- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Oscillations and Waves презентация
Содержание
- 1. Oscillations and Waves
- 2. Aims To know what a wave is To review previous knowledge of waves
- 3. What is a wave? YouTube - Water bubble in Space (zero gravity)
- 4. Waves Waves can transfer energy and information
- 5. Waves Waves can transfer energy and information
- 6. Homework Can you read pages 216 to 237 of your book before next lesson?
- 7. Wave fronts Wave fronts highlight the part
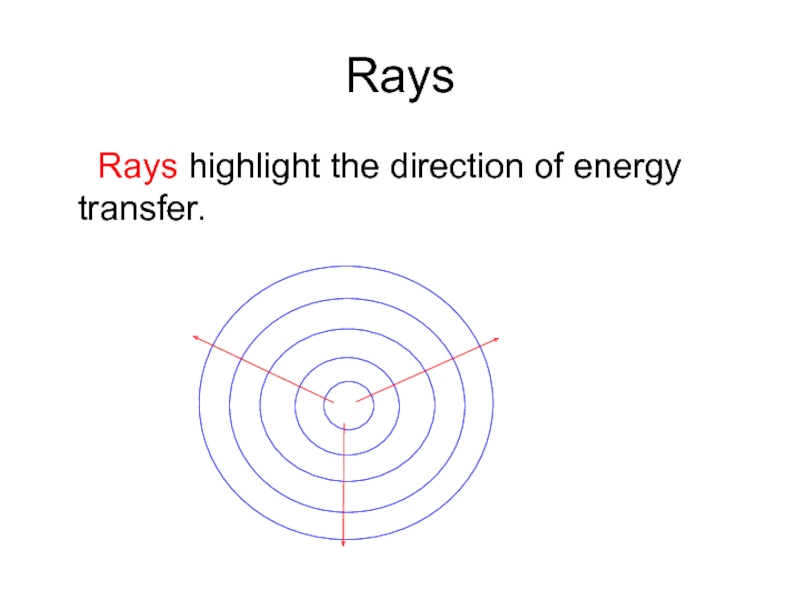
- 8. Rays Rays highlight the direction of energy transfer.
