Generally Established
- 39. Generally Established Procedures: PIT – 10%; Social
- 40. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is an IE: Generally
- 41. Special Tax Regime - Patent: PIT –
- 42. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is an IE: Patent
- 43. Special Tax Regime – Simplified Declaration: PIT
- 44. SERVICE CONTRACT Arman is an IE: Simplified
- 45. Types of Taxes
- 46. For Legal Entities: Taxable Income = (Aggregate
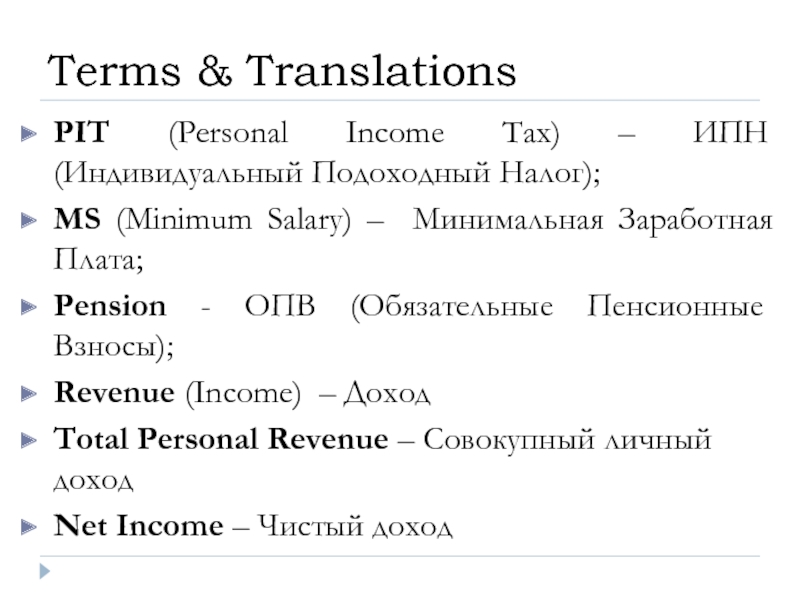
Слайд 2PIT (Personal Income Tax) – ИПН (Индивидуальный Подоходный Налог);
MS (Minimum Salary)
Pension - ОПВ (Обязательные Пенсионные Взносы);
Revenue (Income) – Доход
Total Personal Revenue – Совокупный личный доход
Net Income – Чистый доход
Terms & Translations
Слайд 3Tax Burden under Employment Contract;
Tax Burden under Civil Contract;
Tax Burden of
Goal
Слайд 4Tax Legislation is based on the:
Constitution;
Code of the RK on Taxes
and other Normative Legal Acts.
Governing Laws
Слайд 5Tax Law regulate the government-directed relations associated with establishing, introduction and
Tax Law
Слайд 6Sub-par.34 par.1 art.1 TC
Taxes - obligatory monetary payments to the budget
Tax Law
Слайд 7Subject of the tax law – taxpayer who obliged to pay
Taxpayers divided into physical persons and legal entities; as well they could be divided into residents and non-residents.
Subject of the Tax Law
Слайд 8Article 27. A Taxable Item and (or) Item Related to Taxation
The
Tax Law
Слайд 9Principle of Personal Law – attraction of national (local) physical persons
Principle of Territorial Law – obligation to pay taxes regardless of nationality;
Principle of Residence – divide into residents and non-residents, later to pay taxes from revenues derived from sources in the country of taxation.
Subject of the Tax Law
Слайд 11VAT, taxable items:
taxable turnovers (selling goods, works and services in the
taxable import.
VAT – equals to 12%;
VAT
The minimum turnover shall be 30 000 MCI.
Слайд 12Excisable Products:
Alcohol;
Tobacco;
Gasoline;
Diesel;
Crude Oil;
Gas Condensate;
Excise Duty
Subjects – producers/importers of excisable products.
Слайд 14Hydrocarbon Resources;
Solid Minerals;
Common Minerals.
