- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
How do you spell your name презентация
Содержание
- 1. How do you spell your name
- 2. How do you spell your name?
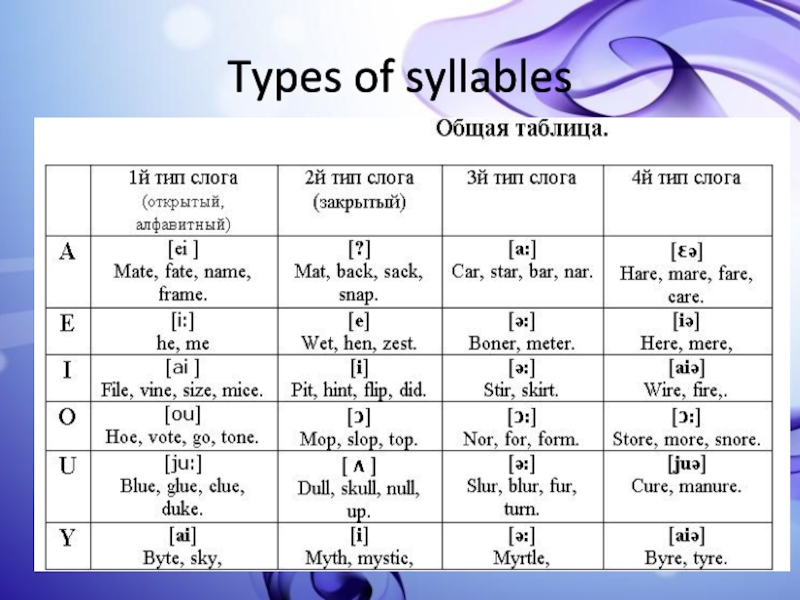
- 4. Types of syllables
- 5. Pronouns - Местоимения I – my You
- 6. Nice to meet you! Hello/Hi!
- 7. Introduction Hello. What's your name? Tom. Are
- 8. Colours What is your favorite colour? My
- 9. GREEN
- 10. BLUE
- 11. Red
- 12. Pink
- 13. Yellow
- 14. Orange
- 15. Purple
- 16. Violet
- 17. Black
- 18. White
- 19. Brown
- 20. Grey
- 22. I Like/Love/Don’t like/+V-ing What do you like
- 24. Yes or No? Hello / Hi Goodbye
- 25. Can you read? [‘saikl] [‘sei] [teik] [bait]
- 26. Numbers 56 759 2456 31900 104227 8923458
- 27. 23+57=80 twenty plus fifty seven is eighty 79+11= 142-32= 567+33= 111-87= 1567-876= 25890+110= 3489660-1824560=
- 28. Plural Book Memory Dance Dress Hero Wolf
- 29. Possessive case Singular Boy’s toy Woman’s bag
- 30. Professional foreign language Professional foreign language as
- 31. Key words profession term language style
- 32. Key questions What does mean “professional language”?
- 33. Recommendations: First students work with Glossary and
- 34. What is science? Science is “knowledge attained
- 35. Scientific Method Basic Elements: Formulation of a
- 36. Cross-lag analysis of longitudinal associations between primary school students’ writing
- 37. Key words: Reading; Writing; Primary school; Cross-lagged design panel Key
- 38. Questions What is this article about? It
- 39. Special terms Education (bachelor-master-PhD) Pedagogy Elementary education
- 40. Lesson #2 Verb to be Appearance, body
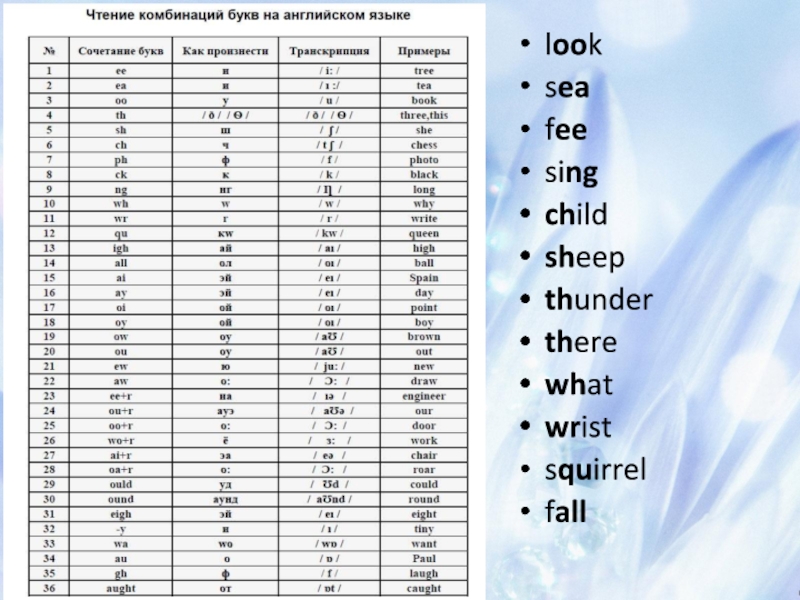
- 41. look sea fee sing child sheep thunder there what wrist squirrel fall
- 42. + To be Singular I am a
- 43. + To be Plural We are teachers
- 44. ?
