- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Diagnosis and troubleshooting of automotive electrical презентация
Содержание
- 2. OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 38, the reader
- 3. OBJECTIVES Explain the troubleshooting procedures to follow
- 4. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE It is important
- 5. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE Verify the Problem
- 6. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE Retrieve the Diagnostic
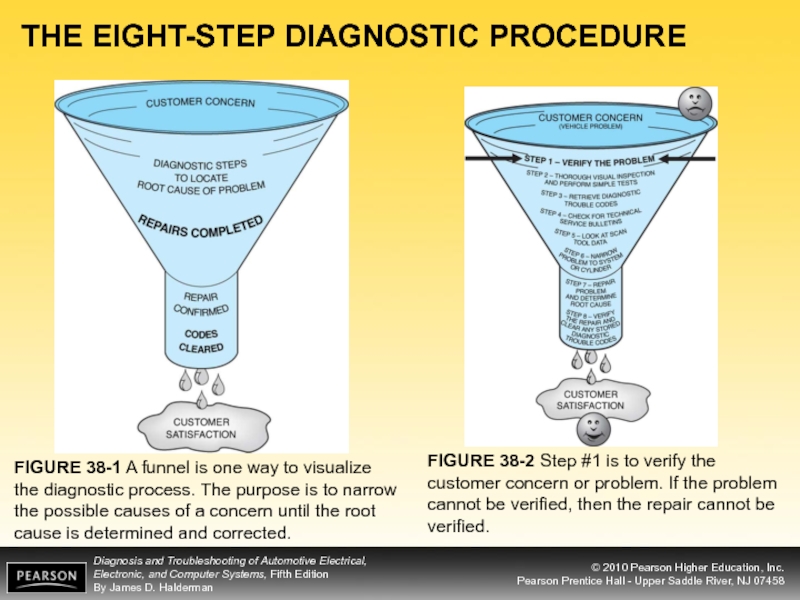
- 7. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FIGURE 38-1 A
- 8. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FIGURE 38-3 A
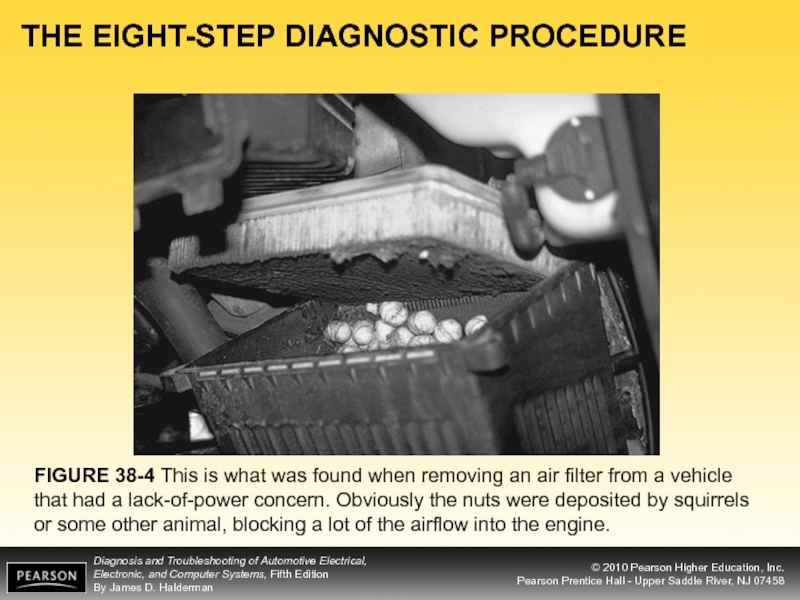
- 9. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FIGURE 38-4 This
- 10. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FIGURE 38-5 Using
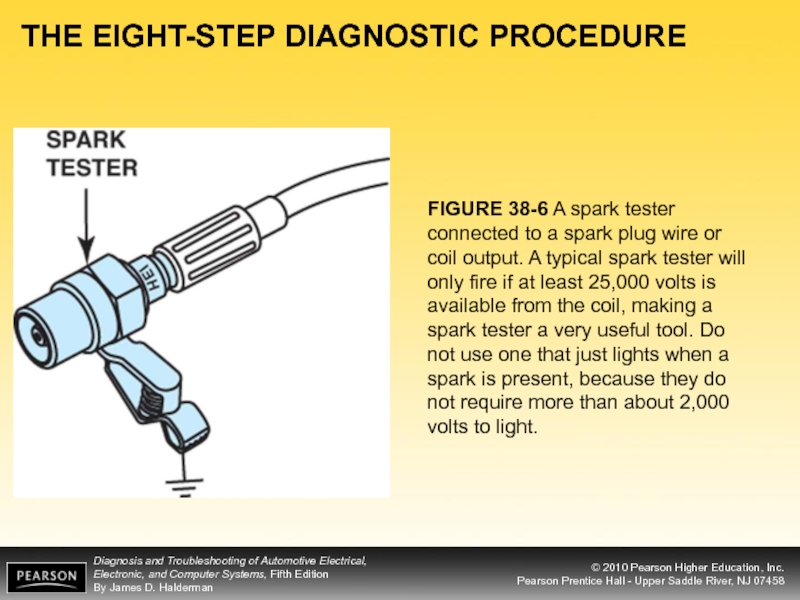
- 11. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FIGURE 38-6 A
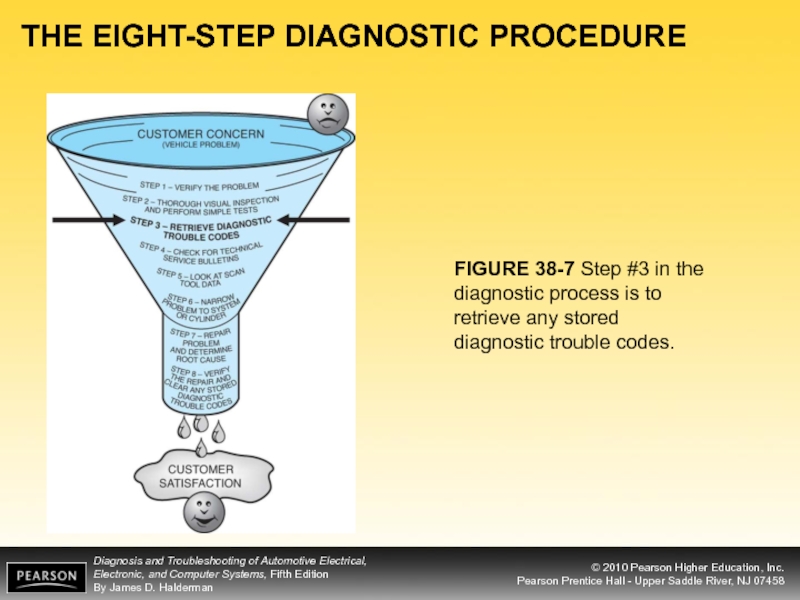
- 12. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FIGURE 38-7 Step
- 13. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FIGURE 38-8 After
- 14. THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE FIGURE 38-9 Looking
- 15. SCAN TOOLS Scan tools are the workhorse
- 16. SCAN TOOLS FIGURE 38-11 A TECH 2
- 17. RETRIEVAL OF DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION To retrieve diagnostic