Subsurface Users
Special Payments and Taxes of Subsurface Users:
Слайд 16Article 26. Tax Liability
The tax liability the taxpayer’s obligation to be
Tax Law
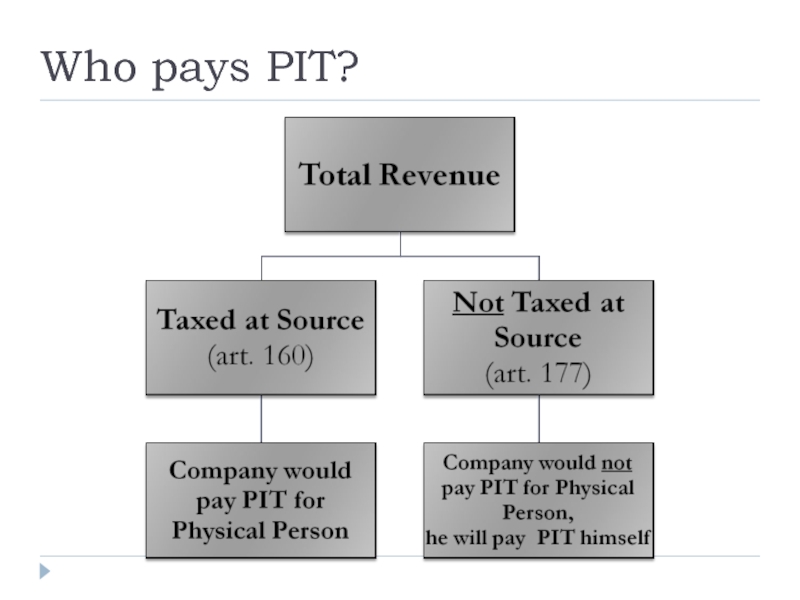
Слайд 17Who has to pay PIT?
Subjects of the PIT:
Physical person – resident;
Physical
Personal Income Tax
Слайд 19Object of the PIT:
Revenues taxed at source (i.e. income from: salary,
Revenues not taxed at source (property income, income of IE, lawyers, private notaries, income derived from sources outside of RK).
Personal Income Tax
Слайд 20Rates of the PIT:
Revenues taxed at source - at the rate
Income from dividends – at a rate of 5%;
Other rates stipulated by the Tax Code.
Personal Income Tax
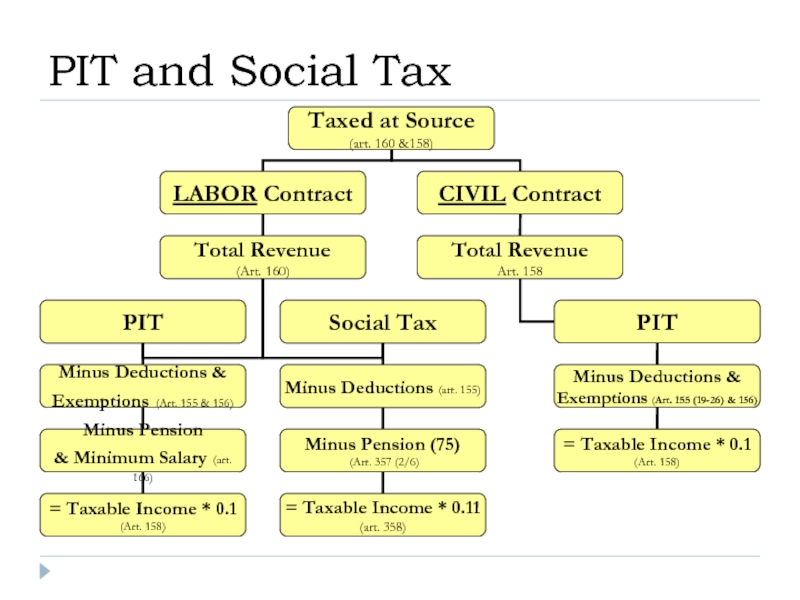
Слайд 21Labor Contract:
Your Official Salary is KZT 500,000;
What will be the amount
What will be your Net Income?
Case
Слайд 23Calculation:
Monthly pension payments are 10%;
Minimum Salary equals to – 21,364 tenge.
The rest amount is subject for the PIT equal to 10%.
PIT
Слайд 24Calculation:
Salary – Deductions and Exemptions;
– Pension;
– Minimum Salary;
– Personal Income Tax.
I.e:
Case
Слайд 25Calculation:
Salary – Pension = (500,000 * 10%) = 450,000;
PIT = (450,000*10%)
PIT = 45,000 (Wrong)
Wrong Calculation!!!
