- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Parts of speech презентация
Содержание
- 1. Parts of speech
- 2. PLAN 1. The notion of parts of
- 3. 1. The notion of parts of
- 4. 1. Criteria for parts of speech discrimination
- 5. 1. Criteria for parts of speech discrimination
- 6. 1. Criteria for parts of speech discrimination
- 7. ATTENTION! Compare the following paradigms:
- 8. 1. Criteria for parts of speech discrimination
- 9. 1. The notion of parts of speech
- 10. 1. The notion of parts of speech
- 11. 2. The main notional parts of
- 12. 2. The main notional parts of speech
- 13. 2. The main notional parts of speech
- 14. 2. The main notional parts of speech
- 15. 2. The main notional parts of speech
- 16. 2. The main notional parts of speech
- 17. 3. The main functional parts of speech
- 18. 3. The main functional parts of speech
- 19. 3. The main functional parts of speech
- 20. 4. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
- 21. 4. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
- 22. 4. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
- 23. 4. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
- 24. 5. Parts of speech migration.
- 25. 5. Parts of speech migration.
Слайд 2PLAN
1. The notion of parts of speech and the criteria for
their discrimination.
2. The main notional parts of speech and their characteristics.
3. The main functional parts of speech and their characteristics.
4. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
5. Parts of speech migration.
2. The main notional parts of speech and their characteristics.
3. The main functional parts of speech and their characteristics.
4. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
5. Parts of speech migration.
Слайд 3
1. The notion of parts of speech
Study the following words
and try to classify them. Argue the basis of your classification.
Book, swim, beautiful, girl, one, classify, third, nicely, in, tables, write, came, under.
Parts of speech are grammatically relevant classes of words (or lexemes) obtaining more or less common features.
Book, swim, beautiful, girl, one, classify, third, nicely, in, tables, write, came, under.
Parts of speech are grammatically relevant classes of words (or lexemes) obtaining more or less common features.
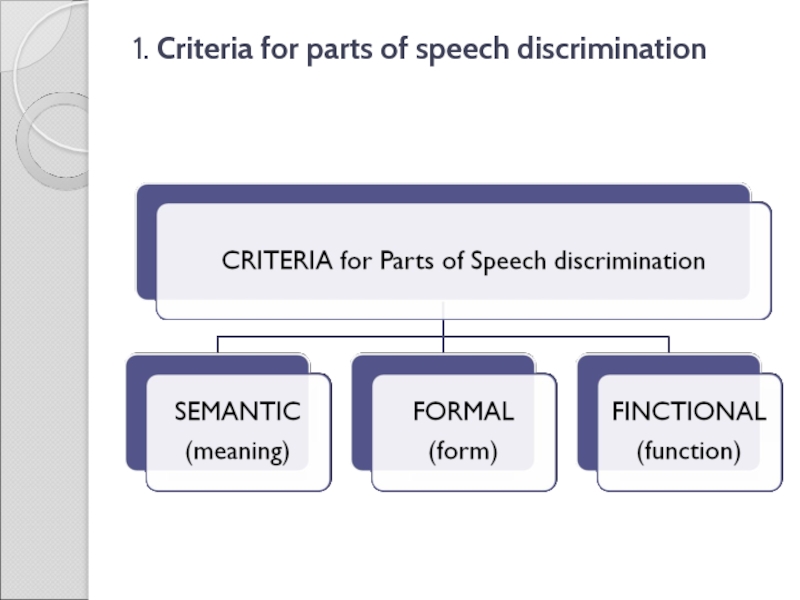
Слайд 51. Criteria for parts of speech discrimination
SEMANTIC
The categorial (lexico-grammatical) meaning of
the part of speech.
It means the generalized meaning characteristic to all the words in a given part of speech.
Example:
Noun - substance, thingness.
Verb - action, process, etc.
It means the generalized meaning characteristic to all the words in a given part of speech.
Example:
Noun - substance, thingness.
Verb - action, process, etc.
Слайд 61. Criteria for parts of speech discrimination
FORMAL
A) Specific forms of derivation.
Some typical stem-building and lexico- grammatical affixes.
Examples:
Noun affixes: -tion, -ship, -dom, -ism, etc.
B) Morphological grammar categories. Thus, the paradigm of a word shows to what part of speech it belongs.
Examples:
Noun - case, number.
Verb - tense, aspect, voice, person, etc.
Examples:
Noun affixes: -tion, -ship, -dom, -ism, etc.
B) Morphological grammar categories. Thus, the paradigm of a word shows to what part of speech it belongs.
Examples:
Noun - case, number.
Verb - tense, aspect, voice, person, etc.