- 9. Transverse waves The oscillations are perpendicular to
- 10. Transverse waves peak trough
- 11. Transverse waves Water ripples Light On a rope/slinky Earthquake
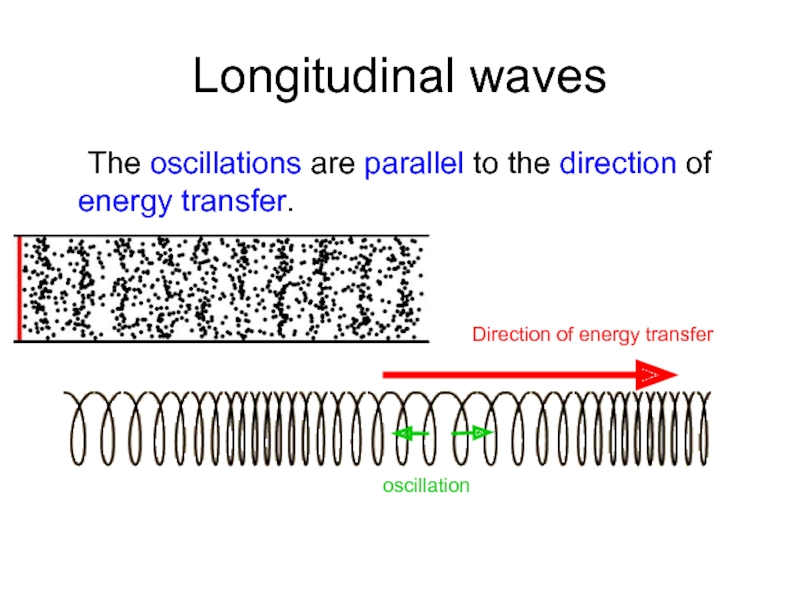
- 12. Longitudinal waves The oscillations are parallel to
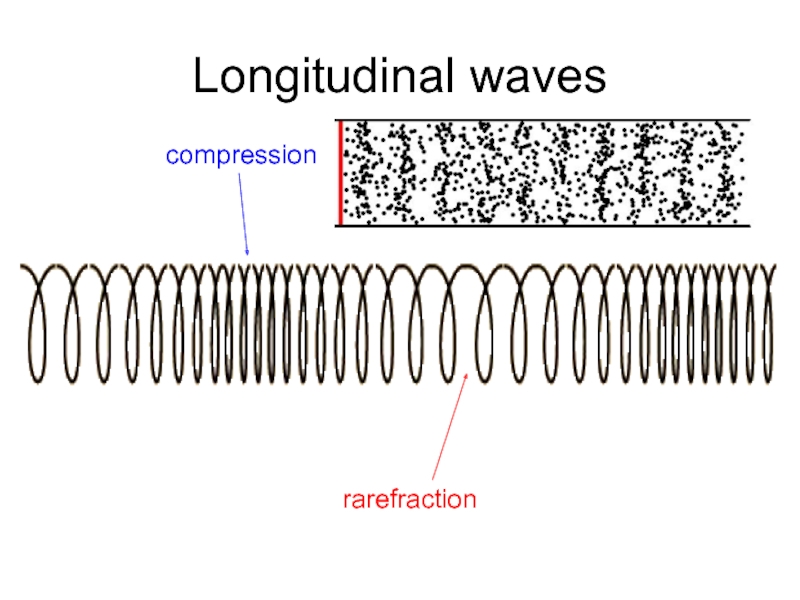
- 13. Longitudinal waves compression rarefraction
- 14. Longitudinal waves Sound Slinky Earthquake
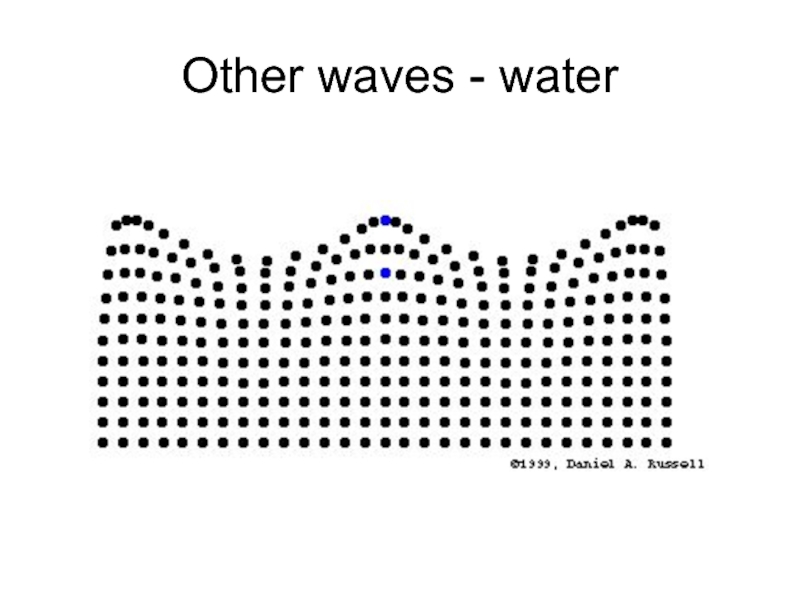
- 15. Other waves - water
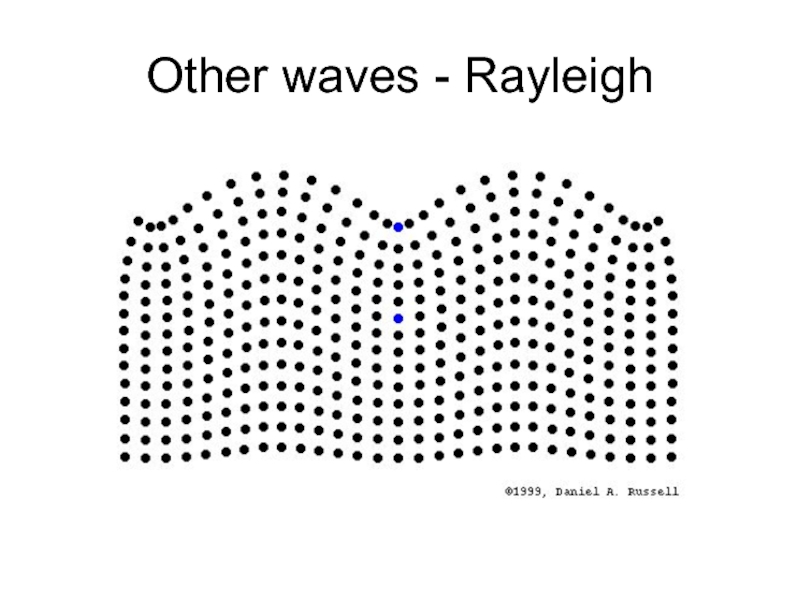
- 16. Other waves - Rayleigh
- 17. Displacement - x This measures the change