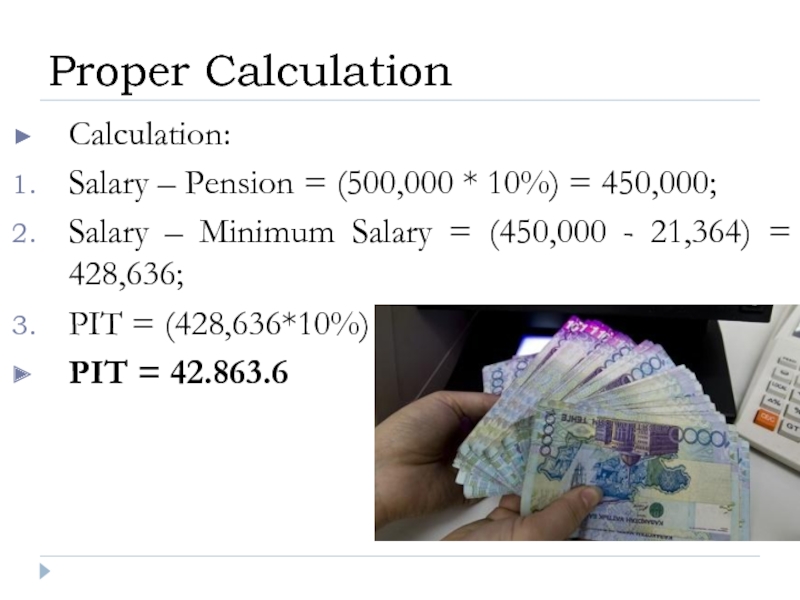
Слайд 26Calculation:
Salary – Pension = (500,000 * 10%) = 450,000;
Salary – Minimum
PIT = (428,636*10%) = 42,863.6;
PIT = 42.863.6
Proper Calculation
Слайд 29“LLP GARANT” wants to sign a contract for provision of legal
Who will pay PIT for Arman, if they sign:
Labor Contract?
Service Contract assuming that Arman is not IP?
Service Contract assuming that Arman is IP?
Case
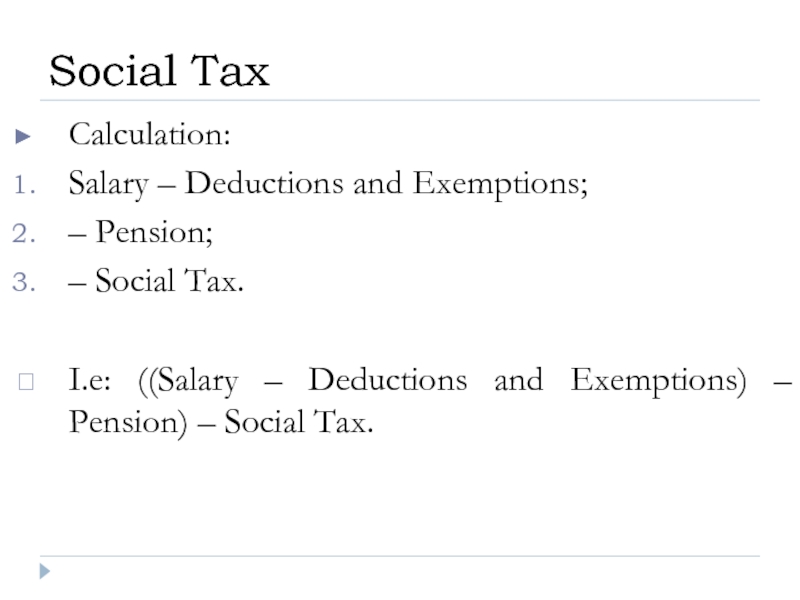
Слайд 31Calculation:
Salary – Deductions and Exemptions;
– Pension;
– Social Tax.