- 18. TROUBLESHOOTING USING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES Pinning down
- 19. TROUBLESHOOTING USING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES Methods for Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 20. FLASH CODE RETRIEVAL ON OBD-I GENERAL MOTORS
- 21. FLASH CODE RETRIEVAL ON OBD-I GENERAL MOTORS
- 22. RETRIEVING FORD DIAGNOSTIC CODES The best tool
- 23. RETRIEVING FORD DIAGNOSTIC CODES FIGURE 38-14 A
- 24. RETRIEVING FORD DIAGNOSTIC CODES Key On–Engine Off
- 25. PUT A WIRE IN THE ATTIC AND
- 26. FLASH CODE RETRIEVAL ON CHRYSLER VEHICLES To
- 27. OBD-II DIAGNOSIS Starting with the 1996 model
- 28. OBD-II DIAGNOSIS FIGURE 38-16 A typical OBD-II
- 29. OBD-II ACTIVE TESTS OBD-II Drive Cycle Types
- 30. SERVICE/FLASH PROGRAMMING Remote Programming Direct Programming Off-Board Programming
- 31. SERVICE/FLASH PROGRAMMING FIGURE 38-17 The first step
- 32. SERVICE/FLASH PROGRAMMING FIGURE 38-18 Follow the on-screen instructions.
- 33. SERVICE/FLASH PROGRAMMING FIGURE 38-19 An Internet connection
- 34. SERVICE/FLASH PROGRAMMING FIGURE 38-20 Connecting cables and a computer to perform offboard programming.
- 35. J2534 REPROGRAMMING Legislation has mandated that vehicle
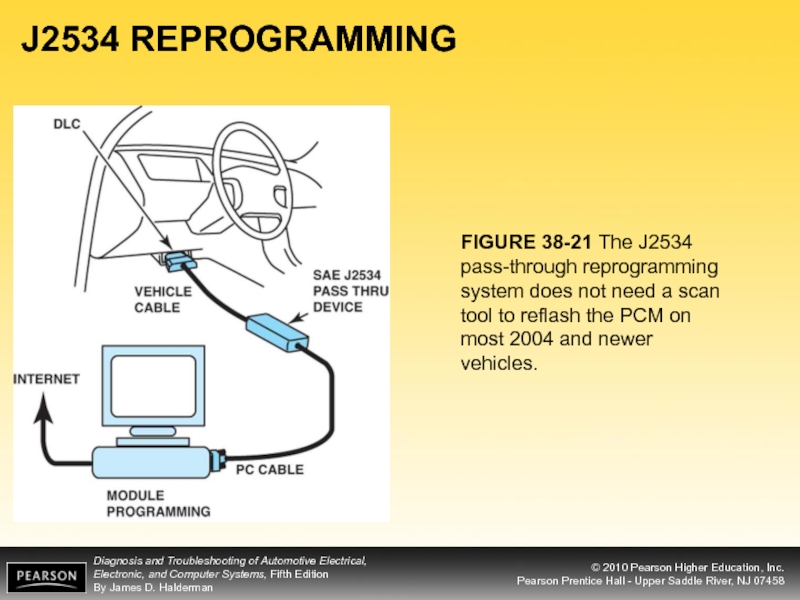
- 36. J2534 REPROGRAMMING FIGURE 38-21 The J2534 pass-through
- 37. J2534 REPROGRAMMING FIGURE 38-22 A typical J2534 universal reprogrammer that uses the J2534 standards.
