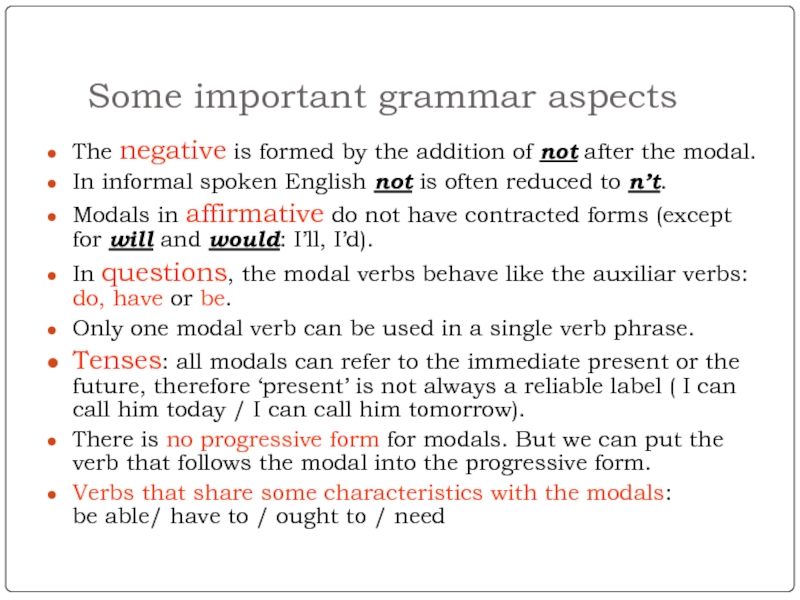
Modal verbs can be used to express different levels of politeness.
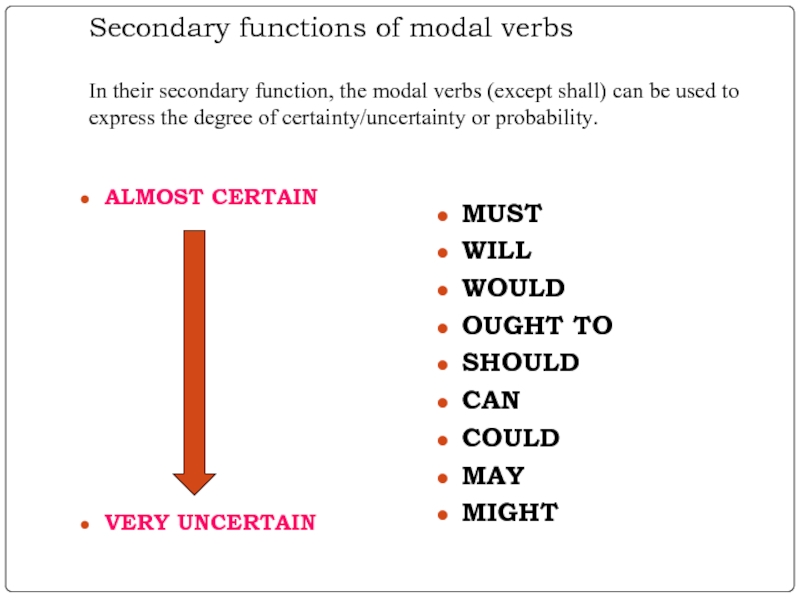
We can also use them to express different degrees of probability.
Modal verbs have two major functions which can be defined as primary (dictionary meaning) and secondary (probability).
MODAL VERBS