I.e: ((Salary – Deductions
Social Tax
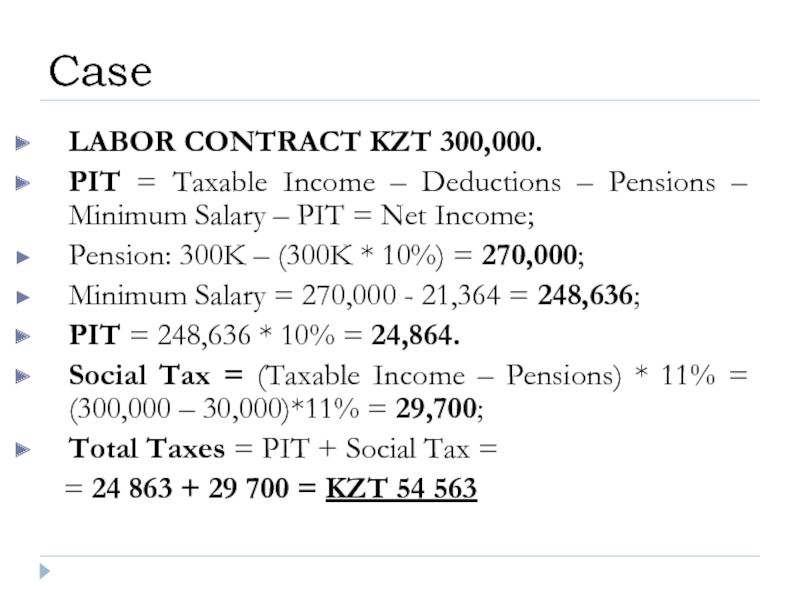
Слайд 32LABOR CONTRACT KZT 300,000.
PIT = Taxable Income – Deductions – Pensions
Pension: 300K – (300K * 10%) = 270,000;
Minimum Salary = 270,000 - 21,364 = 248,636;
PIT = 248,636 * 10% = 24,864.
Social Tax = (Taxable Income – Pensions) * 11% = (300,000 – 30,000)*11% = 29,700;
Total Taxes = PIT + Social Tax =
= 24 863 + 29 700 = KZT 54 563
Case
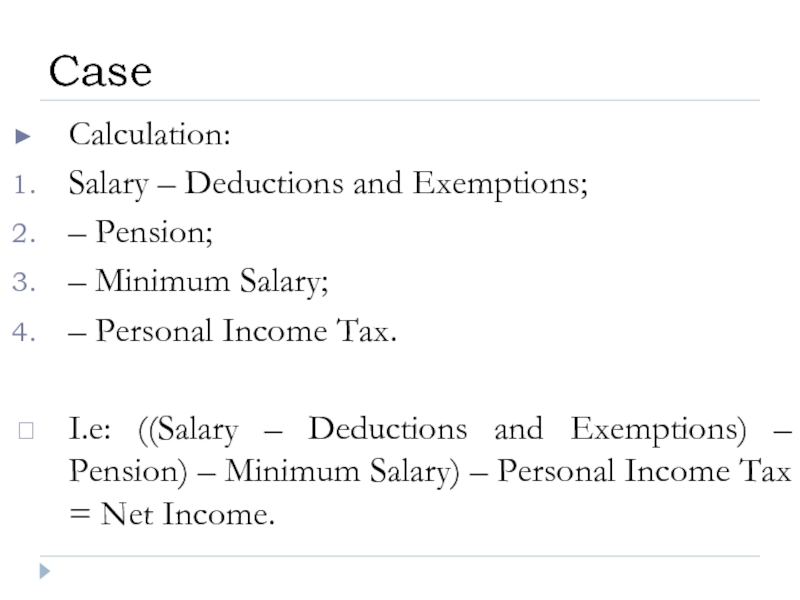
Слайд 33Calculation:
Salary – Deductions and Exemptions;
– Pension;
– Minimum Salary;
– Personal Income Tax.