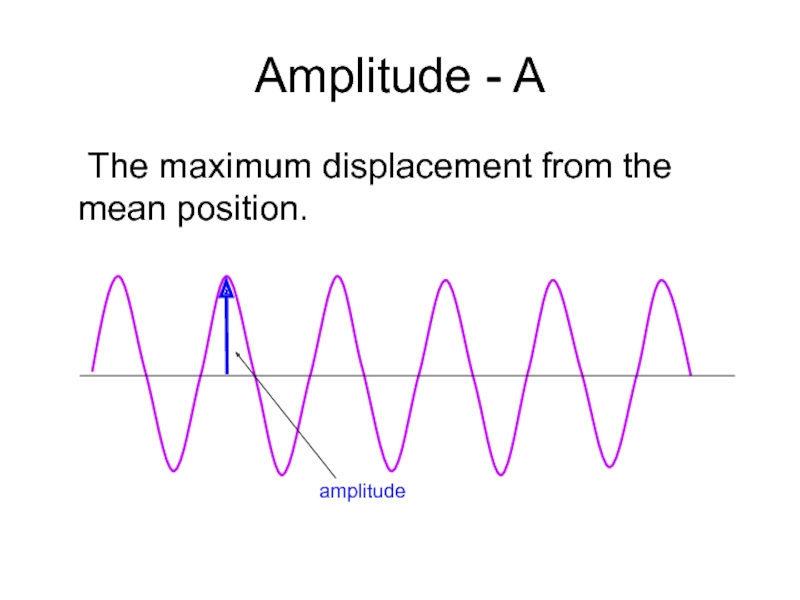
- 18. Amplitude - A The maximum displacement from the mean position. amplitude
- 19. Period - T The time taken (in
- 20. Frequency - f The number of oscillations
- 21. Wavelength - λ The shortest distance between
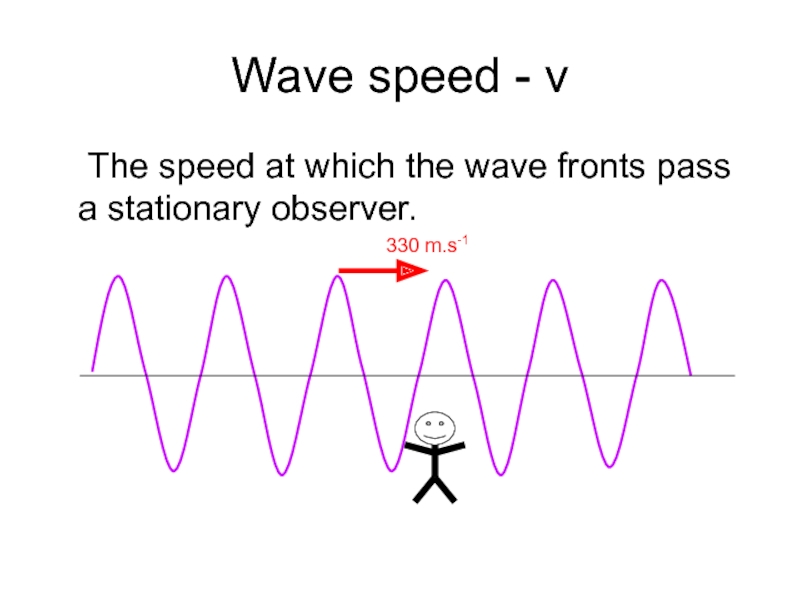
- 22. Wave speed - v The speed at
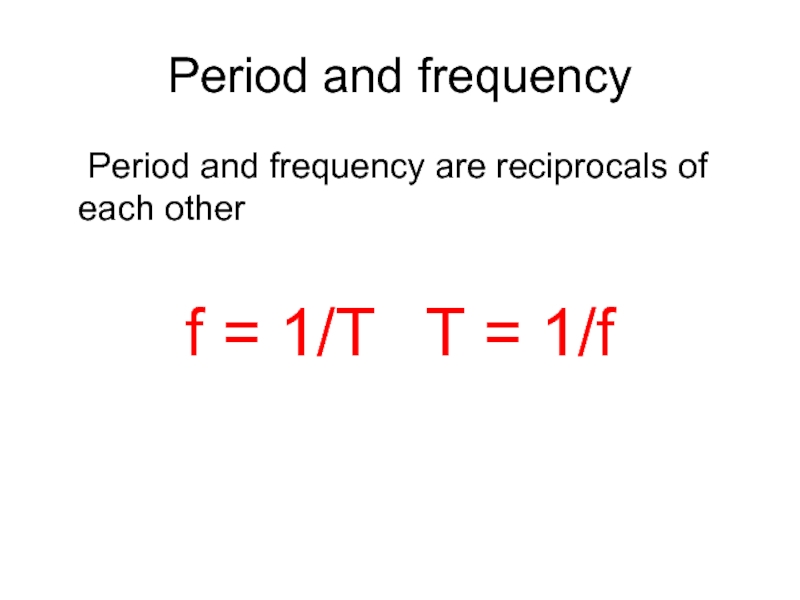
- 23. Period and frequency Period and frequency are
- 24. The Wave Equation The time taken for
- 25. A water wave has a frequency of
- 26. Example A stone is thrown onto still