Слайд 7
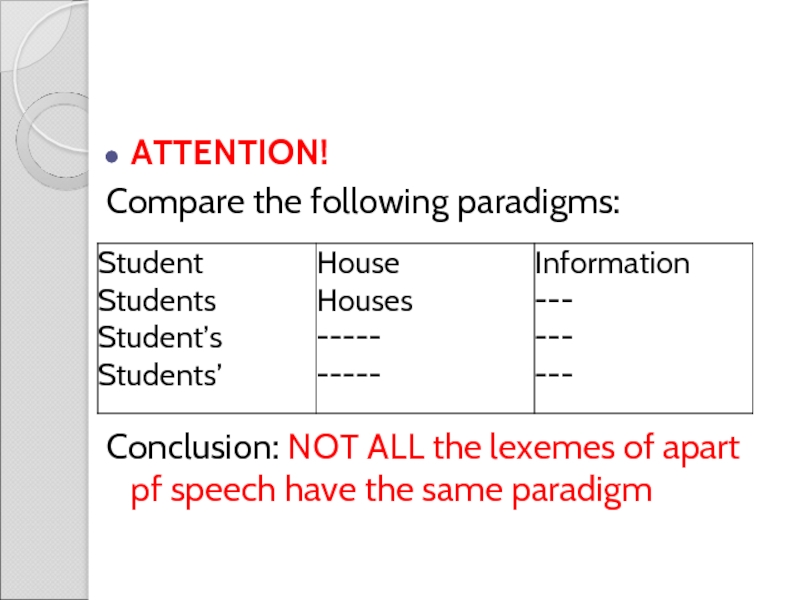
ATTENTION!
Compare the following paradigms:
Conclusion: NOT ALL the lexemes of apart pf
speech have the same paradigm
Слайд 81. Criteria for parts of speech discrimination
FUNCTIONAL
A) Typical combinability. Left-hand and
right-hand connections. (Combinability is the power of a class of words to form combinations of definite patterns with words of certain classes irrespective of their lexical or grammatical meanings)
Art+Noun (a/the book); Prep +Noun (to/from/at school);
B) Syntactical functions in the sentence.
Examples:
Noun – Subject, Predicative, Object…
Verb - Predicate
Art+Noun (a/the book); Prep +Noun (to/from/at school);
B) Syntactical functions in the sentence.
Examples:
Noun – Subject, Predicative, Object…
Verb - Predicate
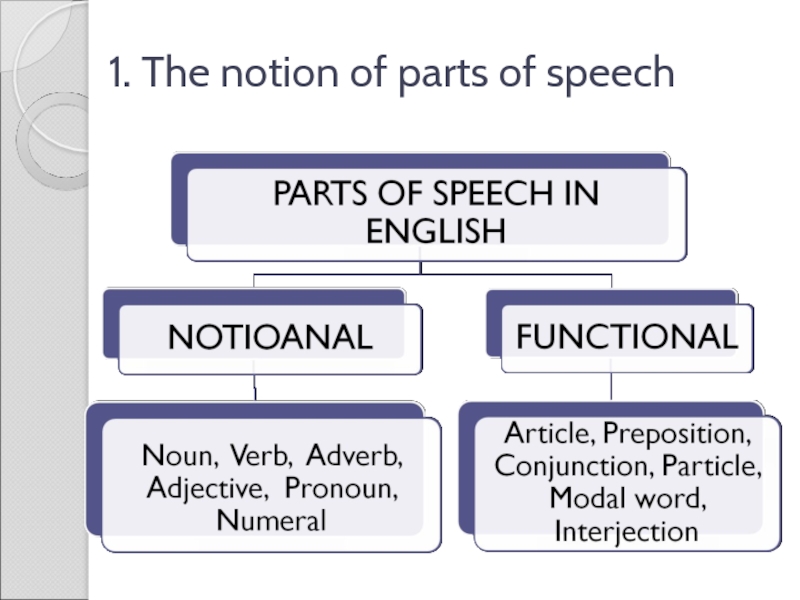
Слайд 101. The notion of parts of speech
FEATURES of the functional parts
of speech
They have very general and comparatively weak lexical meanings.
They obtain obligatory unilateral (articles, particles) or bilateral combinability (prepositions, conjunctions).
They have the functions of linking (prepositions, conjunctions) or specifying (articles, particles) words.
They have very general and comparatively weak lexical meanings.
They obtain obligatory unilateral (articles, particles) or bilateral combinability (prepositions, conjunctions).
They have the functions of linking (prepositions, conjunctions) or specifying (articles, particles) words.
Слайд 11
2. The main notional parts of speech and their characteristics.
The features
of the noun : 1) the categorial meaning of substance ("thingness"); 2) the changeable forms of number and case; the specific suffixal forms of derivation (prefixes in English do not discriminate parts of speech as such); 3) the substantive functions in the sentence (subject, object, substantival predicative); prepositional connections; modification by an adjective.
Слайд 122. The main notional parts of speech and their characteristics.