I.e:
Case
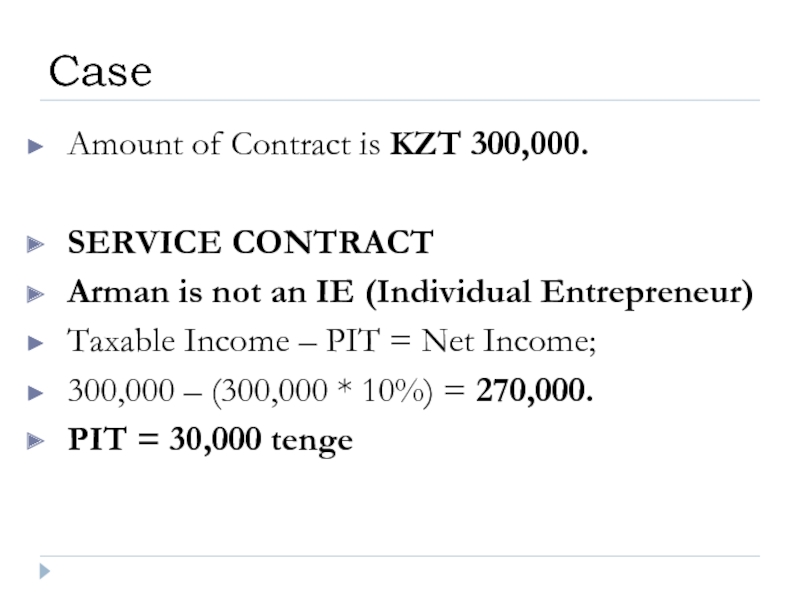
Слайд 34Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000.
SERVICE CONTRACT
Arman is not an IE
Taxable Income – PIT = Net Income;
300,000 – (300,000 * 10%) = 270,000.
PIT = 30,000 tenge
Case
Слайд 35Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000.
SERVICE CONTRACT
Arman is not an IE
Company has to pay = 30,000.
Case
Слайд 36Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000.
SERVICE CONTRACT
Arman is an IE (Individual
Company doesn’t have to pay any taxes for Arman.
Case
Слайд 37“LLP GARANT” wants to sign a contract for provision of legal
Who will pay PIT for Arman, if they sign:
Labor Contract = 54 563 tenge
Service Contract:
Arman is not IP = 30,000 tenge;
Arman is an IP = 0 tenge.
Case
Слайд 38Tax Regimes of the IP:
Generally Established Procedures;
Special Tax Regimes:
On the Basis
On the Basis of Simplified Declaration;
Individual Entrepreneur
Слайд 39Generally Established Procedures:
PIT – 10%;
Social Tax – 2 MS for oneself
Pension: personally identify the income from which pension contributions will be paid. Shall not be less than 10 MS (10* 21,364) and not more than 75 MS (75* 21,364).
Individual Entrepreneur
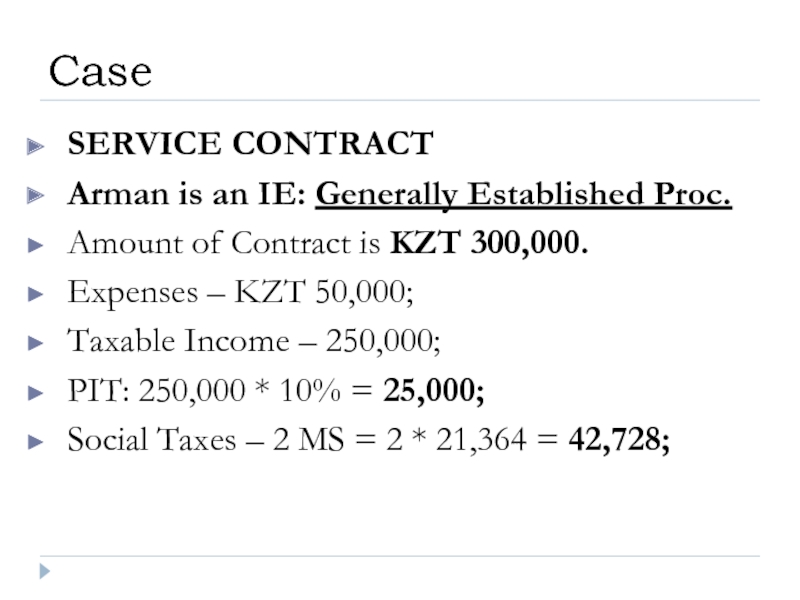
Слайд 40SERVICE CONTRACT
Arman is an IE: Generally Established Proc.