- 27. Example A stone is thrown onto still
- 28. Example A stone is thrown onto still
- 29. Example A stone is thrown onto still
- 30. Example A stone is thrown onto still
- 31. Let’s try some questions! Page 225 Questions
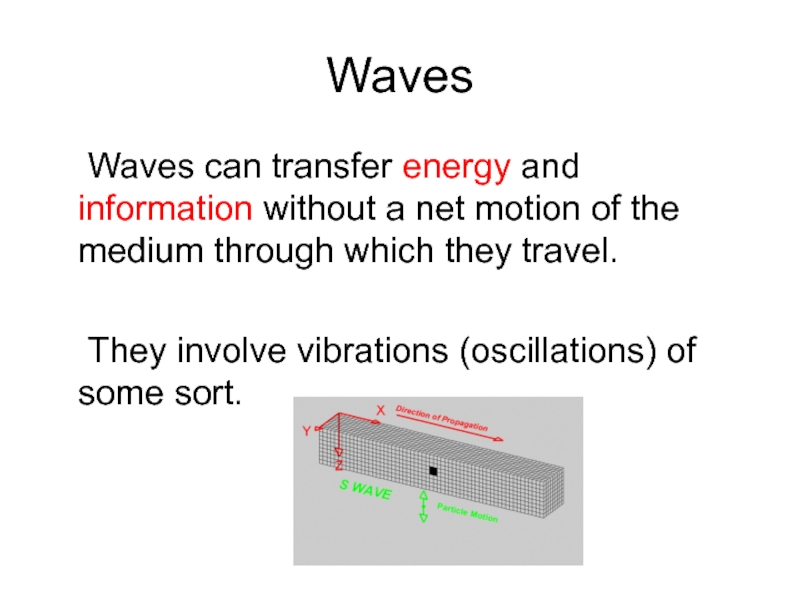
Слайд 4Waves
Waves can transfer energy and information without a net motion of
They involve vibrations (oscillations) of some sort.
Слайд 5Waves
Waves can transfer energy and information without a net motion of
They involve vibrations (oscillations) of some sort.
Can you do something very boring and traditional………
Can you copy this please?