The features
of the adjective: 1) the categorial meaning of property (qualitative and relative); 2) the forms of the degrees of comparison (for qualitative adjectives); the specific suffixal forms of derivation; 3) adjectival functions in the sentence (attribute to a noun, adjectival predicative).
Слайд 132. The main notional parts of speech and their characteristics.
The features
of the numeral: 1) the categorial meaning of number (cardinal and ordinal); 2) the narrow set of simple numerals; the specific forms of composition for compound numerals; the specific suffixal forms of derivation for ordinal numerals; 3) the functions of numerical attribute and numerical substantive.
Слайд 142. The main notional parts of speech and their characteristics.
The features
of the pronoun: 1) the categorial meaning of indication (deixis); 2) the narrow sets of various status with the corresponding formal properties of categorial changeability and word-building; 3) the substantival and adjectival functions for different sets.
Слайд 152. The main notional parts of speech and their characteristics.
The features
of the verb: 1) the categorial meaning of process (presented in the two upper series of forms, respectively, as finite process and non-finite process); 2) the forms of the verbal categories of person, number, tense, aspect, voice, mood; the opposition of the finite and non-finite forms; 3) the function of the finite predicate for the finite verb; the mixed verbal — other than verbal functions for the non-finite verb.
Слайд 162. The main notional parts of speech and their characteristics.
The features
of the adverb: 1) the categorial meaning of the secondary property, i.e. the property of process or another property; 2) the forms of the degrees of comparison for qualitative adverbs; the specific suffixal forms of derivation; 3) the functions of various adverbial modifiers.
Слайд 173. The main functional parts of speech and their characteristics
The article
expresses the specific limitation of the substantive functions.
The preposition expresses the dependencies and interdependences of substantive referents.
The conjunction expresses connections of phenomena.
The interjection, occupying a detached position in the sentence, is a signal of emotions.
The preposition expresses the dependencies and interdependences of substantive referents.
The conjunction expresses connections of phenomena.
The interjection, occupying a detached position in the sentence, is a signal of emotions.
Слайд 183. The main functional parts of speech and their characteristics
The particle
unites the functional words of specifying and limiting meaning. To this series, alongside of other specifying words, should be referred verbal postpositions as functional modifiers of verbs, etc.
Слайд 193. The main functional parts of speech and their characteristics
The modal
word, occupying in the sentence a detached position, expresses the attitude of the speaker to the reflected situation and its parts. Here belong the functional words of probability (probably, perhaps, etc.), of qualitative evaluation (fortunately, unfortunately, luckily, etc.), and also of affirmation and negation.
Слайд 204. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
Each part of speech is
further subdivided into subclasses on the basis of semantico-functional or formal features.
Слайд 214. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
NOUN subclasses:
Proper – common
Example:
Mary – person
Animate – inanimate
Example: Lion – field
Concrete – abstract
Example: coin - honesty
Countable – uncountable
Example: notebook - news
Animate – inanimate
Example: Lion – field
Concrete – abstract
Example: coin - honesty
Countable – uncountable
Example: notebook - news
Слайд 224. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
VERB subclasses:
Finite – non-finite (fully
predicative – partially predicative)
Example: goes – to go, going, gone
Transitive – intransitive
Example: put, take – live, ache
Actional – statal
Example: play, ride – exist, suffer
Regular– irregular
Example: work – go, put
Example: goes – to go, going, gone
Transitive – intransitive
Example: put, take – live, ache
Actional – statal
Example: play, ride – exist, suffer
Regular– irregular
Example: work – go, put
Слайд 234. Subcategorization of the parts of speech.
ADJECTIVE subclasses:
Qualitative – relative
Example:
long, comfortable – deaf, wooden
Factive – evaluative
Example: tall, mental – kind, brave
Factive – evaluative
Example: tall, mental – kind, brave
Слайд 24
5. Parts of speech migration.
The stems of two or more lexemes
may belong to different parts of speech. Such words are called polyfunctional.
Examples: love – to love, doctor – to doctor, man – to man, home (n) – home (adv.)
This is a result of words migration. The lexemes have different paradigms:
Examples: doctor – doctors – doctor’s – doctors’ and to doctor, doctored, doctoring, etc.
Examples: love – to love, doctor – to doctor, man – to man, home (n) – home (adv.)
This is a result of words migration. The lexemes have different paradigms:
Examples: doctor – doctors – doctor’s – doctors’ and to doctor, doctored, doctoring, etc.
Слайд 25
5. Parts of speech migration.
The new parts of speech are built
by conversion in such examples. Polyfunctional words are present both in the notional and semi-notional parts of speech.
Examples: He arrived before seven (preposition). I have never seen you before (adverb). Wash your hands before you have dinner (subordinating conjunction).
Examples: He arrived before seven (preposition). I have never seen you before (adverb). Wash your hands before you have dinner (subordinating conjunction).