- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Adjective and adverb презентация
Содержание
- 1. Adjective and adverb
- 2. b) the category of comparison of adverbs
- 3. on the basis of their function:
- 4. In evaluative function adverbs distinguish the category
- 5. Synthetic and analitical forms are in complimentary distribution to each other.
- 6. The superlative degree form can be used
- 7. When used in the specificative function, adverbs
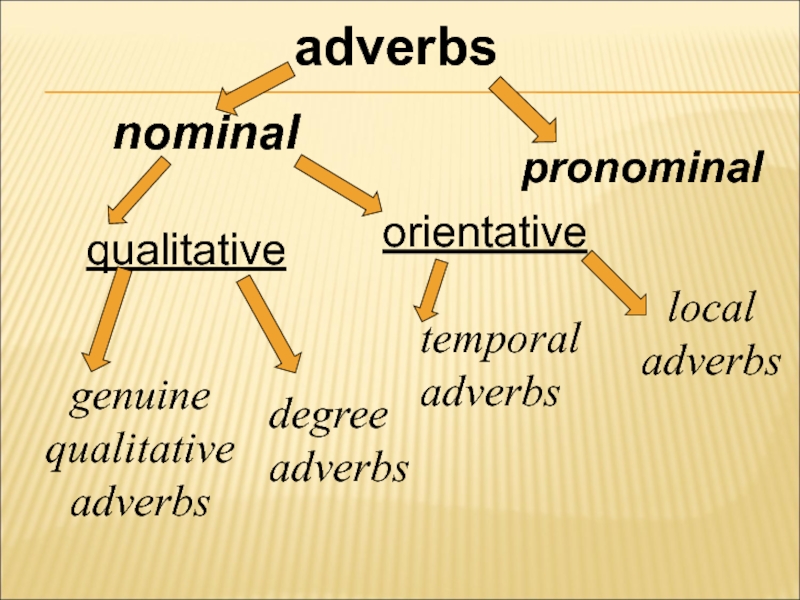
- 8. c) Semantic subdivisions of adverbs
- 9. on the basis of their semantic
- 10. on the basis of their general semantics:
- 11. They include genuine qualitative adverbs, e.g.:
- 12. - adverbs of high degree (intensifiers),
- 13. 2) the quantitative adverbs show quantity
- 14. 3) the circumstantial adverbs denote mainly
- 15. Circumstantial adverbs can be notional and
- 16. 2) functional circumstantial adverbs pronominal
- 17. They substitute notional adverbs or
- 18. adverbs nominal pronominal qualitative orientative genuine qualitative
Слайд 4In evaluative function adverbs distinguish the category of comparison
? five
morphological forms:
one positive,
two comparative (direct and reverse)
two superlative (direct and reverse),
e.g.: bitterly – more bitterly, less bitterly – most bitterly, least bitterly.
one positive,
two comparative (direct and reverse)
two superlative (direct and reverse),
e.g.: bitterly – more bitterly, less bitterly – most bitterly, least bitterly.
Слайд 6The superlative degree form can be used
in the absolute sense
= absolute superiority
in the elative sense = a high degree of the property,
e.g.: The youngest kid cried most bitterly of all. – The kid cried most bitterly.
in the elative sense = a high degree of the property,
e.g.: The youngest kid cried most bitterly of all. – The kid cried most bitterly.
Слайд 7When used in the specificative function, adverbs are unchangeable
e.g.: We
meet today; We came ashore.
Слайд 9 on the basis of their semantic value:
- genuine, or
notional (nominal) adverbs of full semantic value
- semi-functional (pronominal) adverbs of partial semantic value.
- semi-functional (pronominal) adverbs of partial semantic value.
Слайд 10on the basis of their general semantics:
the qualitative adverbs
denote the inherent qualities of actions and other qualities;
derived from qualitative adjectives,
e.g.: bitterly, hard, beautifully, well, etc.
Слайд 11They include
genuine qualitative adverbs, e.g.: bitterly, hard, beautifully, well, etc.
semi-functional
words of degree, quality evaluators:
Слайд 12- adverbs of high degree (intensifiers),
e.g.: very, greatly, absolutely, pretty;
- adverbs of excessive degree, e.g.: too, awfully, tremendously;
- adverbs of unexpected degree, e.g.: surprisingly, astonishingly;
- adverbs of moderate degree, e.g.: fairly, relatively, rather.
- adverbs of excessive degree, e.g.: too, awfully, tremendously;
- adverbs of unexpected degree, e.g.: surprisingly, astonishingly;
- adverbs of moderate degree, e.g.: fairly, relatively, rather.
Слайд 132) the quantitative adverbs
show quantity measure;
derived from numerals,
e.g.:
twice, three times, tenfold, manifold, etc.
They belong to the group of semi-functional adverbs.
They belong to the group of semi-functional adverbs.
Слайд 143) the circumstantial adverbs
denote mainly the circumstances of time and
place
e.g.: today, here, when, far, ashore, abroad, often, etc.
e.g.: today, here, when, far, ashore, abroad, often, etc.
Слайд 15 Circumstantial adverbs can be notional and functional.
1) Notional (genuine)
circumstantial adverbs denote
time and frequency e.g.: tomorrow, never, recently, late;
space and direction orientation, e.g.: homeward, ashore, outside, far.
time and frequency e.g.: tomorrow, never, recently, late;
space and direction orientation, e.g.: homeward, ashore, outside, far.
Слайд 16 2) functional circumstantial adverbs
pronominal adverbs of time, place, manner,
cause, consequence,
e.g.: here, when, where, so, thus, nevertheless, otherwise, etc.
e.g.: here, when, where, so, thus, nevertheless, otherwise, etc.
Слайд 17 They substitute notional adverbs or other words used in
the function of adverbial modifiers in a sentence,
cf.: He stayed at school. – He stayed there;
cf.: He stayed at school. – He stayed there;