- 38. MANUFACTURER’S DIAGNOSTIC ROUTINES Each vehicle manufacturer has
- 39. COMPLETING SYSTEM REPAIRS After the repair has
- 40. PROCEDURES FOR RESETTING THE PCM The PCM
- 41. ROAD TEST (DRIVE TRACE) Use the freeze-frame
- 42. EUROPEAN BOSCH DIAGNOSIS Diagnosing a European brand
- 43. SUMMARY Funnel diagnostics—Visual approach to a diagnostic
- 44. REVIEW QUESTIONS Explain the procedure to follow
- 45. CHAPTER QUIZ Technician A says that the
- 46. CHAPTER QUIZ Technician A says that the
- 47. CHAPTER QUIZ 2. Which item is not important
- 48. CHAPTER QUIZ 2. Which item is not important
- 49. CHAPTER QUIZ 3. A paper test can be
- 50. CHAPTER QUIZ 3. A paper test can be
- 51. CHAPTER QUIZ 4. Which step should be performed
- 52. CHAPTER QUIZ 4. Which step should be performed
- 53. CHAPTER QUIZ 5. Technician A says that if
- 54. CHAPTER QUIZ 5. Technician A says that if
- 55. CHAPTER QUIZ 6. The preferred method to clear
- 56. CHAPTER QUIZ 6. The preferred method to clear
- 57. CHAPTER QUIZ 7. Which is the factory scan
- 58. CHAPTER QUIZ 7. Which is the factory scan
- 59. CHAPTER QUIZ 8. Technician A says that reprogramming
- 60. CHAPTER QUIZ 8. Technician A says that reprogramming
- 61. CHAPTER QUIZ 9. Technician A says that knowing
- 62. CHAPTER QUIZ 9. Technician A says that knowing
- 63. CHAPTER QUIZ 10. Which method can be used
- 64. CHAPTER QUIZ 10. Which method can be used
- 65. END
Слайд 2OBJECTIVES
After studying Chapter 38, the reader will be able to:
Prepare for
List the steps of the diagnostic process.
Describe the simple preliminary tests that should be performed at the start of the diagnostic process.
List six items to check as part of a thorough visual inspection.
Слайд 3OBJECTIVES
Explain the troubleshooting procedures to follow if a diagnostic trouble code
Explain the troubleshooting procedures to follow if no diagnostic trouble code has been set.
Discuss the type of scan tools that are used to assess vehicle components.
Describe the methods that can be used to reprogram (reflash) a vehicle computer.
Слайд 4THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
It is important that all automotive service technicians
The diagnostic process is a strategy that eliminates known-good components or systems in order to find the root cause of automotive engine performance problems.
All vehicle manufacturers recommend a diagnostic procedure, and the plan suggested in this chapter combines most of the features of these plans plus additional steps developed over years of real-world problem solving.
Слайд 5THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
Verify the Problem (Concern)
Perform a Thorough Visual Inspection
Check for obvious problems (basics, basics, basics).
Check everything that does and does not work.
Look for evidence of previous repairs.
Check oil level and condition.
Check coolant level and condition.
Use the paper test
Ensure adequate fuel level.
Check the battery voltage.
Check the spark using a spark tester.
Check the fuel pump pressure
Слайд 6THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
Retrieve the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Check for Technical
Look Carefully at Scan Tool Data
Narrow the Problem to a System or Cylinder
Repair the Problem and Determine the Root Cause
Verify the Repair and Clear Any Stored DTCs
Слайд 7THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
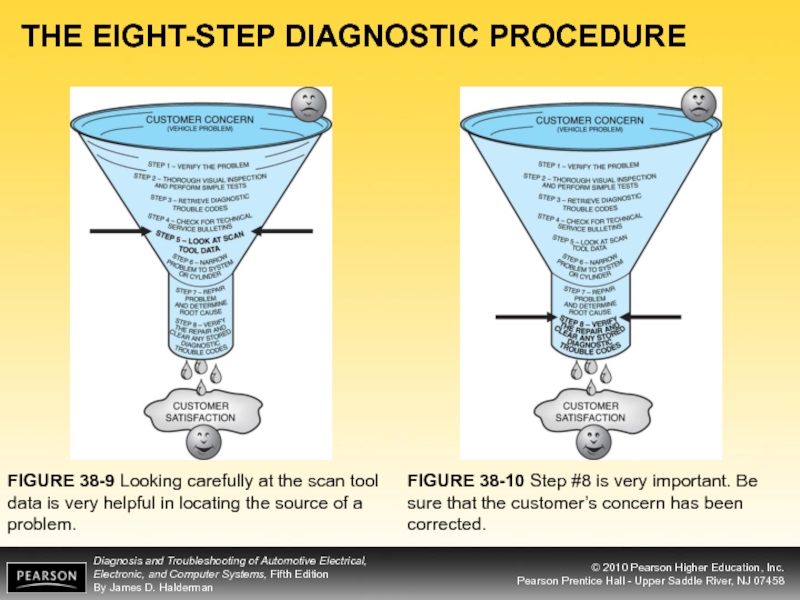
FIGURE 38-1 A funnel is one way to
FIGURE 38-2 Step #1 is to verify the customer concern or problem. If the problem cannot be verified, then the repair cannot be verified.