- 45. HAVE/HAS - иметь I have a dog.
- 46. Have/has ache - боль have a headache
- 47. Appearance - внешность I have an oval
- 49. He has a thin face, a
- 56. Mental functions Perception Thinking Awareness Speech Volition Sensation Emotion Memory
- 57. Questions Dialogue: What is your specialty (major)?
- 59. My family My family consists of five
- 60. Translate into English the following sentences:
- 64. Translate into English: 1. Он – инженер.
- 65. Translate into English: 1. Он – противный
- 66. Translate into English: 1. Она моя мама.
- 67. Translate into English: 1. Я голодный. Ты
- 68. Vocabulary веселый – merry глупый – silly
Слайд 5Pronouns - Местоимения
I – my
You – your
He – his
She – her
It
We - our
They – their
Я – мой
Ты, вы, Вы – твой, ваш, Ваш
Он – его
Она – ее
Оно, это –его, ее
Мы – наш
Они - их
Слайд 6Nice to meet you!
Hello/Hi!
What is your name/surname? My name is …
How old are you? I’m nineteen/twenty…
Where are you from? I’m from Kazakhstan.
What do you do? I’m a student/teacher.
I’m an artist.
How are you?
I’m fine/OK/bad.
Have a nice day!
Thank you! You’re welcome.
Nice to meet you. Nice to meet you too.
Слайд 7Introduction
Hello. What's your name?
Tom.
Are you Tom Banks?
No, l'm not. I'm Tom
You're in room 2.
Sorry?
You are in room 2.
OK. Thank you.
Excuse me.
Hello. Are you Tom?
Yes. Nice to meet you.
Nice to meet you.
Am I late?
Yes, you are.
Sorry!
Слайд 8Colours
What is your favorite colour?
My favourite colour is blue.
My favourite colours
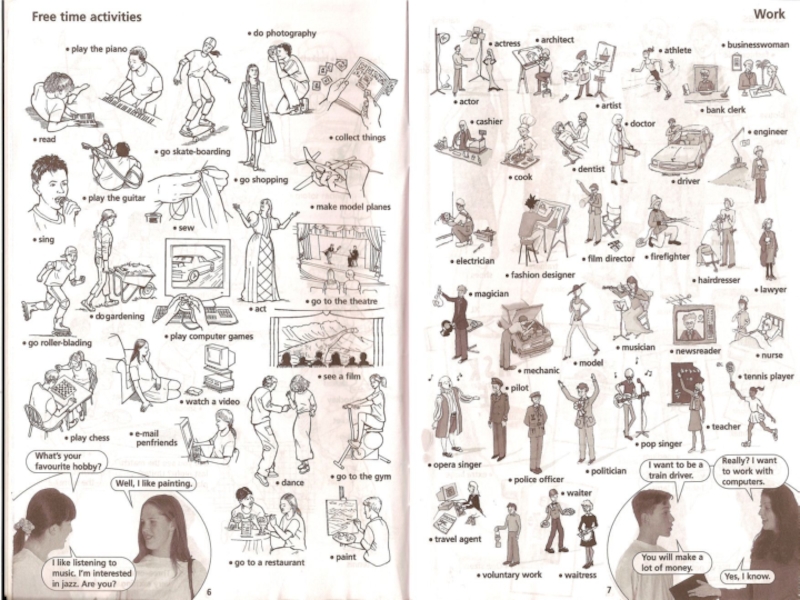
Слайд 22I Like/Love/Don’t like/+V-ing
What do you like doing?
I like reading/dancing/dreaming/ surfing the
What don’t you like doing?
I don’t like cleaning the house/washing the dishes.
I love going out/chatting with my friends.
I hate dancing/knitting.
Do you like watching movies? + Yes, I do.
- No, I don’t.
Слайд 25Can you read?