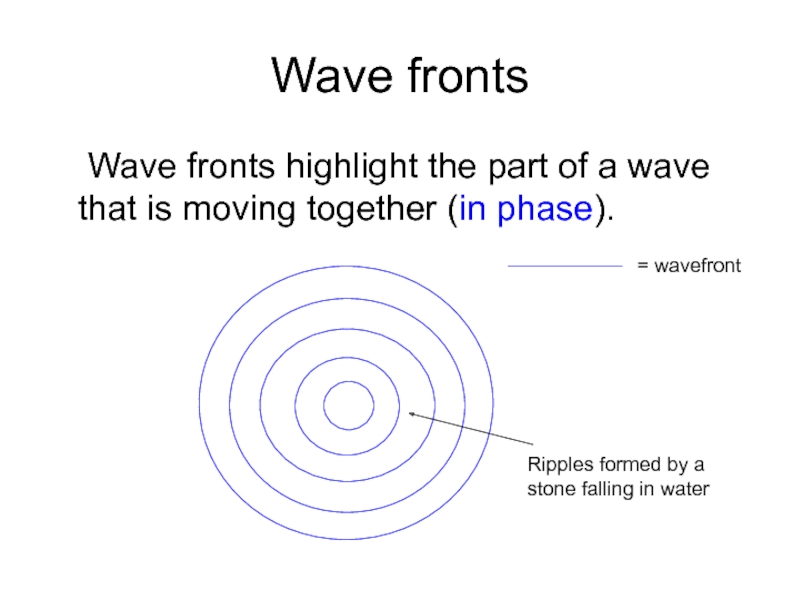
Слайд 7Wave fronts
Wave fronts highlight the part of a wave that is
= wavefront
Ripples formed by a stone falling in water
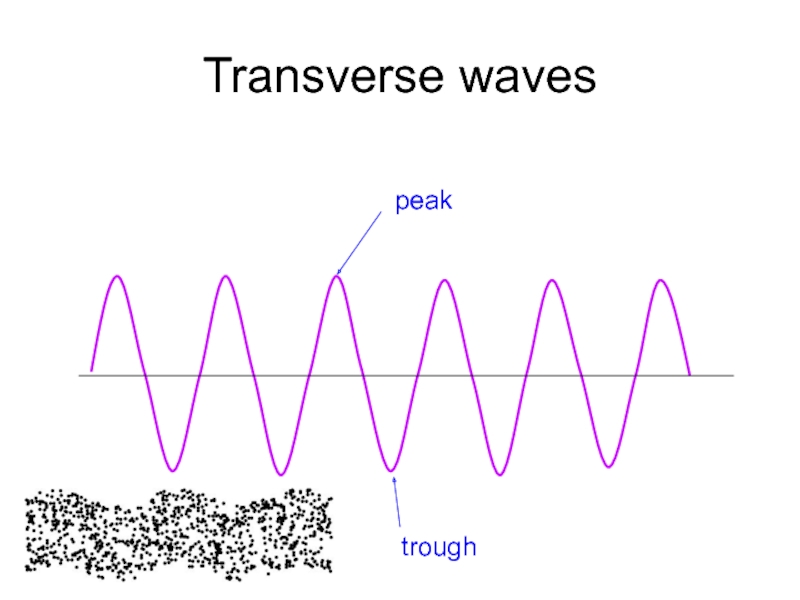
Слайд 9Transverse waves
The oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
Direction
oscillation
Слайд 12Longitudinal waves
The oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
Direction
oscillation
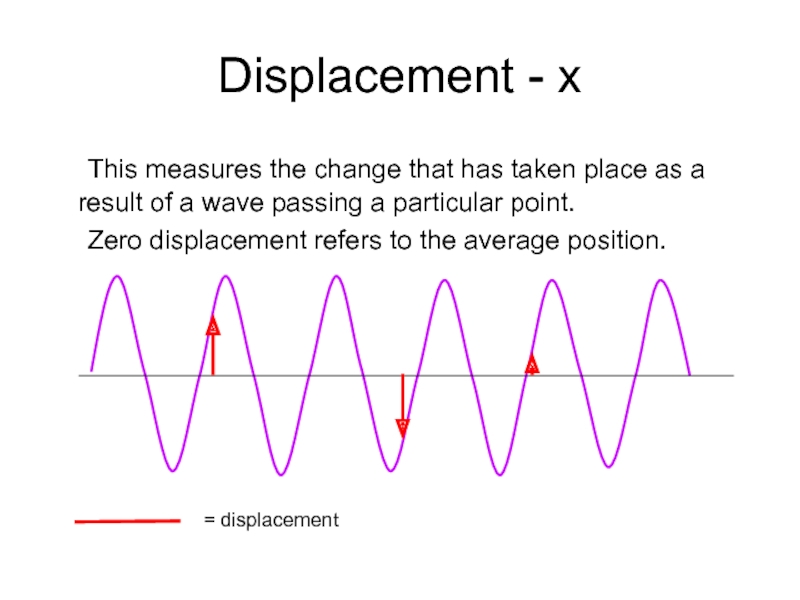
Слайд 17Displacement - x
This measures the change that has taken place as
Zero displacement refers to the average position.