Слайд 8THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
FIGURE 38-3 A form that the customer should
Слайд 9THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
FIGURE 38-4 This is what was found when
Слайд 10THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
FIGURE 38-5 Using a bright light makes seeing
Слайд 11THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
FIGURE 38-6 A spark tester connected to a
Слайд 12THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
FIGURE 38-7 Step #3 in the diagnostic process
Слайд 13THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
FIGURE 38-8 After checking for stored diagnostic trouble
Слайд 14THE EIGHT-STEP DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
FIGURE 38-9 Looking carefully at the scan tool
FIGURE 38-10 Step #8 is very important. Be sure that the customer’s concern has been corrected.
Слайд 15SCAN TOOLS
Scan tools are the workhorse for any diagnostic work on
Scan tools can be divided into two basic groups:
Factory scan tools.
Aftermarket scan tools
Слайд 16SCAN TOOLS
FIGURE 38-11 A TECH 2 scan tool is the factory
FIGURE 38-12 Some scan tools use pocket PCs which make it very convenient to use.
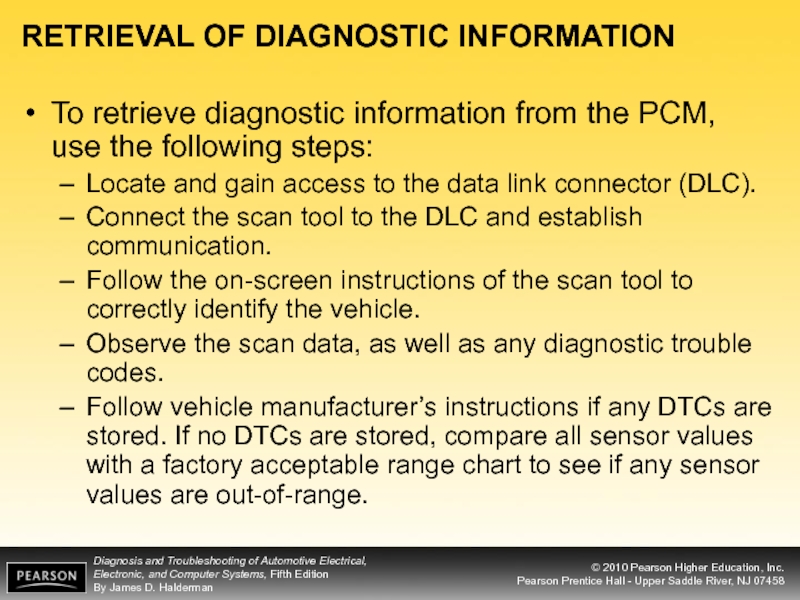
Слайд 17RETRIEVAL OF DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION
To retrieve diagnostic information from the PCM, use
Locate and gain access to the data link connector (DLC).
Connect the scan tool to the DLC and establish communication.
Follow the on-screen instructions of the scan tool to correctly identify the vehicle.
Observe the scan data, as well as any diagnostic trouble codes.
Follow vehicle manufacturer’s instructions if any DTCs are stored. If no DTCs are stored, compare all sensor values with a factory acceptable range chart to see if any sensor values are out-of-range.
Слайд 18TROUBLESHOOTING USING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Pinning down causes of the actual problem
For example, if a code indicates an open throttle position (TP) sensor (high resistance), clear the code and create a shorted (low-resistance) condition.
This can be accomplished by using a jumper wire and connecting the signal terminal to the 5-volt reference terminal.