[‘saikl]
[‘sei]
[teik]
[bait]
[pəul]
[dei]
[flu:t]
[nju:]
[‘pi:tə]
[‘bi:və]
[dȝim]
[gugl]
[gɜ:l]
[nɜ:s]
[‘a:tist]
[‘məudəl]
[pə’li:s]
[ti’tʃə]
[‘ri:də]
[peint]
[plei]
[‘æƟlit]
[bæt]
[kuk]
[‘pailət]
[steik]
[smail]
[weitə]
[‘æktris]
Слайд 26Numbers
56
759
2456
31900
104227
8923458
34271891
What is your telephone number?
My telephone number is 87772345678
(eight-seven-seven-seven-…)
Слайд 2723+57=80
twenty plus fifty seven is eighty
79+11=
142-32=
567+33=
111-87=
1567-876=
25890+110=
3489660-1824560=
Слайд 28Plural
Book
Memory
Dance
Dress
Hero
Wolf
Boy
Man
Child
Tooth
News
Progress
Toy
Girl
Woman
Dog
Cat
Watch
Lady
Day
Monkey
Loaf
Dream
Goose
Mouse
Ox
1 variant
2 variant
Слайд 29Possessive case
Singular
Boy’s toy
Woman’s bag
Cat’s tail
Tom’s car
Adam’s wife
Jane’s eyes
Plural
Boys’ toys
Cats’ eyes
The Potters’
Women’s bags
Children’s toys
Mice’s tails
Слайд 30Professional foreign language
Professional foreign language as an educational discipline.
Special terminology.
Scientific style.
Слайд 31Key words
profession
term
language
style
science
training
development
mental functions (perception, memory, thinking, volition, emotion),
cognition
knowledge
research
abstract
article
journal.
Слайд 32Key questions
What does mean “professional language”?
What is term? What kinds of
What are ways of word-formation?
What is a style? What styles do you know?
What is science? What are basic elements of scientific method?
What features of scientific style?
Слайд 33Recommendations:
First students work with Glossary and find the meaning of necessary
Make up a list of special terms you use in their profession and learn them.
Study ways of word formation and complete practical exercises.
Reading the text about scientific style. (Text #1)
Analyze the abstract of the article as an example. (Text #2)
Grammar
1. Review of noun categories: plural forms, article, possessive case, singular and plural forms.
2. Verb to be in Present, Past and Future Tenses.
3. Personal and possessive pronouns.
4. Word-formation rules.
Слайд 34What is science?
Science is “knowledge attained through study or practice” or
Слайд 35Scientific Method Basic Elements: Formulation of a question, Hypothesis, Prediction, Testing,
DNA example
The basic elements of the scientific method are illustrated by the following example from the discovery of the structure of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid):
Question: How genetic information was stored in DNA?
Hypothesis: Linus Pauling, Francis Crick and James D. Watson hypothesized that DNA had a helical structure.
Prediction: If DNA had a helical structure, its X-ray diffraction pattern would be X-shaped.
Experiment: Rosalind Franklin crystallized pure DNA and performed X-ray diffraction to produce photo 51. The results showed an X-shape.
Analysis: When Watson saw the detailed diffraction pattern, he immediately recognized it as a helix.
Слайд 36Cross-lag analysis of longitudinal associations between primary school students’ writing and reading skills
Abstract
The present
Слайд 37
Key words: Reading; Writing; Primary school; Cross-lagged design panel
Key words Plus: transparent orthography; emergent literacy; acquisition; dyslexia; children; language; fluency; difficulties; ability
Research
Language: English
Слайд 38Questions
What is this article about? It is about …
What special terms
Find highlighted words and explain their meanings.
Complete sentences with the words:
Reading competencies: _________________________________________________.
Writing competencies: __________________________________________________.
Early ________________ in spelling becomes a resource for later reading _____________.
Слайд 39Special terms
Education (bachelor-master-PhD)
Pedagogy
Elementary education
Primary/elementary school
Preschool
Schoolchild/ren
Preschool children
Training
Teach/er
Learn/er
Psychology
Adaptation
Activity
Method
Methodology
Didactics
Specialty
Discipline
Aim
Objective/task
Pattern
Subject
Technology
Science
Research
Competence
Слайд 40Lesson #2
Verb to be
Appearance, body parts, personality, family words
Verb has/has
Special terminology
Letter
Elementary/primary school teacher
Dialogue about your profession
Слайд 42+ To be
Singular
I am a student (I’m) / I am happy
You
He is a dentist (He’s) / He is hot
She is an actress (She’s) She is clever
It is a dog (It’s) / It is brown
Слайд 43+ To be
Plural
We are teachers (we’re)/ We are hungry
You are cooks
They are pilots (they’re)
/ They are cold
Слайд 44?
Am I sad?