Amount of Contract is
Expenses – KZT 50,000;
Taxable Income – 250,000;
PIT: 250,000 * 10% = 25,000;
Social Taxes – 2 MS = 2 * 21,364 = 42,728;
Case
Слайд 41Special Tax Regime - Patent:
PIT – 1%;
Social Tax – 1%
*Note: IP
Individual Entrepreneur
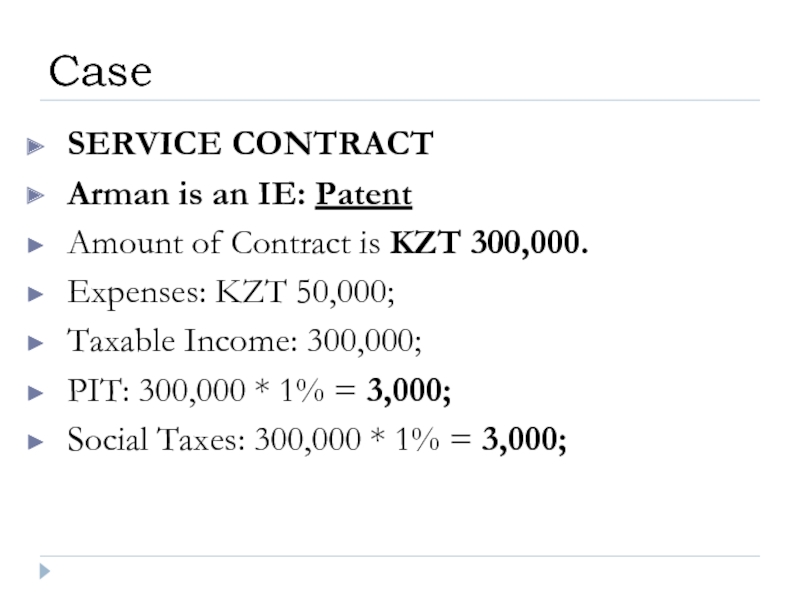
Слайд 42SERVICE CONTRACT
Arman is an IE: Patent
Amount of Contract is KZT 300,000.
Expenses:
Taxable Income: 300,000;
PIT: 300,000 * 1% = 3,000;
Social Taxes: 300,000 * 1% = 3,000;
Case
Слайд 43Special Tax Regime – Simplified Declaration:
PIT – 1,5%;
Social Tax – 1,5%;
*Note:
Individual Entrepreneur
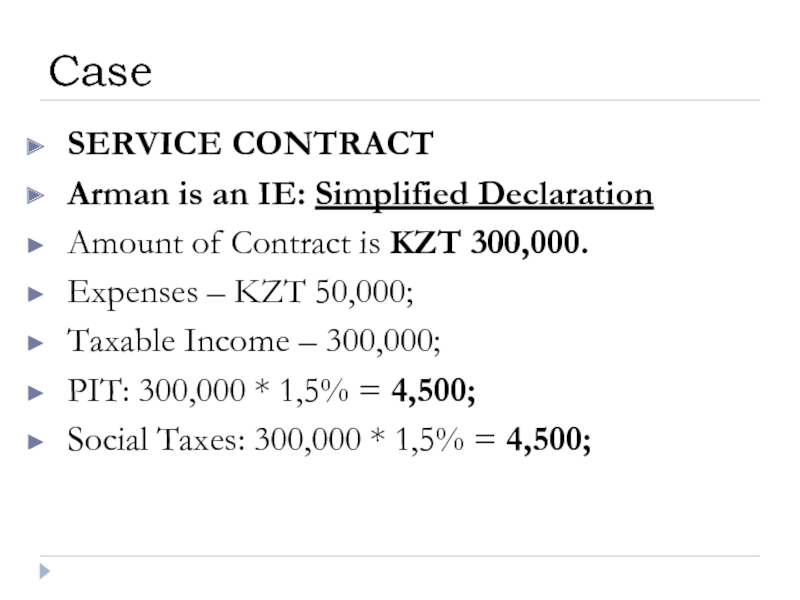
Слайд 44SERVICE CONTRACT
Arman is an IE: Simplified Declaration
Amount of Contract is KZT
Expenses – KZT 50,000;
Taxable Income – 300,000;
PIT: 300,000 * 1,5% = 4,500;
Social Taxes: 300,000 * 1,5% = 4,500;
Case
Слайд 46For Legal Entities:
Taxable Income = (Aggregate Annual Income) - (Deductions);
Aggregate Annual
Tax Law