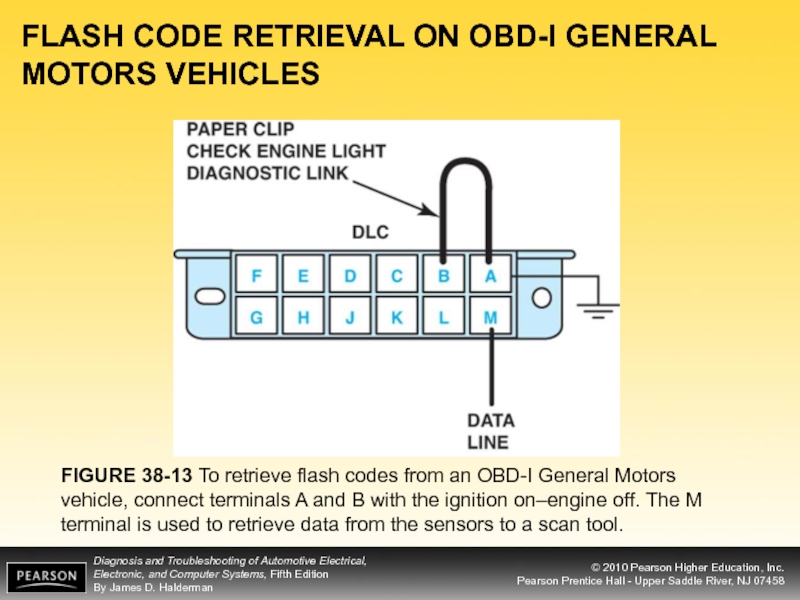
Слайд 20FLASH CODE RETRIEVAL ON OBD-I GENERAL MOTORS VEHICLES
The GM system uses
Most General Motors diagnostic trouble codes can be retrieved by using a metal tool and contacting terminals A and B of the 12-pin DLC
Слайд 21FLASH CODE RETRIEVAL ON OBD-I GENERAL MOTORS VEHICLES
FIGURE 38-13 To retrieve
Слайд 22RETRIEVING FORD DIAGNOSTIC CODES
The best tool to use during troubleshooting of
If a STAR tester or scan tool is not available, a needle (analog) type of voltmeter can be used for all OBD-I (prior to 1996) systems.
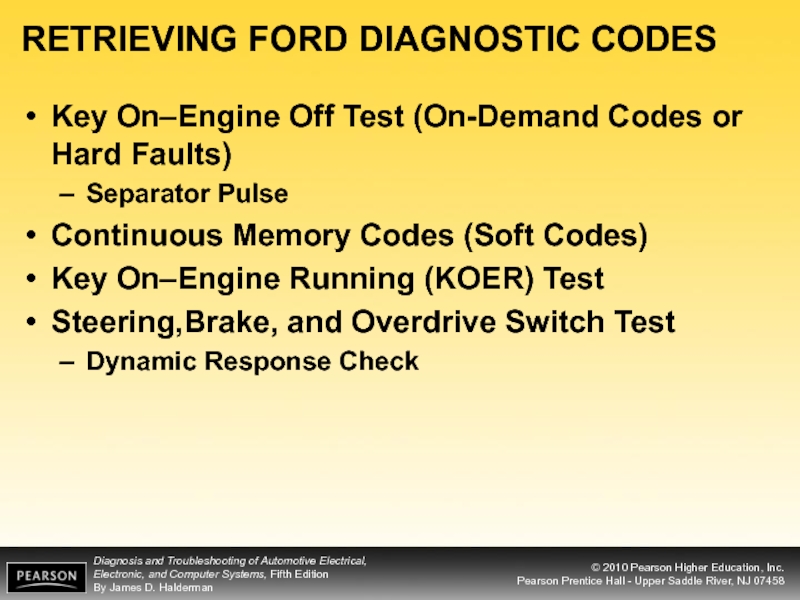
Слайд 23RETRIEVING FORD DIAGNOSTIC CODES
FIGURE 38-14 A Ford OBD-I self-test connector. The
Слайд 24RETRIEVING FORD DIAGNOSTIC CODES
Key On–Engine Off Test (On-Demand Codes or Hard
Separator Pulse
Continuous Memory Codes (Soft Codes)
Key On–Engine Running (KOER) Test
Steering,Brake, and Overdrive Switch Test
Dynamic Response Check
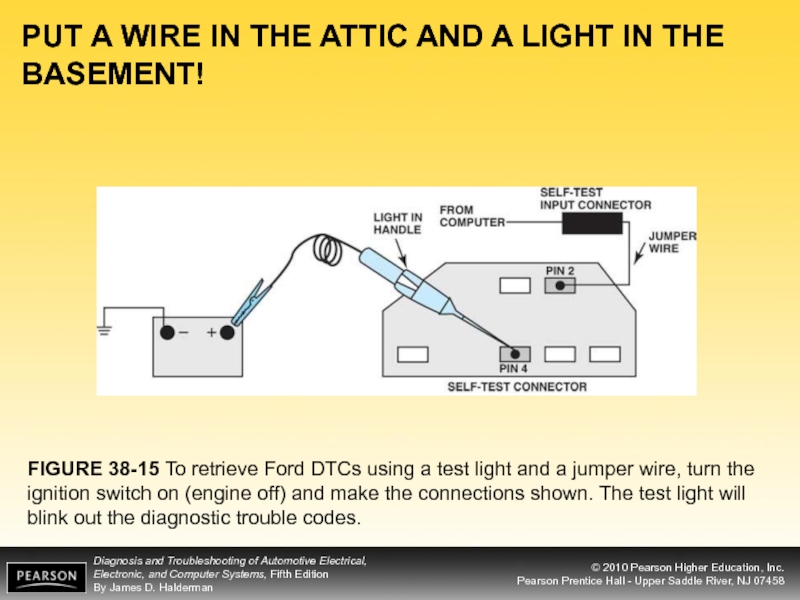
Слайд 25PUT A WIRE IN THE ATTIC AND A LIGHT IN THE
FIGURE 38-15 To retrieve Ford DTCs using a test light and a jumper wire, turn the ignition switch on (engine off) and make the connections shown. The test light will blink out the diagnostic trouble codes.