Is he a magician?
Are you a singer?
Are we nurses?
Is it a cat?
Are they clever?
I am not (I’m not) sad.
He is not (isn’t) a magician.
You are not (aren’t) a singer.
It is not (isn’t) a cat.
They are not (aren’t) clever.
Слайд 45HAVE/HAS - иметь
I have a dog.
You have a car.
He has a
She has a lot of books.
It (cat) has a tail and fur.
We have a big house.
They have breakfast at 7 a.m.
The Smiths have lunch at 2 p.m.
Jane has dinner with her family at 6 p.m.
Слайд 46Have/has
ache - боль
have a headache – иметь головную боль/болит голова
have a
have a stomachache
have a backache
have a heartache
have fun – веселиться
have breakfast – завтракать
have lunch - обедать
have dinner - ужинать
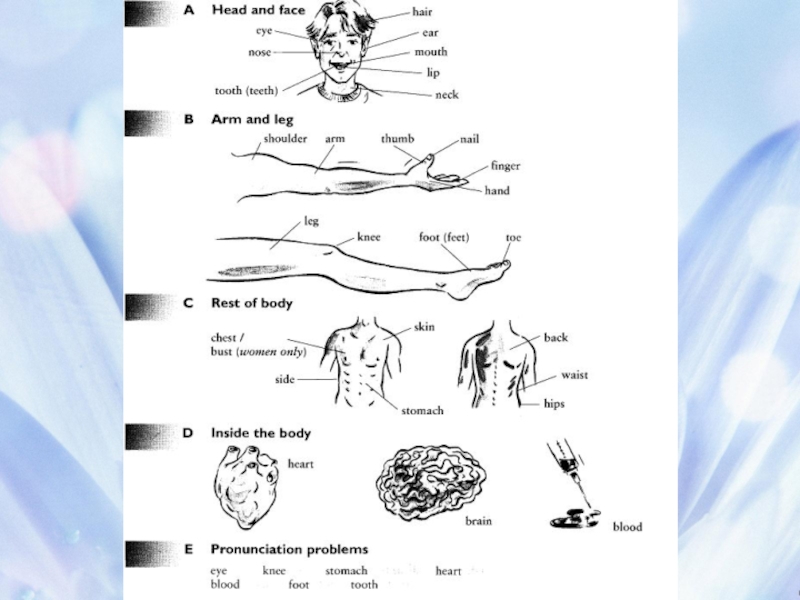
Слайд 47Appearance - внешность
I have an oval face, long dark hair, a
She has a round face, straight fair hair, blue eyes, a small nose and a small mouth. She’s of medium height.
He has a square face, short black hair, hazel (brown) eyes. He’s short.
Personality:
I’m smart and kind. He is romantic and lively. You are friendly and active. She is nasty and nervous.
Слайд 49
He has a thin face, a big nose, curly fair hair
He is kind and quiet.
Слайд 57Questions
Dialogue:
What is your specialty (major)?
My specialty (major) is Pedagogy and
Why do you want to be an elementary school teacher?
I want to be an elementary school teacher because … I love children and I want to contribute to our country’s education.
What are the main tasks of elementary school teacher?
The main tasks of elementary school teacher are:
to teach and educate young learners,
to make calendar and lesson plans,
to conduct extracurricular work,
to be a good member of a school team,
to consult parents,
…
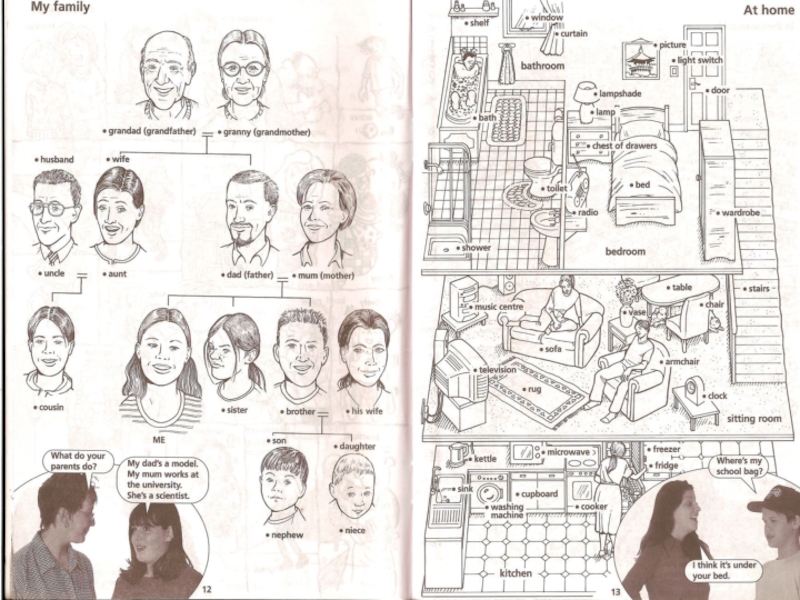
Слайд 59My family
My family consists of five members: my mother, my father,
Слайд 64Translate into English:
1. Он – инженер.
