- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Relative clauses презентация
Содержание
- 1. Relative clauses
- 2. What are relative clauses? Subordinate clauses which
- 3. Relative clauses are introduced just after the
- 4. After preposition you write whom for people
- 5. DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES They give essential information
- 6. Relative pronouns can’t be omitted if
- 7. If the relative pronoun is followed by
- 8. NON-DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES
- 9. The antencedent is usually a proper name
- 10. Main Features: Between commas ‘That’ is
- 11. fgfgfghfgh
Слайд 2What are relative clauses?
Subordinate clauses which allow us to add information
about people or things we are talking to, without a need to repeat the name
e.g. That is the house. The house was built on the main road.
That is the house which was built on the main road.
e.g. That is the house. The house was built on the main road.
That is the house which was built on the main road.
Слайд 3 Relative clauses are introduced just after the antecedent and are introduced
by a pronoun or a relative adverb. The most frequent ones are:
who; whom; which; that (only in defining relative clauses) and relative adverbs: where; when; why.
who; whom; which; that (only in defining relative clauses) and relative adverbs: where; when; why.
Слайд 4 After preposition you write whom for people and which for things,
but it is more common to place prepositions at the end of the sentence (and it is more usual in spoken English).
e.g. This is the boy about whom you were asking me
This is the boy (who) you were asking me about.
Only whom and which, you can’t use it with ‘that’
e.g. This is the boy about whom you were asking me
This is the boy (who) you were asking me about.
Only whom and which, you can’t use it with ‘that’
Слайд 5DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES
They give essential information about their antecedent and without
them, the meaning will be incompleted. That is why you write them without commas. (oracions especificatives)
The computer which we bought is very expensive
The man who is coming will bring us the present
The computer which we bought is very expensive
The man who is coming will bring us the present
Слайд 6
Relative pronouns can’t be omitted if it’s the subject of the
relative clauses.
The man who visited yesterday is an actor
The house that was so old was rebuilt.
But if it’s not the subject it can be omitted
the man (whom/that) I met at the party told me the truth
The house (which/that) we bought is very comfortable
The man who visited yesterday is an actor
The house that was so old was rebuilt.
But if it’s not the subject it can be omitted
the man (whom/that) I met at the party told me the truth
The house (which/that) we bought is very comfortable
Слайд 7If the relative pronoun is followed by a verb,
then it can’t
be omitted. If the relative is followed
by a subject + verb, then it’s almost sure you can
drop it
whose can’t be omitted, though it’s never a
subject
e.g. the horse whose leg you broke had to be killed
‘what’ means ‘el que’ ‘les coses que’ and is used when the antecedent is understood
e.g. I know what you did last summer.
by a subject + verb, then it’s almost sure you can
drop it
whose can’t be omitted, though it’s never a
subject
e.g. the horse whose leg you broke had to be killed
‘what’ means ‘el que’ ‘les coses que’ and is used when the antecedent is understood
e.g. I know what you did last summer.
Слайд 8NON-DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES
If we remove this relative clause,
there’s no problem to understand the main sentence, since it gives extra information. Thus, we write it between commas.
e.g. The European Police Force, which began working in 1999, is called Europol.
e.g. The European Police Force, which began working in 1999, is called Europol.
Слайд 9The antencedent is usually a proper name of a person or
thing and it contains a possessive like ‘my’, ‘his’, ‘her’, the definite article ‘the’ or demonstratives like ‘this’, ‘that’, ‘these’ or ‘those’:
My house, which is quite comfortable, needs
redecorating.
This book, which I bought last week, is not as interesting as I thought.
My house, which is quite comfortable, needs
redecorating.
This book, which I bought last week, is not as interesting as I thought.
Слайд 10Main Features:
Between commas
‘That’ is not allowed
The relative pronoun can’t be
omitted
It’s less frequent than defining relative clauses. It is more formal and usually used in written texts.
It’s less frequent than defining relative clauses. It is more formal and usually used in written texts.
Слайд 11fgfgfghfgh
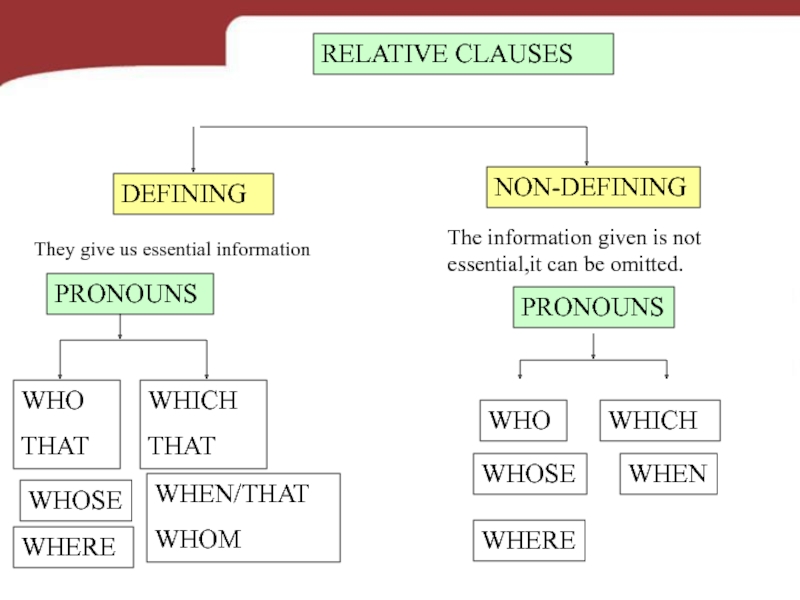
RELATIVE CLAUSES
DEFINING
NON-DEFINING
WHO
THAT
WHICH
THAT
PRONOUNS
WHERE
PRONOUNS
WHO
WHICH
WHOSE
WHEN
WHERE
WHEN/THAT
WHOM
WHOSE
They give us essential information
The information given is not
essential,it can
be omitted.