Слайд 26FLASH CODE RETRIEVAL ON CHRYSLER VEHICLES
To put the computer into the
The computer will flash a series of fault codes.
Older Chrysler brand products flash the “check engine” lamp on the dash.
Слайд 27OBD-II DIAGNOSIS
Starting with the 1996 model year, all vehicles sold in
Retrieving OBD-II Codes
Слайд 28OBD-II DIAGNOSIS
FIGURE 38-16 A typical OBD-II data link connector (DLC). The
Слайд 29OBD-II ACTIVE TESTS
OBD-II Drive Cycle
Types of OBD-II Codes
Type A Codes.
Type B
Type C and D Codes.
OBD-II Freeze-Frame
Diagnosing Intermittent Malfunctions
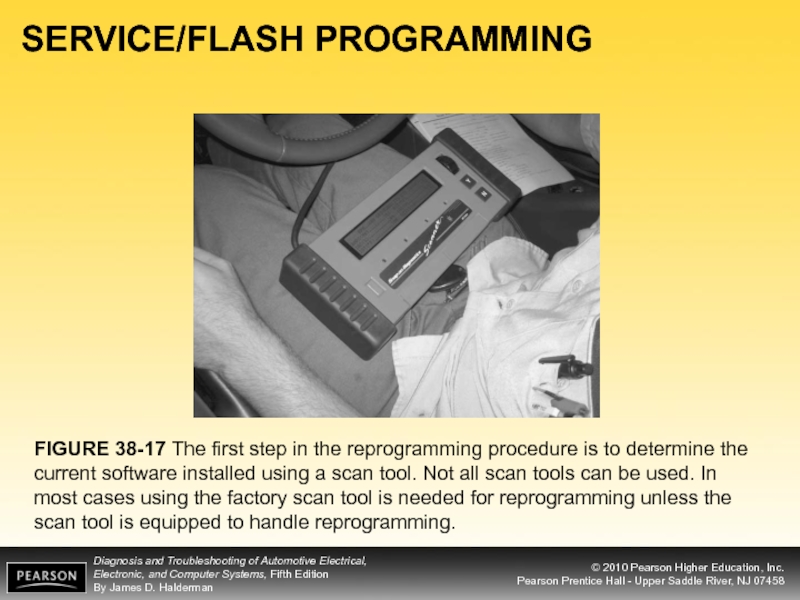
Слайд 31SERVICE/FLASH PROGRAMMING
FIGURE 38-17 The first step in the reprogramming procedure is
Слайд 33SERVICE/FLASH PROGRAMMING
FIGURE 38-19 An Internet connection is usually needed to perform
Слайд 34SERVICE/FLASH PROGRAMMING
FIGURE 38-20 Connecting cables and a computer to perform offboard
Слайд 35J2534 REPROGRAMMING
Legislation has mandated that vehicle manufacturers meet the SAE J2534
This standard enables independent service repair operators to program or reprogram emissions-related ECMs from a wide variety of vehicle manufacturers with a single tool.
Слайд 36J2534 REPROGRAMMING
FIGURE 38-21 The J2534 pass-through reprogramming system does not need
Слайд 37J2534 REPROGRAMMING
FIGURE 38-22 A typical J2534 universal reprogrammer that uses the
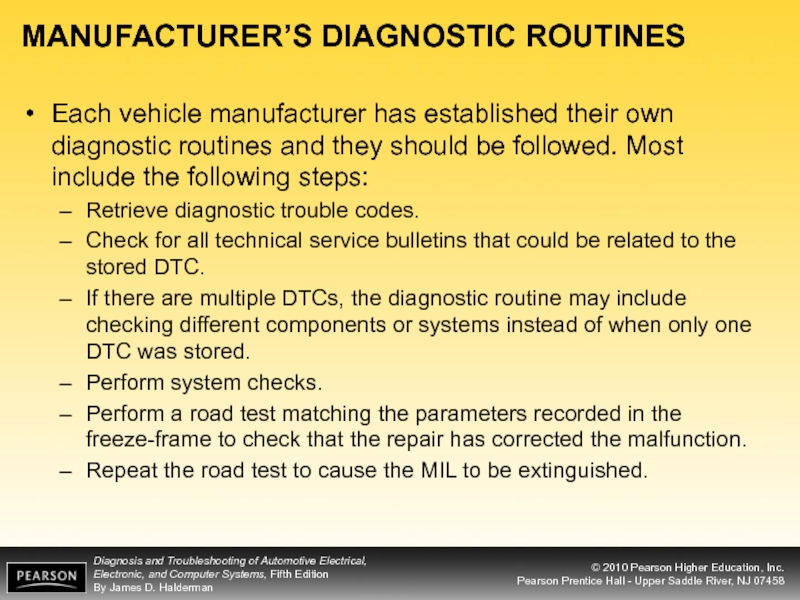
Слайд 38MANUFACTURER’S DIAGNOSTIC ROUTINES
Each vehicle manufacturer has established their own diagnostic routines
Retrieve diagnostic trouble codes.