2. Она – юрист.
3. Мы –
4. Вы – фокусники.
5. Они – продавцы.
6. Ты – ученик.
7. Он – художник.
8. Я – пилот.
9. Они – певцы.
10. Ты – парикмахер.
Слайд 65Translate into English:
1. Он – противный лентяй.
2. Она – выдающаяся личность.
3.
4. Я – симпатичный оптимист.
5. Они – отвратительные педанты.
6. Мы – печальные пессимисты.
7. Вы – противный везунчик.
8. Я – веселый фантазер
Слайд 66Translate into English:
1. Она моя мама.
2. Он твой сын.
3. Они твои
4. Он мой брат.
5. Ты мой муж.
6. Они мои двоюродные братья.
7. Это моя дочь.
8. Она моя дочь
9. Они их родители.
10. Вы ее отец.
Слайд 67Translate into English:
1. Я голодный. Ты голодный. Он голодный. Она голодная.
2.
3. Я умный. Ты умный. Он умный. Она умная.
4. Я глупый. Ты глупый. Он глупый. Она глупая.
5. Я веселый. Ты веселый. Он веселый. Она веселая.
6. Мне холодно. Тебе холодно. Ему холодно. Ей холодно.
7. Мне жарко. Тебе жарко. Ему жарко. Ей жарко.
8. Мне скучно. Тебе скучно. Ему скучно. Ей скучно.
9. Я занят. Ты занят. Он занят. Она занята.
10. Я обеспокоен. Ты обеспокоен. Он обеспокоен. Она обеспокоена. 1. Мы голодные. Вы голодные. Они голодные.
2. Мы счастливые. Вы счастливые. Они счастливые.
3. Мы умные. Вы умные. Они умные.
4. Мы глупые. Вы глупые. Они глупые.
5. Мы веселые. Вы веселые. Они веселые.
6. Нам холодно. Вам холодно. Им холодно.
7. Нам жарко. Вам жарко. Им жарко.
8. Нам скучно. Вам скучно. Им скучно.
9. Мы заняты. Вы заняты. Они заняты.
10. Мы обеспокоены. Вы обеспокоены. Они обеспокоены.
Слайд 68Vocabulary
веселый – merry
глупый – silly
голодный – hungry
горячий – hot
грустный – sad
довольный
жаркий – hot
занятой – busy
застенчивый – shy
злой – wicked
обеспокоенный – worried
печальный – sad
сердитый – angry
скучный (испытывающий скуку) – bored
скучный (наводящий скуку) – dull, boring
счастливый – happy
уверенный в себе – confident
умный – clever, smart
холодный – cold
мне скучно – I am bored
когда – when
активный – active
великолепный – fine, splendid, excellent
выдающийся – outstanding
замечательный – great
замкнутый – reserved
красивый – beautiful
милый – nice
общительный – sociable
обыкновенный – ordinary/average
очаровательный – charming, fascinating
пассивный – passive
плохой – bad
прекрасный – wonderful
ужасный – terrible, horrible, awful
уродливый – ugly
хороший – good
чудный – lovely
везунчик – a lucky fellow
домосед – a stay-at home
зануда – a bore
лентяй – an idler, a lazy person
лидер – a leader
личность – a personality
неудачник – a failure; a loser; an unlucky fellow/person
оптимист – an optimist
паникер – a panic-monger, a scaremonger
педант – a pedant
пессимист – a pessimist
подлиза – a lickspittle
работяга – a hard-worker
сплетник – a news-monger
транжира – a spender
трус – a coward
фантазер – a dreamer
храбрец – a man of courage





















![Can you read?[‘saikl][‘sei][teik][bait][pəul][dei][flu:t][nju:][‘pi:tə][‘bi:və][dȝim][gugl][gɜ:l][nɜ:s][‘a:tist][‘məudəl][pə’li:s][ti’tʃə][‘ri:də][peint][plei][‘æƟlit][bæt][kuk][‘pailət][steik][smail][weitə][‘æktris]](/img/tmb/5/442110/cdde92a67145089c6e7cf2058330e201-800x.jpg)