= displacement
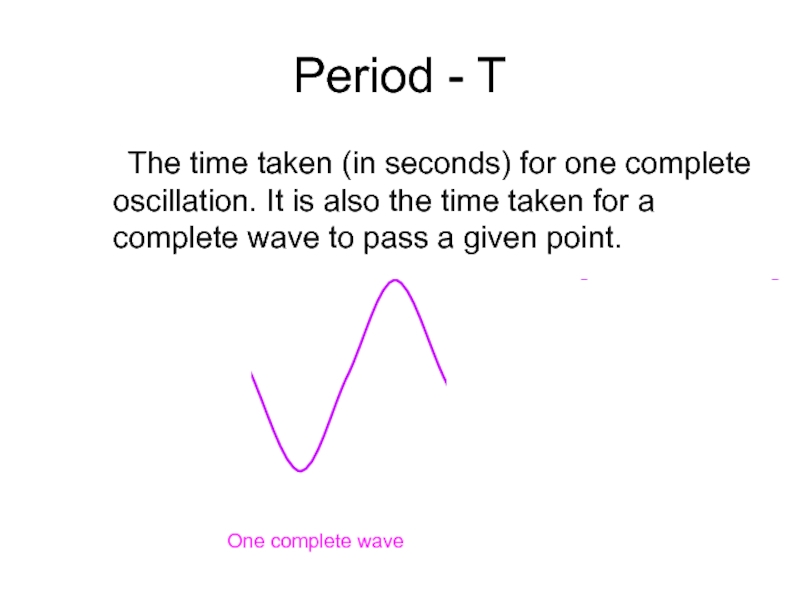
Слайд 19Period - T
The time taken (in seconds) for one complete oscillation.
One complete wave
Слайд 20Frequency - f
The number of oscillations in one second. Measured in
50 Hz = 50 vibrations/waves/oscillations in one second.
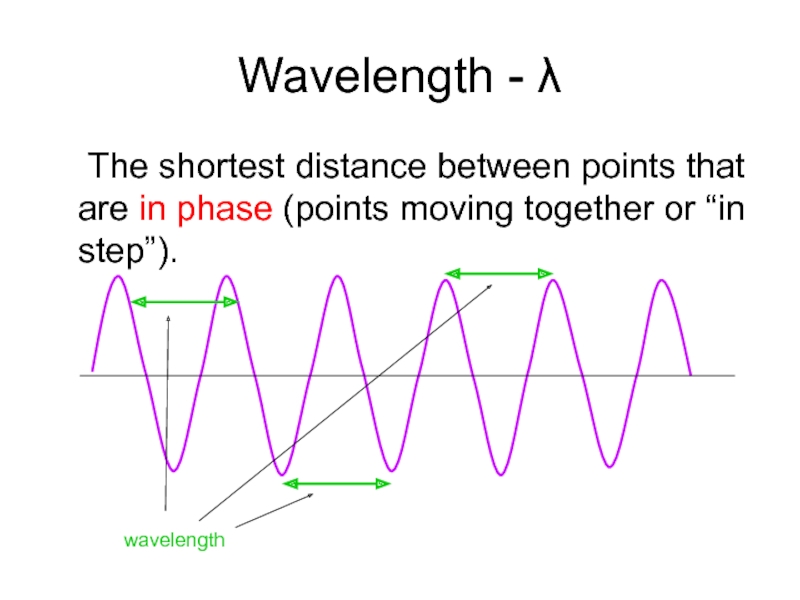
Слайд 21Wavelength - λ
The shortest distance between points that are in phase
wavelength
Слайд 24The Wave Equation
The time taken for one complete oscillation is the
The speed of the wave therefore is distance/time
v = λ/T = fλ
Let’s try some questions
Слайд 25A water wave has a frequency of 2Hz and a wavelength
A water wave travels through a pond with a speed of 1m/s and a frequency of 5Hz. What is the wavelength of the waves?