Check for all technical service bulletins that could be related to the stored DTC.
If there are multiple DTCs, the diagnostic routine may include checking different components or systems instead of when only one DTC was stored.
Perform system checks.
Perform a road test matching the parameters recorded in the freeze-frame to check that the repair has corrected the malfunction.
Repeat the road test to cause the MIL to be extinguished.
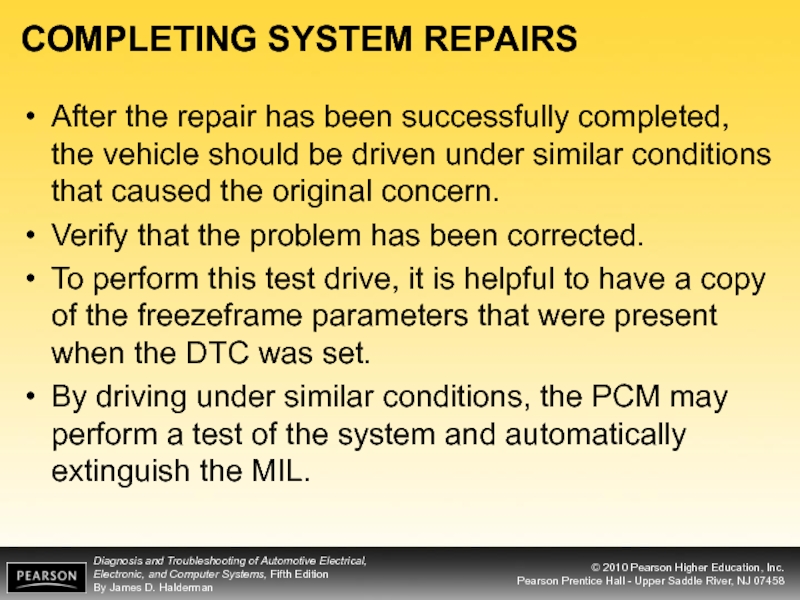
Слайд 39COMPLETING SYSTEM REPAIRS
After the repair has been successfully completed, the vehicle
Verify that the problem has been corrected.
To perform this test drive, it is helpful to have a copy of the freezeframe parameters that were present when the DTC was set.
By driving under similar conditions, the PCM may perform a test of the system and automatically extinguish the MIL.
Слайд 40PROCEDURES FOR RESETTING THE PCM
The PCM can be reset or cleared
Driving the Vehicle.
Clear DTCs Using a Scan Tool.
Battery Disconnect.
Слайд 41ROAD TEST (DRIVE TRACE)
Use the freeze-frame data and test-drive the vehicle
If the battery has been disconnected, then the vehicle may have to be driven under conditions that allow the PCM to conduct monitor tests
Universal Drive Cycle
Слайд 42EUROPEAN BOSCH DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosing a European brand vehicle, such as a Volkswagen,
One of the challenges is that global (generic) scan tools, while capable of supplying the specified data, do not allow access to many diagnostic trouble codes that might be set and stored.
Using factory-level scan tools, such as VAG-COM, launch X431, or Baum iscan, results in some terms that are not familiar such as:
Address word.
Function
Display group
Using Function 04
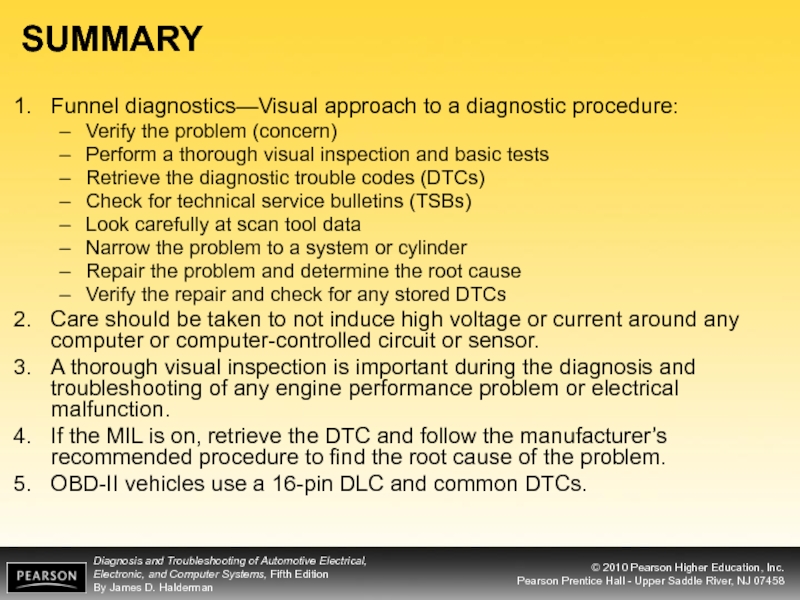
Слайд 43SUMMARY
Funnel diagnostics—Visual approach to a diagnostic procedure:
Verify the problem (concern)
Perform a
Retrieve the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
Check for technical service bulletins (TSBs)
Look carefully at scan tool data
Narrow the problem to a system or cylinder
Repair the problem and determine the root cause
Verify the repair and check for any stored DTCs
Care should be taken to not induce high voltage or current around any computer or computer-controlled circuit or sensor.
A thorough visual inspection is important during the diagnosis and troubleshooting of any engine performance problem or electrical malfunction.
If the MIL is on, retrieve the DTC and follow the manufacturer’s recommended procedure to find the root cause of the problem.
OBD-II vehicles use a 16-pin DLC and common DTCs.
Слайд 44REVIEW QUESTIONS
Explain the procedure to follow when diagnosing a vehicle without
Discuss what the PCM does during a drive cycle to test emission-related components.
Explain the difference between a type A and type B OBD-II diagnostic trouble code.
List three things that should be checked as part of a thorough visual inspection.
List the eight-step funnel diagnostic procedure.
Explain why a bulletin search should be performed after stored DTCs are retrieved.
List the three methods that can be used to reprogram a PCM.
Слайд 45CHAPTER QUIZ
Technician A says that the first step in the diagnostic
Technician A only
Technician B only
Both Technicians A and B
Neither Technician A nor B
Слайд 46CHAPTER QUIZ
Technician A says that the first step in the diagnostic
Technician A only
Technician B only
Both Technicians A and B
Neither Technician A nor B
Слайд 47CHAPTER QUIZ
2. Which item is not important to know before starting the
List of previous repairs
The brand of engine oil used
The type of gasoline used
The temperature of the engine when the problem occurs
Слайд 48CHAPTER QUIZ
2. Which item is not important to know before starting the
List of previous repairs
The brand of engine oil used
The type of gasoline used
The temperature of the engine when the problem occurs
Слайд 49CHAPTER QUIZ
3. A paper test can be used to check for a
The ignition system (bad spark plug wire)
A faulty injector on a multiport engine
A burned valve
All of the above
Слайд 50CHAPTER QUIZ
3. A paper test can be used to check for a
The ignition system (bad spark plug wire)
A faulty injector on a multiport engine
A burned valve
All of the above
Слайд 51CHAPTER QUIZ
4. Which step should be performed last when diagnosing an engine
Checking for any stored diagnostic trouble codes
Checking for any technical service bulletins (TSBs)
Performing a thorough visual inspection
Verify the repair
Слайд 52CHAPTER QUIZ
4. Which step should be performed last when diagnosing an engine
Checking for any stored diagnostic trouble codes
Checking for any technical service bulletins (TSBs)
Performing a thorough visual inspection
Verify the repair
Слайд 53CHAPTER QUIZ
5. Technician A says that if the opposite DTC can be
Technician A only
Technician B only
Both Technicians A and B
Neither Technician A nor B
Слайд 54CHAPTER QUIZ
5. Technician A says that if the opposite DTC can be
Technician A only
Technician B only
Both Technicians A and B
Neither Technician A nor B
Слайд 55CHAPTER QUIZ
6. The preferred method to clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) is
Disconnect the negative battery cable for 10 seconds
Use a scan tool
Remove the computer (PCM) power feed fuse
Cycle the ignition key on and off 40 times
Слайд 56CHAPTER QUIZ
6. The preferred method to clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) is
Disconnect the negative battery cable for 10 seconds
Use a scan tool
Remove the computer (PCM) power feed fuse
Cycle the ignition key on and off 40 times
Слайд 57CHAPTER QUIZ
7. Which is the factory scan tool for Chrysler brand vehicles
Star Scan
Tech 2
NGS
Master Tech
Слайд 58CHAPTER QUIZ
7. Which is the factory scan tool for Chrysler brand vehicles
Star Scan
Tech 2
NGS
Master Tech
Слайд 59CHAPTER QUIZ
8. Technician A says that reprogramming a PCM using the J2534
Technician A only
Technician B only
Both Technicians A and B
Neither Technician A nor B
Слайд 60CHAPTER QUIZ
8. Technician A says that reprogramming a PCM using the J2534
Technician A only
Technician B only
Both Technicians A and B
Neither Technician A nor B
Слайд 61CHAPTER QUIZ
9. Technician A says that knowing if there are any stored
Technician A only
Technician B only
Both Technicians A and B
Neither Technician A nor B
Слайд 62CHAPTER QUIZ
9. Technician A says that knowing if there are any stored
Technician A only
Technician B only
Both Technicians A and B
Neither Technician A nor B