The speed of sound is 330m/s (in air). When Dave hears this sound his ear vibrates 660 times a second. What was the wavelength of the sound?
Purple light has a wavelength of around 6x10-7m and a frequency of 5x1014Hz. What is the speed of purple light?
Some example wave equation questions
0.2m
0.5m
0.6m/s
3x108m/s
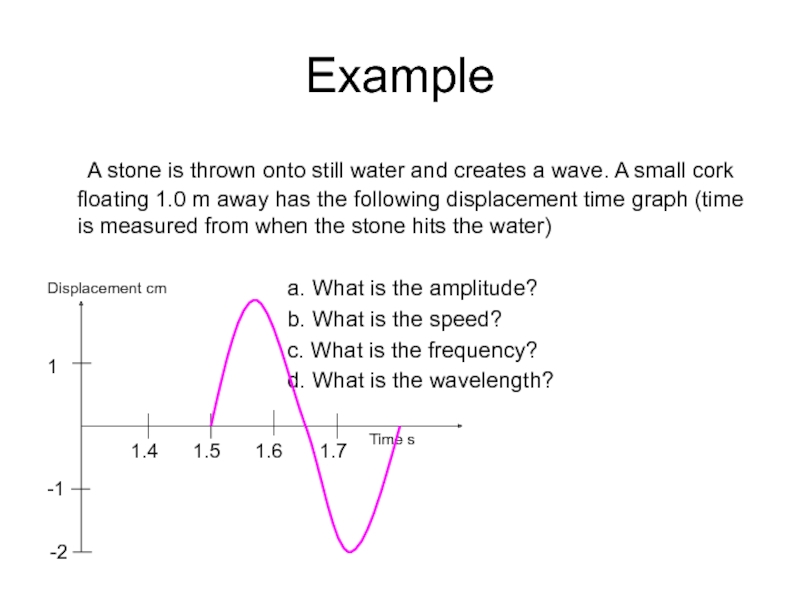
Слайд 26Example
A stone is thrown onto still water and creates a wave.
a. What is the amplitude?
b. What is the speed?
c. What is the frequency?
d. What is the wavelength?
Displacement cm
Time s
1
-1
-2
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
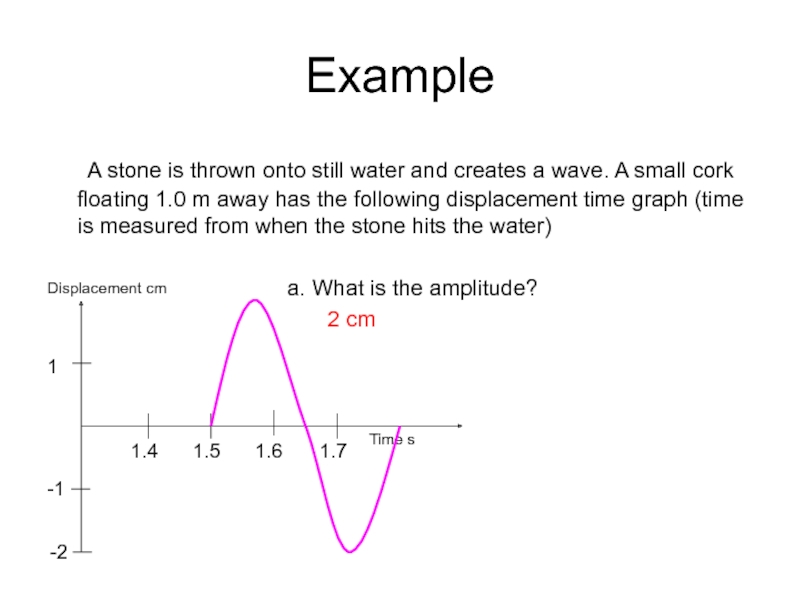
Слайд 27Example
A stone is thrown onto still water and creates a wave.
a. What is the amplitude?
2 cm
Displacement cm
Time s
1
-1
-2
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
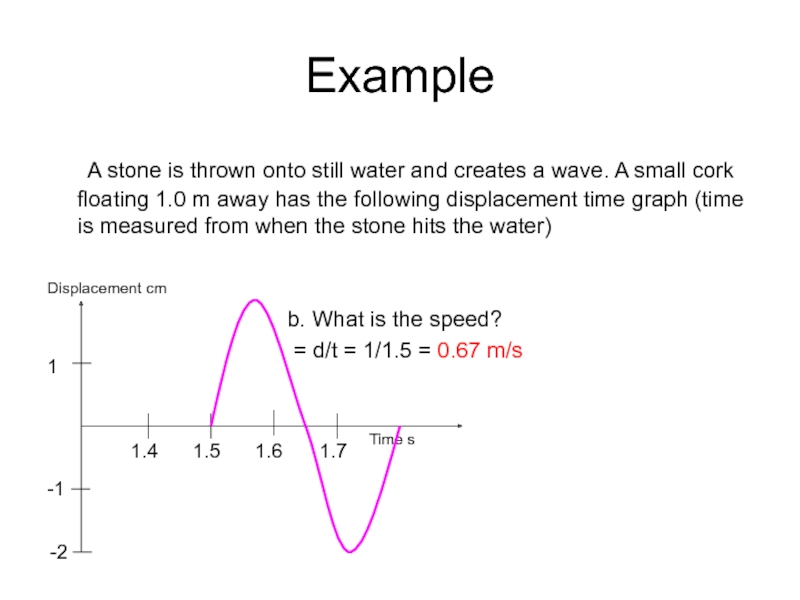
Слайд 28Example
A stone is thrown onto still water and creates a wave.
b. What is the speed?
= d/t = 1/1.5 = 0.67 m/s
Displacement cm
Time s
1
-1
-2
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
Слайд 29Example
A stone is thrown onto still water and creates a wave.
c. What is the frequency?
f = 1/T = 1/0.3 = 3.33 Hz
Displacement cm
Time s
1
-1
-2
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
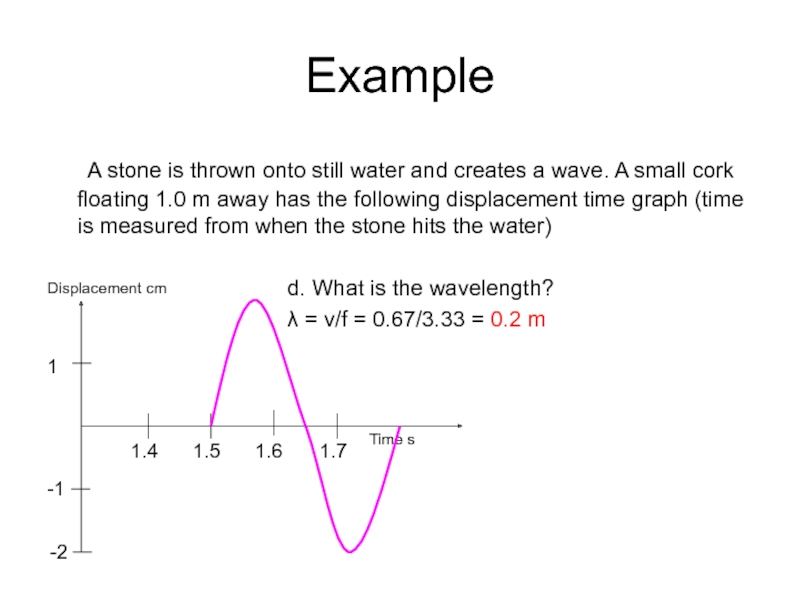
Слайд 30Example
A stone is thrown onto still water and creates a wave.
d. What is the wavelength?
λ = v/f = 0.67/3.33 = 0.2 m
Displacement cm
Time s
1
-1
-2
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
Слайд 31Let’s try some questions!
Page 225 Questions 3, 4
Page 226 Questions 7,
Page 227 Question 15, 17